The ‘group policies’ are a fundamental tool for IT administrators since they provide a centralized form of manage and enforce all kinds of configurations of operating systems, applications and configuration of users in an environment of Active Directory. These configurations are maintained by a domain controller and individual client equipment cannot cancel them.
Its use is common in the configuration of business networks, organizations or schools, and can be managed with the editor of group directives in Windows. An internal tool of Microsoft operating systems that allows a greater control of the PC operation or the ability to make some adjustments that are not available using other less advanced managers such as the control panel or the general system configuration.
Although Windows is not exactly a simple operating system to customize at the client level, administrative efforts are better covered and this manager is an example. Think about her as a control panel, but much more powerful. You can restrict access to parts of the system, force a certain home page for all users or execute certain scripts Every time a computer turns on or off. Internally, most of the group editor options in Windows simply make adjustments in the registration of the system.
However, this application provides a much more friendly interface to administer these options without having to manually search in the registry. We review your access and expose examples of functions that can be used by an administrator to improve the control of the local network machines or shared PCs.
How to access group directives in Windows
This manager is available in Professional, educational and business versions of Windows 11 and Windows 10. Microsoft does not officially offer it on Windows 10 Home, although external applications such as Policy Plusan open source tool that provides access to the configuration of the group policy editor and the Windows registration. Your access is very simple. And in several ways:
- Open the start menu, look for “group directive” and start the application.
- O Press the “Windows + R” keyboard and write the gpedit.msc command to start the editor.
Most configurations require the restart of the computer before implementing them. If you want to avoid it, after the changes you can open the Windows console with administrator privileges and execute the command gpupdate /force to activate.
10 examples of use for client machines
There are hundreds of different options, preferences and configurations that can be activated. Of course, you have to know what is being done because this set of rules control the work environment environment and equipment, and basically allow control what can be done or not on the PC. A bad adjustment can cause unwanted problems or behaviors.
However, there are simple controls that can be useful for local networks or client machines and that serve to begin to know the possibilities of this manager. As an example:
– Restrict access to the control and configuration panel. The restrictions on access to these controls are vital for business networks and school environments, but they can also be useful in the home for computers shared among multiple users. If you want to prevent your kid changes the system configuration, this is a good step to follow. The configuration is always done since the same way:
- Go to the User Configuration Route> Administrative templates> Control Panel> Prohibit access to PC configuration and control panel
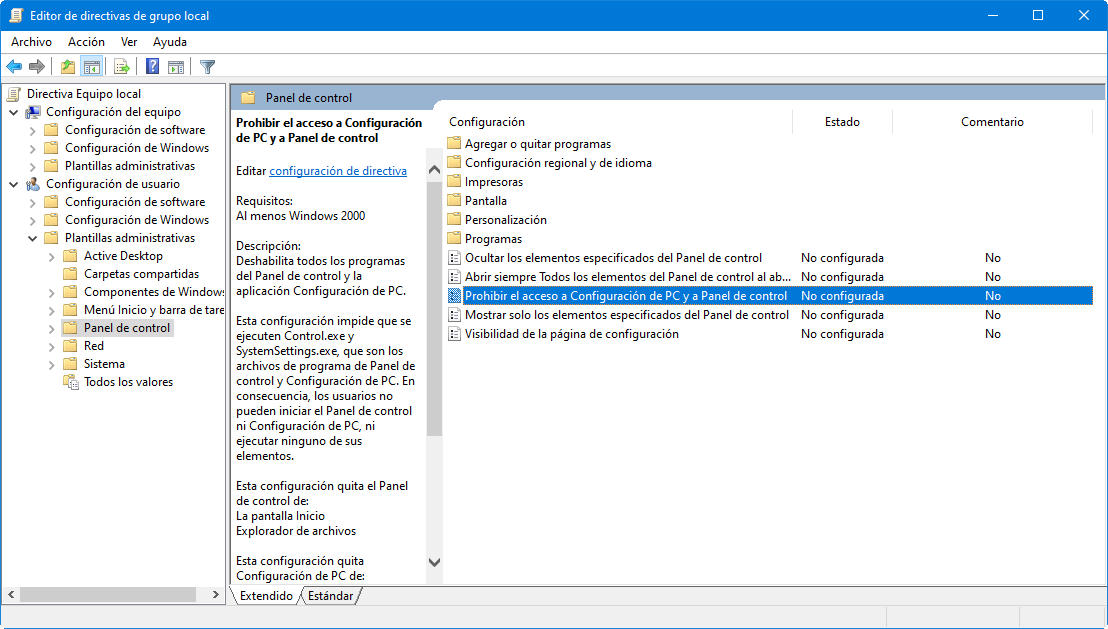
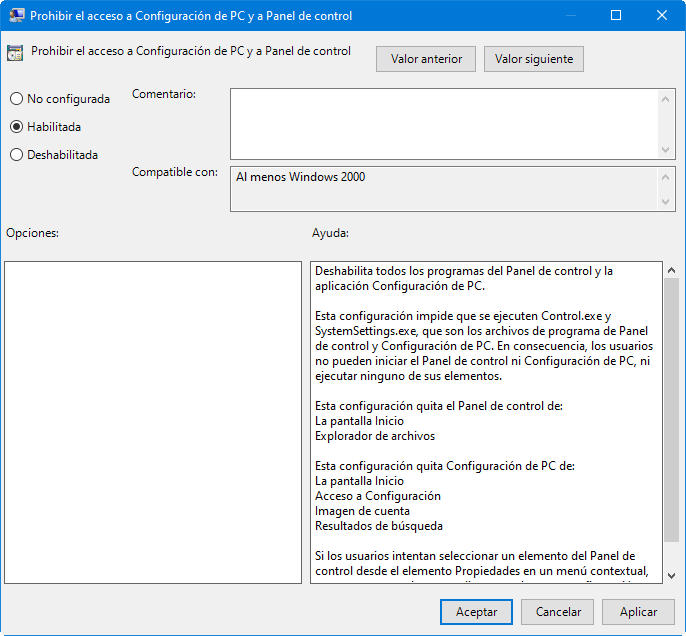
This policy allows to disable all access or only to certain parts of the control panel.
Block access to the system symbol. The Windows console is very powerful and Windows Terminal is an interesting reunification of all system command lines. But in wrong hands, it can be a big problem for security or equipment stability. To disable it, edit:
User Configuration> Administrative Templates> System> Prevent access to the system symbol
This policy prevents the execution of the system symbol and also the execution of files by lots in CMD or BAT formats.
Prevent software installation. Another key action to prevent malware introduction or garbage applications, and reduce system load and maintenance.
Equipment configuration> Administrative templates> Windows components> Windows Installer> Disable Windows Installer
This policy only affects Win32 software, Windows Store apps could still be installed by third parties.
Disable forced reset. Although there are other options options to postpone it, Windows 10 will eventually restart the computer when you have pending updates. You can recover control by enabling an element of group policy. From there, Windows will only apply pending updates when the user manually restarts.
Equipment configuration> Administrative templates> Windows components
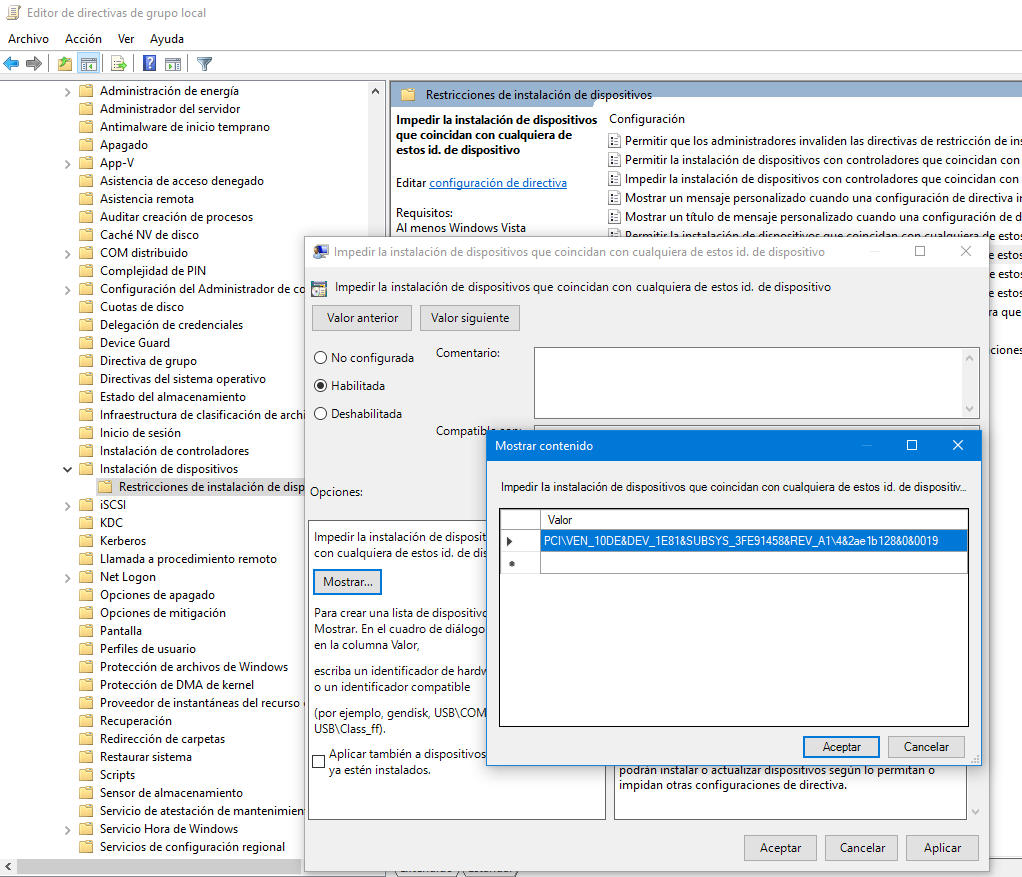
Disable automatic controller updates. Windows 10 can update the controllers without implicit permission of the user and on many occasions it is a problem because you can want to use a personalized controller or the latest version provided by Microsoft does not work correctly with a particular hardware. To disable automatic controller updates, see this route:
Equipment configuration> Administrative templates> System> Device installation> Devices installation restrictions> Prevent the installation of devices that coincide with any of these IDs. of device.
Once enabled, you must provide the hardware ID for devices whose drivers update you want to limit. You can get them from the control panel manager. In the example we prevent the update of the driver of our graphics card to always use the manual controller that we have installed with the Nvidia external software.
– Disable removable units. External units such as optical means or those used by flash memories and connect to USB are very useful, but they are potentially a preferred way of introduction of malware. This limitation in Windows group directives is used by default in companies, but also in domestic networks and client machines that use several users.
User Configuration> Administrative Templates> System> Removable Storage Access
In that policy you can deactivate the reading or writing access of optical means, the floppy disks or flash storage units, although the persistent USBs are always the most problematic.
– Hide notifications. We use them daily on mobile devices and Microsoft or Apple have also introduced them into their systems for PCs. I don’t know. For me they are a real pain when I am working on the desk and bother more than the supposed usefulness they offer. It can be disabled from:
User Configuration> Administrative templates> Start menu and taskbar
There you can deactivate the notifications of balloon and the rest, in addition to making a lot of customizations.
– Delete OneDrive. Microsoft integrated OneDrive by default in Windows 10 with the aim of promoting its own cloud storage service. Personally I use it with Office 365 and the truth is that it works perfectly. But if you do not use it or if you have another storage service, it is a nuisance to have it from starting or occupying unnecessary space in the file explorer. Although it can be uninstalled by other methods, the action in the Windows group directives is definitive for the current version of the system and following updates, and is carried out from the route:
Equipment configuration> Administrative templates> Windows components> OneDrive> Prevent the use of OneDrive to store files
– Delete Windows Defender. The antivirus integrated in Windows 10 has improved so much that most users avoid the installation of third -party safety software. Defender is administered on its own and will stop working automatically if you install a third -party antivirus. That is the theory, because we have seen conflicts in the past with this type of facilities. If the change does not work correctly and use external security software, it can be completely disabled here:
Equipment configuration> Administrative templates> Windows components> Windows Defender> Turn off Windows Defender
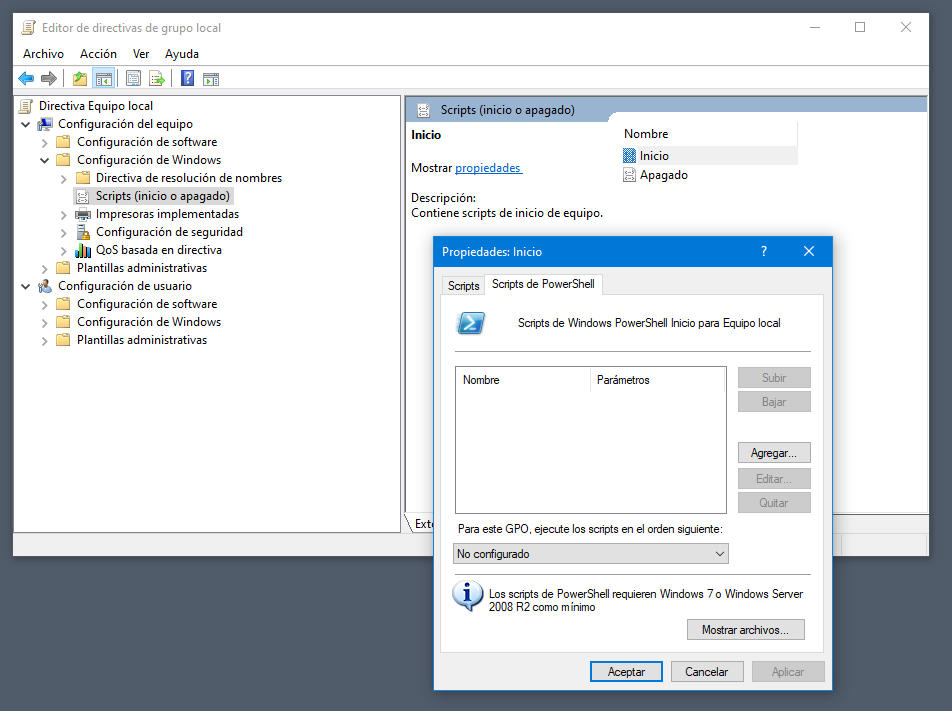
– Execute scripts at the login / start / off. The last example is more advanced than the previous ones. It is also widely used by administrators, but the vast majority of users will not use it. If you are an advanced user and you feel comfortable with these batch files that can be written on the Powershell console, they can automatically activate with group policies.
Team configuration> Windows> Scripts configuration
These command sequences can be activated both for the beginnings / off of the machines, and for the logs / session closures.
There are only some examples of use of these Windows group directives because there are tens / hundreds of actions that can be used in each section of this editor, in a simpler way than having to be playing in the system record. In addition, each of them includes a small written tutorial of what affects.
Obviously, most of these policies are created thinking of companies, organizations or schools, but can also be used in Domestic networks and shared customer equipment where the main user wants to maintain their control and safety or customize the operation of a lot of sections of the PC.











