Ever felt like you were talking to a robot when you contacted customer support? Well, it’s time to flip the script.
Imagine a world where your customers don’t just get answers; they get personalized experiences. A world where their every question, every need, is understood and addressed with precision. That’s the power of AI Intent Classification.
Let’s take a real-world example. You’re a customer of a major airline. You’ve lost your boarding pass and need to reschedule your flight. With AI Intent Classification, the airline’s chatbot would instantly understand your request, verify your identity, and provide you with the necessary steps to reschedule. No more waiting on hold for hours or navigating complex phone menus.
Intrigued? Let’s explore how AI Intent Classification can transform your customer journeys.
What is Intent Classification?
Intent Classification is the process of identifying the underlying goal or purpose of a user’s utterance or query. In simpler terms, it’s like understanding what a customer wants to achieve when they interact with a business. Customer intents are the underlying goals or purposes that drive customer interactions with a business. Understanding these intents is essential for providing relevant and effective customer experiences.
(Image Source: Link)
Here are the four primary types of customer intents:
| Type of Intent | Explanation | Example | Keyword Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| User is ready to take an action such as making a purchase or signing up for a service. | “I want to buy the latest iPhone.” | purchase, sign-up, order, booking | |
| User seeks specific information, such as product details or service inquiries. | “What are the features of the latest iPhone?” | product details, service inquiries, specifications | |
| User is trying to find specific pages or sections within a website or platform | “Where can I find the refund policy?” | finding pages, help sections, FAQs | |
| User’s message reveals an emotional state, such as frustration or satisfaction. | “I’m really frustrated with this product’s performance.” | frustration, satisfaction, confusion, disappointment |
Let’s illustrate this with a customer journey example:
Imagine you’re shopping for a new smartphone. You visit a popular online retailer’s website.
1. Initial Search: You start by typing “best smartphones under 50000” into the search bar. Your intent here is to informational. You’re seeking information about available options within a specific price range.
2. Product Page: You click on one of the search results, leading you to the product page of a particular smartphone. Your intent now might be navigational. You’re trying to explore more details about this specific product.
3. Customer Review: You read a customer review that mentions a battery issue. Your intent shifts to informational again, as you want to know more about the battery’s performance.
4. Comparison Tool: You decide to use the website’s comparison tool to compare the selected smartphone with another model. Your intent is navigational as you’re trying to find a specific feature on the website.
5. Add to Cart: After comparing and deciding, you add the smartphone to your cart. Your intent has transitioned to transactional. You’re ready to purchase the product.
6. Checkout Process: You proceed to the checkout page. Your intent remains transactional as you complete the purchase process.
Role of Intent Classification in Automated Customer Journeys
Throughout each stage of the customer journey to purchasing a product, intent classification plays a pivotal role. By accurately identifying customer needs—whether they are informational, transactional, or support-related—automated systems can deliver timely and relevant responses that enhance the overall experience. Let’s explore each stage in detail:
Stage 1: Awareness
Sarah, a marketing manager at a mid-sized e-commerce company, realizes her team needs to improve their customer communication strategy. While browsing online, she comes across an ad for an Automated SMS Marketing Software. Intrigued, she clicks on the link and visits the website.
- Intent Classification: Sarah’s initial intent is informational—she’s exploring options available in the market. The website features a chatbot that detects her interest and engages her with a welcome message.
Chatbot Interaction:
Chatbot: “Hi, Sarah! Looking to enhance your customer communication? I can help you find the right SMS Marketing Software. What specific features are you interested in?”
Sarah: “I want to know how it can help with customer engagement.”
Stage 2: Consideration
After chatting with the bot, Sarah receives an automated email summarizing the features discussed, along with a link to a case study showing how other e-commerce businesses improved engagement using the software.
- Intent Classification: The intent is clear—Sarah is considering her options. The system detects her interest in customer engagement features and provides tailored information to aid her decision-making.
Email Example:
Subject: “See How Our SMS Marketing Software Boosts Engagement!”
Content: “Hi Sarah, check out how [Company Name] increased their engagement rates by 30% using our SMS solutions!”
Stage 3: Decision
After reviewing the email and the case study, Sarah decides to sign up for a free trial. During the registration process, she encounters some confusion regarding the payment options. Frustrated, she types a message into the chatbot for assistance.
- Intent Classification: Here, Sarah’s intent shifts to support. The system identifies her emotional state and escalates her query to a live support agent for immediate assistance.
Chatbot Interaction:
Chatbot: “It seems like you need help with payment options. Let me connect you to a support agent who can assist you right away!”
Stage 4: Purchase
With the support agent’s help, Sarah completes her registration and makes her first payment. Shortly after, she receives a confirmation email outlining her subscription details and a warm welcome to the software community.
- Intent Classification: Sarah’s intent is transactional—she’s ready to finalize her purchase. The system automates the confirmation process to ensure she receives the necessary information promptly.
Email Example:
Subject: “Welcome to [Software Name] – Your Subscription is Active!”
Content: “Thank you for joining us, Sarah! Here are your subscription details and helpful resources to get started.”
Stage 5: Onboarding
Now that Sarah has access to the software, she receives automated onboarding messages that guide her through setting up her account and utilizing key features effectively.
- Intent Classification: Sarah is now in an onboarding phase where her intent is to learn how to use the software. The system recognizes this need and sends her targeted tutorials and tips.
Onboarding Email Example:
Subject: “Let’s Get Started with Your SMS Marketing Software!”
Content: “Hi Sarah, here’s a quick start guide to help you set up your account and begin sending your first SMS campaign. Click here for video tutorials!”
Use Cases of AI Intent Classification in Customer Journeys
AI intent classification can be applied to various customer journey stages to enhance customer experiences and drive business outcomes. Here are some key use cases:
1. E-commerce
( Image Source: Link)
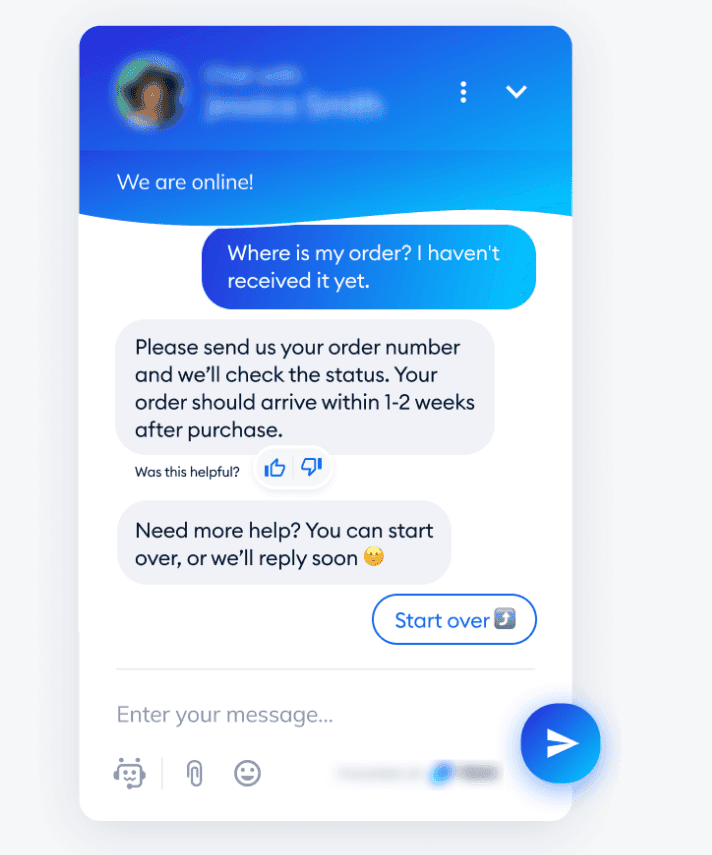
Scenario: Emma, a shopper on an online clothing store, adds several items to her cart but leaves the website without completing the purchase.
- Intent Detection: The e-commerce platform utilizes AI intent classification to detect Emma’s purchase intent through her actions—specifically, adding items to her cart.
- Automated Response: A few hours later, Emma receives an automated SMS reminding her of the items left in her cart and offering a discount to encourage her to complete the purchase.
Example SMS:
“Hi Emma! We noticed you left some stylish outfits in your cart. Complete your purchase within the next 24 hours and enjoy 10% off! [Link to Cart]”
2. SaaS
Scenario: Alex, a product manager, signs up for a free trial of a project management software but feels overwhelmed by the features.
- Intent Detection: The SaaS platform classifies Alex’s intent during the onboarding process. His behavior, such as frequently visiting the help center, indicates he needs assistance.
- Automated Nurture Sequence: The system triggers a series of automated emails tailored to guide him through the features, offering video tutorials and tips for maximizing the software’s benefits.
Example Email:
Subject: “Getting the Most Out of Your Trial!”
Content: “Hi Alex! We’ve noticed you’re exploring our features. Here are some tips and resources to help you get started with ease. [Link to Tutorials]”
3. Customer Support
(Image Source: Link)
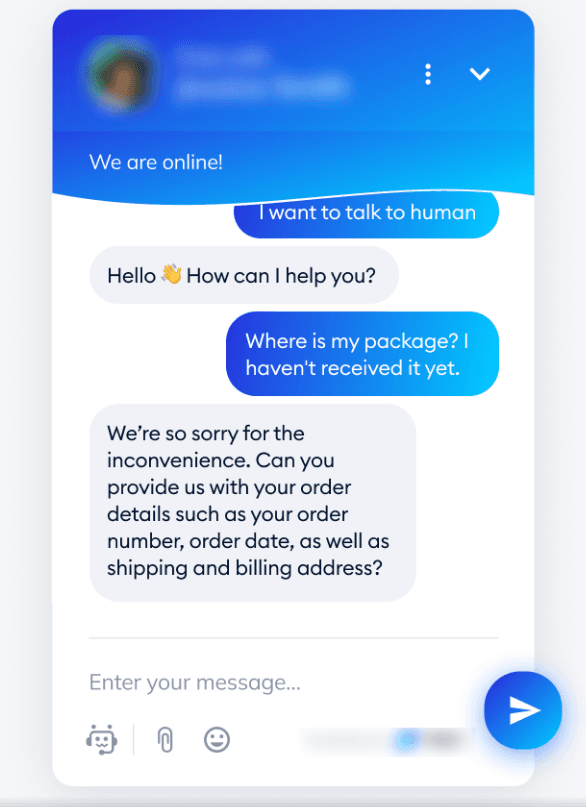
Scenario: Sarah contacts a customer support chatbot with a question about her recent order.
- Intent Detection: The AI-driven chatbot analyzes Sarah’s query and classifies her intent as a support request. It identifies the topic of her question as related to order status.
- Automated Response: The chatbot responds with the current status of her order based on real-time data. If Sarah’s question is complex or specific, the system escalates her case to a live support agent.
Example Chatbot Response:
Chatbot: “Hi Sarah! Your order is currently being processed and will ship within the next 2 days. If you have any other questions, feel free to ask or let me connect you to an agent for further assistance.”
4. Healthcare
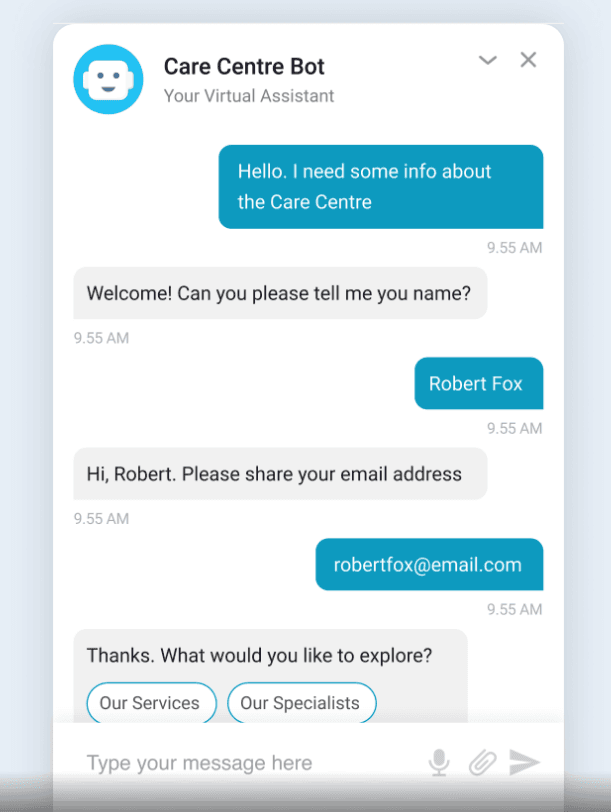
(Image Source: Link)
Scenario: John, a patient, calls a healthcare provider to schedule an appointment.
- Intent Detection: The AI system identifies John’s intent as appointment scheduling based on his query.
- Automated Handling: The system offers automated options for available appointment slots, allowing John to select a time that works best for him without needing to speak to an agent.
Example Automated Response:
“Hi John! I can help you schedule an appointment. Please choose a time from the following options: [List of available slots].”
How AI Intent Classification Works for Social Media Marketing
AI intent classification is changing the face of social media marketing as this allows business to better understand customer interactions in real-time.
Through NLP, machine learning, and contextual analysis, AI categorizes intent but also responds with a strategic move to an interaction, thereby being good at individualized engagement and leading to high customer satisfaction. Let’s see how that works:
Data Collection
AI collects and processes user interactions across various social media platforms. These interactions can include comments, direct messages, posts, likes, shares, and other forms of engagement. By analyzing this data, AI can detect patterns in user behavior and language that signal intent.
Imagine a fitness brand, FitFlex, promoting its new smart fitness tracker on Instagram. Users are engaging with their post by leaving comments, liking the content, and sending direct messages.
- One user comments, “This looks great! Does it track sleep?”
- Another user sends a DM asking, “Do you have a payment plan for this?”
- Others leave generic comments like, “Cool gadget!” or simply like the post without commenting.
In this case, FitFlex’s AI system collects all these interactions to analyze patterns in the language, context, and engagement behavior.
Intent Detection
Using natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning algorithms, AI models analyze the collected data and categorize it into specific intent categories. These categories may include:
- Interest: Users expressing curiosity or desire for more information.
The user who commented, “This looks great! Does it track sleep?” is expressing curiosity and interest in a specific feature of the product.
- Purchase Intent: Clear indications of a user planning to buy a product or service.
The user who messaged, “Do you have a payment plan for this?” is likely interested in purchasing but wants to know more about the payment options—indicating intent to buy.
- Complaints/Queries: Negative feedback or issues that need resolution/ Users seeking information or assistance.
If a user had commented, “I’m having trouble syncing my device, can you help?”, AI would classify this as a query or complaint needing immediate attention.
- Neutral Engagement: General interaction without strong signals toward a specific intent.
A comment like “Cool gadget!” or simply liking the post is categorized as neutral engagement because it shows interest but not strong intent to inquire or purchase.
Personalization
Now that the AI has identified the user’s intentions, the next step is to take action by delivering personalized content or responses based on each user’s intent.
- Interest (User asking about sleep tracking)
FitFlex’s AI-powered chatbot responds to the comment with:
“Yes! The FitFlex tracker monitors sleep patterns. Here’s a blog post that explains how it works!”
Additionally, the brand could retarget this user with ads focusing on the sleep-tracking features of the product.
Purchase Intent (User asking about payment plans)
The AI detects strong purchase intent and triggers an automated message:
“Hi! Yes, we offer flexible payment options. Here’s the link to check them out. Let us know if you need help with anything else!”
The user is then added to a custom audience list for retargeting ads focused on the purchase decision stage.
Neutral Engagement (User saying “Cool gadget!”)
The AI recognizes neutral engagement, and while there’s no immediate purchase intent, it adds the user to a general content marketing funnel. The next time FitFlex releases a product or runs a promo, the user might receive an ad or a post highlighting the product’s cool features.
Complaint or Query (User having syncing issues)
AI immediately flags this comment as a high-priority customer service request, and the bot responds with:
“We’re sorry to hear about the issue! Here’s a step-by-step guide on syncing your device. Let us know if the problem persists, and we’d be happy to help!”
The user receives timely support, reducing frustration and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Implementing AI Intent Classification in Customer Journeys
Implementing AI intent classification effectively requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Start Small and Scale
Begin by focusing on a single use case to test the effectiveness of intent classification. This approach allows businesses to refine their processes and measure success before expanding.
Implementation Steps:
- Identify a specific area, such as customer support or sales, that could benefit from intent classification.
- Run a pilot program to gather data and assess the effectiveness of the AI model in real-world scenarios.
- Analyze the outcomes, including customer satisfaction, response accuracy, and operational efficiency.
Example: A company decides to implement intent classification in their customer support chatbot. After successfully handling FAQs and common inquiries, they expand to include more complex requests, gradually incorporating additional features based on user feedback and performance metrics.
2. Continuous Learning and Improvement
AI models should be dynamic, adapting to new data and changing customer behaviors. Continuous learning ensures that the system remains effective over time.
Implementation Steps:
- Continuously feed new data into the AI system to train and update the model.
- Track the accuracy and performance of the intent classification system regularly.
- Establish a mechanism for collecting feedback from users and agents to inform model improvements.
Example: A retail company analyzes customer interactions and updates their intent classification model quarterly. By incorporating new shopping trends and customer preferences, the AI system becomes more adept at recognizing diverse purchase intents.
3. Human-in-the-Loop Strategy
Incorporating human oversight helps manage situations where AI may misclassify intents or encounter complex scenarios that require human intervention.
Implementation Steps:
- Define clear protocols for when and how to escalate cases from AI to human agents.
- Regularly review misclassifications and complex interactions to identify patterns and improve the AI model.
- Equip human agents with tools and insights from the AI system to handle escalated cases effectively.
Example: A financial services firm employs a chatbot for initial customer inquiries. If the AI detects an ambiguous query or one that requires detailed financial advice, it escalates the case to a qualified financial advisor who can provide personalized assistance.
4. Compliance and Privacy
Ensure that the implementation of AI intent classification complies with data protection regulations like GDPR. Protecting customer data builds trust and mitigates legal risks.
Implementation Steps:
- Establish and enforce policies for data collection, storage, and processing in accordance with legal requirements.
- Use anonymization and encryption techniques to safeguard personal data used for training AI models.
- Clearly communicate data usage policies to customers and provide options for consent.
Example: An e-commerce platform implements intent classification while ensuring that all customer interactions are anonymized. They inform customers about how their data is used to enhance personalization while maintaining compliance with GDPR regulations.
Final Thoughts on AI Intent Classification for Automated Customer Journeys
Why are you waiting? Automate your customer journeys to boost efficiency, enhance engagement, and create tailor-made experiences that keep customers coming back for more by leveraging the power of AI to stay ahead of the competition and redefine what exceptional service looks like.
Don’t just meet expectations—exceed them!