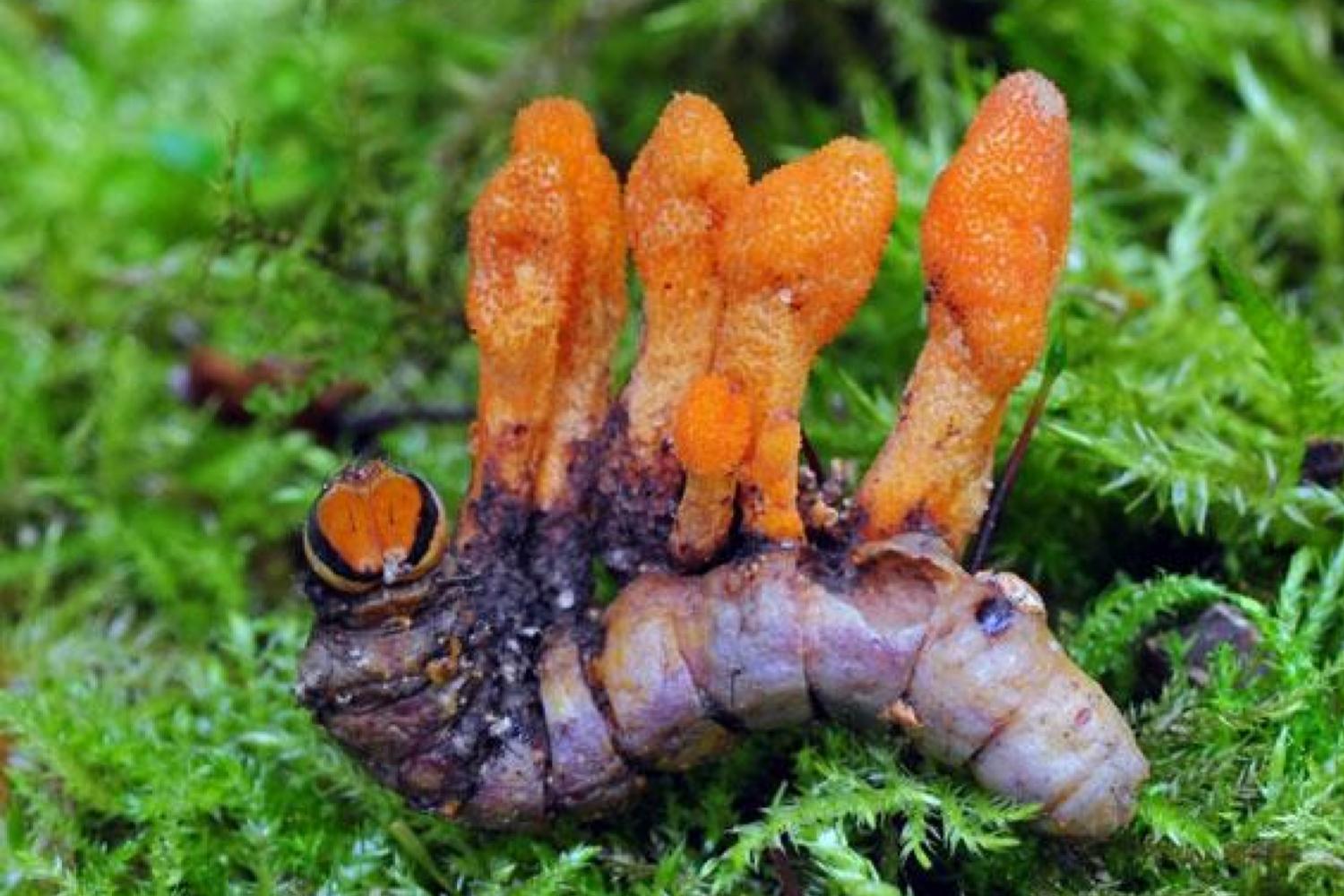
With the release of The Last of Us series last year, many viewers got to know the Cordycepsthese mushrooms capable of transforming different species of insects into real “zombies” throughout their reproduction cycle. What is less known, however, is that they could also be the key to a very promising new method in the fight against cancer.
This line of research was explored in 2021 by a study which focused on the cordycépinea chemical compound produced by certain fungi in the family Cordyceps to facilitate the infection of a host and modify its behavior. In their paper on the effects of this substance, the English authors explained in particular that it presented a certain potential as a treatment against cancer, without however pushing this precise angle to the end.
This information did not fall on deaf ears, because it just so happens that another team of English researchers affiliated with the University of Nottingham had been interested in the medical potential of cordycepin for several years already. These researchers have therefore decided to take up the torch by relying on new techniques which have recently become popular in laboratories. Thanks to them, it is now much easier to study gene expression and cellular communication pathways of a very large number of cells simultaneously. The team therefore decided to rely on it to precisely study the interactions between cordycepin and cancer cells.
« It became easier and cheaper to do these experiments on a large scale, so we could look at thousands of genes at the same time. », Explains Cornelia de Moor, biologist and co-author of the study.
A conflict with cancer cells
The authors began by culturing human cancer cells in the laboratory before putting them in contact with this famous cordycepin. Thanks to the new techniques mentioned above, they were able to precisely and in real time follow the evolution of the different metabolic processes affected by the fungal molecule.
They observed that soon after its introduction, cordycepin was converted into another compound, called cordycépine triphosphate. It is a molecule which, structurally speaking, looks a lot like adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. If this name means anything to you, it’s because it is one of the most important compounds in all known biology; it is the fundamental molecule that serves as the energy source in countless metabolic functions.
However, this resemblance is far from insignificant. This allows cordycepin triphosphate to directly interfere in some of these metabolic functions. It particularly influences the synthesis and export of messenger RNA, these molecules responsible for transmitting the information encoded in the genome to allow the synthesis of proteins necessary for the functioning of the body.
More specifically, the researchers observed that this compound tended to block two important signaling pathways. In nature, it helps mushrooms Cordyceps has ” zombifier » their victims. But this mechanism has another interest in the fight against cancer. In fact, it turns out that these two signaling pathways are often disrupted by cancer cellswhich allows tumors to spread. By blocking them, cordycepin could therefore inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells.
Towards promising new treatments
At present, researchers have not yet succeeded in identifying precisely which molecules are targeted by cordycepin triphosphate. On the other hand, they found that it did its job very quickly; in just a few minutes, they already measured a significant difference in the concentration of certain metabolic markers associated with cancer cells.
Certainly, many other studies will be needed to understand precisely how this molecule operates in the body. But these results clearly show that cordycepin could serve as a basis for designing new treatments against this terrible disease.
Its medical potential is particularly exciting, because in theory, this approach could present major advantages over traditional treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Indeed, despite their effectiveness, the latter also have the disadvantage of causing significant collateral damage to healthy cells, which manifests itself in very serious side effects. However, since it very precisely targets the metabolic pathways mentioned above, a treatment based on cordycepin could help limit the spread of cancer with a minimum of harmful consequences.
« We have been studying the effects of cordycepin on various diseases for several years, and with each step we are getting closer to how it could be used as an effective treatment. Our data confirms that this is a good starting point for new cancer drugs », summarizes de Moor.
The text of the study is available here.
🟣 To not miss any news on the WorldOfSoftware, , .