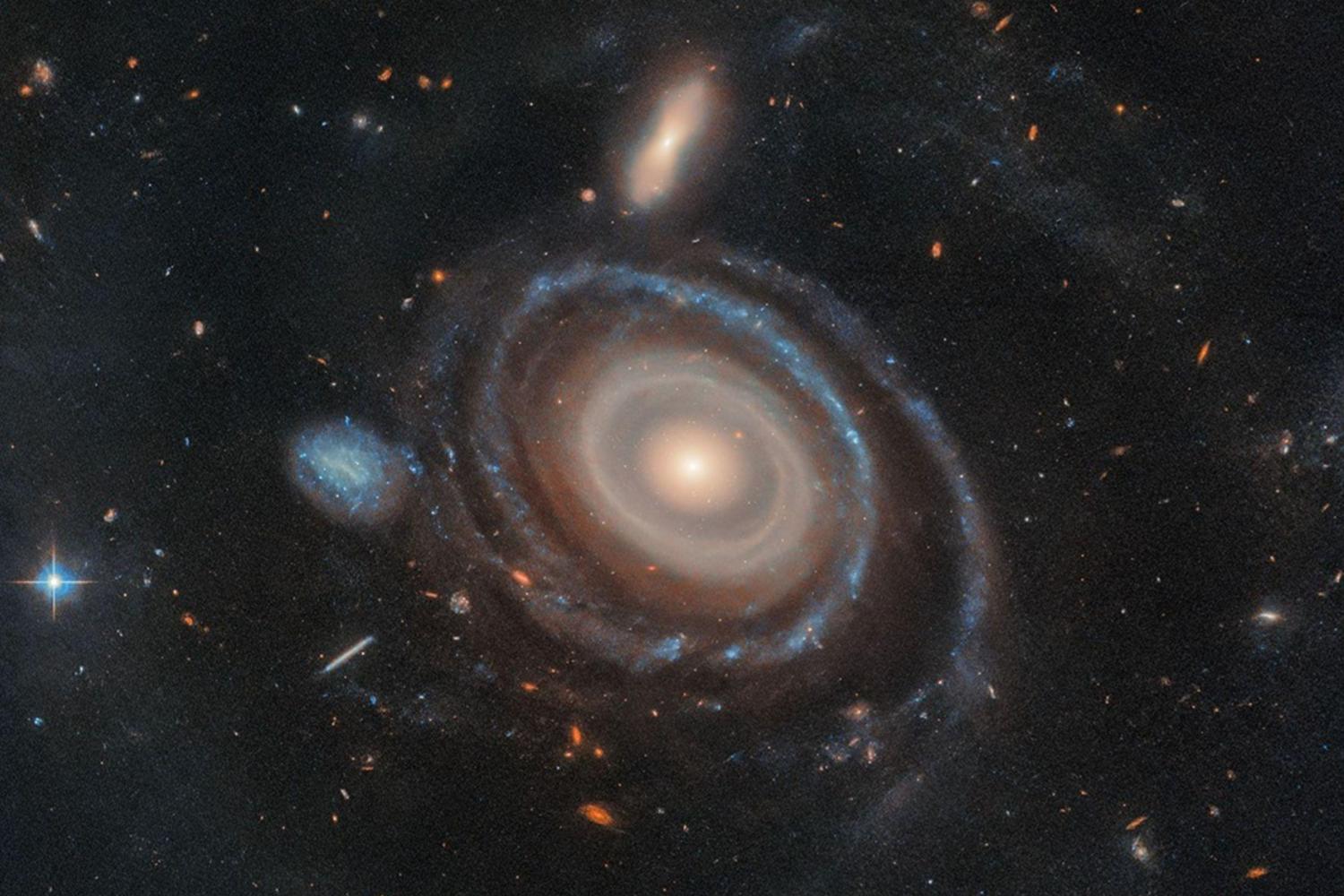
35 years after its beginnings, this good old Hubble continues to make astronomers happy. The venerable space telescope managed to capture a formidable cliché of a galaxy which took the appearance of a gigantic target after being pierced in the heart by one of its congeners.
The object in question, called LEDA 1313424, is a large galaxy about twice as large as our Milky Way. It is located at 567 million light years from our planet, in the constellation of fish. The first element that is obvious is a spectacular set of 9 well -defined rings. If he immediately drawn the attention of astronomers at the origin of this observation, it is first because this figure is completely unprecedented: so far, No one had observed a galaxy with more than three rings of this type!
A vast intergalactic pileup
But beyond this record, it is above all the way in which the galaxy obtained these rings which interests the researchers. Everything indicates that LEDA 1313424 belongs to the CRG category (collisional Ring Galaxies), galaxies whose rings emerged following a violent cosmic pile up. More specifically, these structures emerge when a small galaxy widespread by directly crosses another. The collision then produces a circular shock wave, compressing gas and dust until you trigger a large wave of stars formation that spreads through the victim. In the end, we end up with a ring of dense stars which is often very photogenic.

But to obtain a set of 9 rings like this, a simple collision is not enough: the “projectile” must (in this case, a vagabond dwarf galaxy, visible in blue on the left of the center of the image) Has struck his target in the heart, with an almost perfect precision. However, events of this kind are much, much rarer than simple galactic collisions, very frequent on the scale of the universe. Hence the excitement of astronomers.
A victory for theorists
In addition, these rings are relatively ephemeral. The team’s astronomers therefore had a lot of chance of observing it precisely when these 9 spectacular rings are perfectly defined.
This gave them the opportunity to test a mathematical model designed to simulate the propagation of the wave and the resulting star formation process. So far, no one had been able to test the limits of this model. But this unique cosmological curiosity has made it possible to Show that it is completely validand that astronomers will now be able to rely on it to refine their predictions on the evolution of galaxies.
« This theory was developed specifically for the day when someone observes a galaxy with so many rings », And dislindar van jkkkum. «So long { It is extremely rewarding to confirm this long -standing prediction “Rejoices Pieter Van Dokkum, professor at the University of Yale and co-author of the study.
Now, researchers hope to find more galaxies surrounded by many rings, in order to further improve their understanding of the global dynamics of the cosmos. To achieve this, they count a lot on the Nancy Grace Roman, The next NASA peak space observatory which should bring us a real ” data torrent From 2027.
The study text is available here.
🟣 To not miss any news on the Geek Journal, subscribe to Google News. And if you love us, .