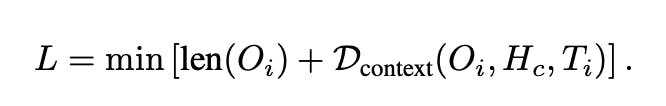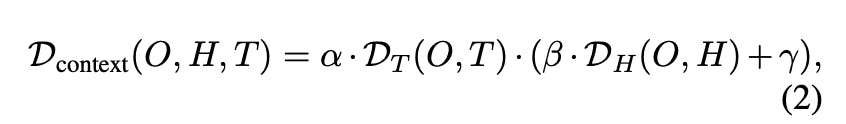As AI systems evolve beyond isolated functionality, the need for efficient and context-aware coordination between agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) is more urgent than ever. In this article, we introduce a rigorous mathematical framework, denoted as the L Function, designed to optimize how LLMs operate within Multi-Agent Systems (MAS) – dynamically, efficiently, and contextually.
🚀 Why We Need a Formal Model for LLMs in MAS
While LLMs demonstrate incredible capabilities in text generation, their integration into MAS environments is often ad hoc, lacking principled foundations for managing context, task relevance, and resource constraints. Traditional heuristics fail to scale in real-time or high-demand environments like finance, healthcare, or autonomous robotics.
This gap motivated the development of the L Function – a unifying mathematical construct to quantify and minimize inefficiencies in LLM outputs by balancing brevity, contextual alignment, and task relevance.
📐 Formal Definition of the L Function
At its core, the L Function is defined as:
LaTeX Notation: L = min left[text{len}({O}{i}) + mathcal{D}{text{context}}({O}{i}, {H}{c}, {T}_{i})right]
Where:
len(O)is the length of the generated output.D_context(O, H, T)is the contextual deviation considering:- Task alignment
- Historical alignment
- System dynamics
🧩 Decomposing D_context(O, H, T)
LaTeX Notation: mathcal{D}{text{context}}(O, H, T) = alpha cdot mathcal{D}{T}(O, T) cdot (beta cdot mathcal{D}_{H}(O, H) + gamma)
D_T(O, T)— Task-specific deviation:- LaTeX Notation:
mathcal{D}_{T}(O, T) = lambda cdot text{len}_{text{optimal}}(O, T) - text{len}(O)
D_H(O, H)— Historical deviation:- LaTeX Notation:
mathcal{D}_{H}(O, H) = 2 cdot (1 - cos(vec{O}, vec{H}))
α, β, γ— Adjustable parameters for weighting task importance, historical coherence, and robustness.λ— A dynamic coefficient computed as:- LaTeX Notation:
lambda(t) = alpha cdot text{J}(t) + beta cdot left(frac{1}{text{R}(t)}right) + gamma cdot text{Q}(t) - Where:
🧠 Why Cosine Similarity?
Cosine similarity is chosen for D_H due to its:
-
Semantic interpretability in high-dimensional spaces.
-
Scale invariance, avoiding vector magnitude distortion.
-
Computational efficiency and geometric consistency.
💡 Use Cases of the L Function in MAS
1. Autonomous Systems
- Context: Self-driving fleets or drone swarms.
- L Function Utility: Prioritizes critical tasks like obstacle avoidance based on historical environment data and mission urgency.
2. Healthcare Decision Support
- Context: Emergency room triage systems.
- L Function Utility: Ensures historical patient data is weighed appropriately while generating succinct and accurate medical responses.
3. Customer Support Automation
- Context: Handling thousands of tickets across varying importance levels.
- L Function Utility: Dynamically reduces verbosity for low-priority tasks while preserving detail in urgent interactions.
📊 Experimental Results: L in Action
Task-Specific Deviation (D_T)
- Setup: 50 synthetic tasks with varying optimal response lengths.
- Outcome: Tasks with
len(O)close tolen_optimalyielded minimalL, proving the alignment logic.
Historical Context Deviation (D_H)
- Observation: Increasing context window size increased deviation, confirming that overloading historical memory introduces semantic noise.
Dynamic λ Scaling
- Simulation: High-priority tasks under low-resource conditions were effectively prioritized using dynamic λ values.
GitHub Experimental Repository: https://github.com/worktif/llm_framework
🔧 Implementation Challenges
- Vector Quality Sensitivity: Low-quality embeddings skew
D_H. PCA or normalization preprocessing is recommended. - Noisy Historical Context: Requires decay strategies to reduce outdated data bias.
- Static Parameters: Consider reinforcement learning to auto-tune
α, β, γ.
📈 Benefits of Adopting the L Function
|
Property |
Impact |
|---|---|
|
Contextual Precision |
Semantic alignment with history and tasks |
|
Response Efficiency |
Shorter, relevant outputs to reduce compute time |
|
Adaptive Prioritization |
Adjusts based on urgency, load, and resource states |
|
Domain-Agnostic Design |
Applicable across healthcare, finance, robotics |
🧪 What’s Next?
Future directions include:
- Integrating reinforcement learning for self-tuning parameters.
- Real-world deployment in distributed MAS environments.
- Noise-robust embedding models for better
D_Hbehavior.
📄 Mathematical and Applied Foundation of the L Function
This article presents the core principles of the L Function for optimizing large language models in multi-agent systems. For a complete and rigorous exposition – including all theoretical derivations, mathematical proofs, experimental results, and implementation details – you can refer to the full monograph:
📘 Title: Mathematical Framework for Large Language Models in Multi-Agent Systems for Interaction and Optimization
Author: Raman Marozau
🔗 Access here: https://doi.org/10.36227/techrxiv.174612312.28926018/v1
If you’re interested in the full theoretical foundation and how to apply this model in production systems, we highly recommend studying the manuscript in detail.
☝️Conclusion
The L Function introduces a novel optimization paradigm that enables LLMs to function as intelligent agents rather than passive generators. By quantifying alignment and adapting in real-time, this framework empowers MAS with contextual intelligence, operational efficiency, and scalable task management — hallmarks of the next generation of AI systems.
“Optimization is not just about speed — it’s about knowing what matters, when.”
For collaboration or deployment inquiries, feel free to reach out.