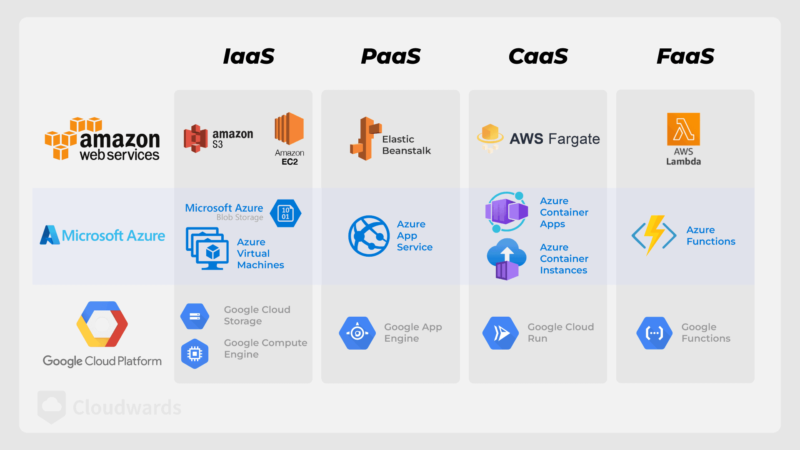
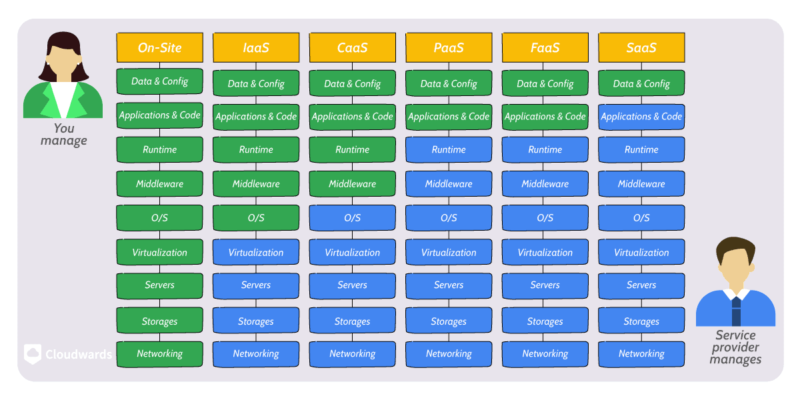
Cloud computing has revolutionized business operations. It offers cost savings, scalability and enhanced digital transformation. However, without a well-defined cloud strategy, companies may face overspending, security gaps and failed cloud adoptions. An effective cloud computing strategy is the key to aligning cloud initiatives with core business objectives for successful cloud adoption.
To develop an effective cloud strategy, you may need to rethink your business operations, service delivery and technology management. Companies that leverage cloud capabilities gain a competitive advantage via faster innovation, improved collaboration and stronger data protection.
This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to creating an effective cloud strategy, ensuring a smooth and successful cloud adoption journey.
What Is a Cloud Computing Strategy?
A cloud computing strategy is a long-term plan that guides how a business uses cloud technology to achieve its objectives. It outlines the best approach to adopt, manage and optimize cloud-based services across various departments and workloads.
Without a clear cloud strategy, businesses often face confusion, rising cloud costs and limited value from their cloud investments.
A typical cloud strategy framework helps you adopt cloud solutions like Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) or Software as a Service (SaaS). It enables you to choose the best cloud deployment model — public, private or hybrid — and cloud provider to suit your organization.
A cloud computing strategy will also assist with security, compliance and cost management. This allows companies to align their goals and broader business strategies to stay on track during their cloud journey.
An effective cloud strategy enables transformation by supporting critical areas like agility, cloud infrastructure scalability, data protection and innovation. By linking cloud capabilities with real-world business processes, organizations can gain a competitive advantage while staying flexible and secure. This ensures that cloud adoption strategies are driven by actual business needs.
A company’s cloud computing strategy is the bridge between its vision and the evolving cloud landscape. It defines the “why,” “what” and “how” behind your transition to the cloud. A clear cloud strategy helps businesses avoid costly mistakes, strengthen collaboration between units and set themselves up for successful cloud adoption.
What Is a Cloud-First Approach?
A cloud-first approach is a business strategy where organizations prioritize cloud-based solutions over traditional on-premises infrastructure for new IT projects and applications. Whenever a business requires a new technology, it must first evaluate whether a cloud platform or cloud-based service can meet that need before turning to legacy systems.
A cloud-first approach encourages businesses to take full advantage of cloud capabilities, such as on-demand resources, scalability, disaster recovery and data security. It promotes smarter cloud adoption strategies, where the cloud becomes the default choice unless there is a strong reason not to use it.
Adopting a cloud-first strategy accelerates digital transformation within an organization. However, you must carefully plan out your cloud security, cost management and integration with existing systems to avoid pitfalls like vendor lock-in or uncontrolled spending. When executed well, a cloud-first mindset modernizes IT infrastructure and fosters a culture of continuous innovation.
What Are the Benefits of Having a Cloud Strategy?
Clearly defined cloud strategies are essential for success in the current digital-first market. A strong strategy aligns a company’s cloud adoption efforts with its business objectives and clarifies how to choose the right cloud solutions. Below are the key benefits of implementing an effective cloud strategy.
- Enhanced cost management: Cloud costs can get out of control without a clear strategy. A well-planned cloud strategy framework helps an organization track its usage, optimize spending and choose the right cloud deployment models that fit its budget.
- Stronger security and compliance: Security is a huge concern in any cloud environment. A strong strategy outlines the cloud security measures needed to protect sensitive data, meet compliance and regulatory requirements, and help you choose a secure, trustworthy cloud provider.
- Aligned technology and business goals: An effective cloud strategy ensures that an organization’s cloud initiatives directly support its broader business strategy. It helps you avoid arbitrary technology choices and focus on specific goals, such as increasing productivity and improving customer service.
- Enhanced scalability and business agility: A cloud strategy includes a clear road map for your business’s cloud adoption journey as you tap into cloud capabilities. A smart strategy helps organizations plan ahead for growth, adjust resources in real time, and support the evolving needs of various business units.
- Fewer risks and faster decision-making: Cloud strategies help all business stakeholders — from IT to leadership — understand an organization’s approach to cloud adoption. When everyone grasps your cloud strategy, it becomes easier to make fast and informed decisions, reducing the operational risks.
What Are the Challenges of Cloud Migration?
Migrating to the cloud can unlock a range of business benefits. However, the migration process comes with its own challenges, which organizations must address for successful implementation. The following are some key challenges of cloud migration that organizations often face.
- Security and compliance concerns: Migrating sensitive data to cloud environments introduces new risks related to cloud security, access management and data protection. Without the right controls in place, companies may expose themselves to breaches or legal issues, especially in highly regulated industries.
- Unexpected costs and budget overruns: While cloud computing promises cost savings, unoptimized resources and inefficient architectures can lead to budget overruns. Pay-as-you-go models need careful monitoring to avoid wasteful spending on underutilized or unnecessary resources.
- Integration issues with existing systems: Many organizations still rely on legacy systems that don’t integrate easily with modern cloud-based solutions. This creates technical challenges and adds complexity to a cloud implementation plan. In some cases, businesses must redesign parts of their existing systems or invest in middleware tools just to ensure smooth cloud operations.
- Skill gaps and change management: Successful cloud adoption strategies require people who understand how to manage and optimize cloud environments. However, many teams lack experience with cloud platform tools, cloud service models or operational procedures. The organization should either train its staff or hire external consultants to implement its cloud adoption framework.
- Unclear cloud strategies: Some organizations migrate to the cloud without a well-defined strategy. They move without fully understanding their goals, needs or risks. This leads to confusion, inconsistent cloud usage and wasted cloud investments. A good cloud strategy ensures that every step in the cloud migration journey supports your overall business objectives.
How to Create a Cloud Strategy Road Map
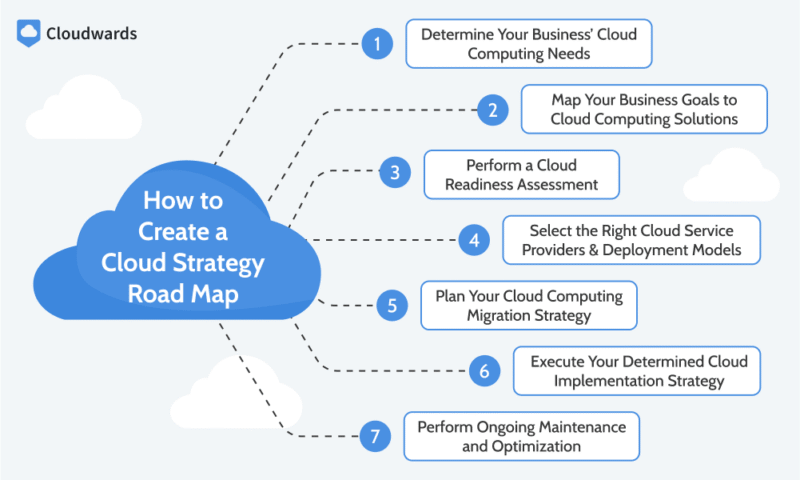
The seven steps to building a successful cloud strategy road map.
The following are the key steps that a business should take when creating its cloud strategy road map.
1. Determine Your Business’ Cloud Computing Needs
A business should assess its current IT infrastructure to evaluate which applications and services are essential. You should determine whether each service can be migrated, refactored or retired. This helps you understand the scale and scope of the cloud adoption process, preventing costly surprises during the migration.
An organization should clearly define its reasons for adopting cloud computing, such as cost savings, scalability, flexibility or innovation. This helps you set clear goals and define what success looks like for the cloud adoption process.
For example, you may aim to reduce IT costs by 20% or maintain 99.99% uptime. This is only possible when organizations clearly understand why they are moving to the cloud.
The cloud adoption team should involve key stakeholders from various departments to gather diverse perspectives, which will help them understand their pain points and expectations. These insights will ensure that the cloud strategy addresses the needs of different business units and aligns with the organization’s overall objectives.
2. Map Your Business Goals to Cloud Computing Solutions
Once you identify your cloud needs, you should link them to specific cloud solutions. Each business goal should have a corresponding cloud service to support it. For example, to achieve cost efficiency, an organization could set up virtual cloud servers to replace expensive on-premises servers.
Categorize your applications and workloads based on their business impact and technical requirements. Customer-facing apps often benefit from auto-scaling and global availability in the public cloud, while legacy systems with complex dependencies may need a hybrid cloud approach for gradual migration.
Prioritize your workloads using factors such as criticality, complexity and cloud compatibility. You should ensure that high-value, low-risk applications migrate first to deliver quick wins and build momentum.
The mapping process must involve collaboration across all business units within an organization. Each department may have different needs that require tailored cloud-based solutions. For instance, the finance team may require better forecasting tools, while the marketing team may need analytics to generate customer insights.
3. Perform a Cloud Readiness Assessment
Before migration, you must evaluate whether your organization is truly ready for the cloud. This involves assessing the technical, operational and cultural factors that could impact success.
Determine whether your current IT infrastructure is compatible with cloud environments, and identify the legacy systems that may pose challenges during the migration process.
You must also evaluate the organization’s operational readiness. Answering these questions will better prepare an organization for its cloud migration.
- Will training be required?
- Is there a plan to manage the transition and address resistance?
- Does the IT team have the necessary skills to manage cloud infrastructure?
In addition, conduct a cost analysis to determine the expenses associated with moving workloads to the cloud. This helps you estimate the costs associated with cloud migration, including any hidden fees. The analysis will allow you to set realistic budgets and avoid unexpected expenditures once the migration process kicks off.
4. Select the Right Cloud Service Providers & Deployment Models
Choosing the right cloud provider is crucial to your cloud adoption road map. Your chosen provider directly impacts the organization’s capabilities, performance, security and compliance.
When evaluating cloud providers, consider factors such as service reliability, regional availability, pricing models, data protection policies, support levels and disaster recovery features.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers the broadest range of
cloud computing services and global infrastructure.
In addition to technical features, check if the provider aligns with your long-term cloud strategy framework. This includes evaluating their governance model, contract flexibility and partnership ecosystem. You should also consider their innovation plan by researching how they invest in new technologies such as AI, machine learning and edge computing.
5. Plan Your Cloud Computing Migration Strategy
A good cloud migration strategy minimizes downtime, reduces risk and ensures a smooth transition from legacy systems to cloud environments.
Conduct a full inventory of your existing workloads, then categorize them using the seven R’s framework to determine the best migration approach for each application:
- Rehost
- Refactor
- Replatform
- Repurchase
- Relocate
- Retire
- Retain
Once your workloads are prioritized, develop a phased migration plan with clear timelines, budget forecasts and roles. You should also include a communication plan to keep stakeholders informed about the migration process. Establish rollback procedures in case of unexpected issues, such as system downtime and failed data transfers.
Plan for client and customer continuity. If the business operates on customer-facing systems, ensure that these services remain stable during the cloud adoption phase. Ideally, customers should not experience downtime during the cloud migration. Prepare measures to ensure continuous service during the migration period.
6. Execute Your Determined Cloud Implementation Strategy
Once your cloud migration strategy is set, it’s time to put it into action. Begin with a phased rollout, starting with non-critical workloads to reduce risk and gather feedback. Make use of pilot environments or proof-of-concept deployments to validate that your configurations, integrations and performance meet your expectations.
During execution, it’s essential to foster close collaboration between IT teams, vendors and third-party providers. Appoint a migration lead or project manager to oversee daily progress, resolve blockers and ensure alignment across departments. Conduct regular status updates and cross-functional check-ins to keep the cloud adoption process on track and promote transparency.
After migration, immediately validate the performance against your predefined success criteria. Conduct smoke tests to verify application functionality, and compare benchmarks — such as response times and uptime — against on-premises baselines. Document the lessons learned to optimize future migrations.
7. Perform Ongoing Maintenance and Optimization
Cloud adoption isn’t a one-time project; it’s an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. After the migration, implement cloud management tools such as AWS CloudWatch to track performance, security and spending in real time. Establish regular review cycles to analyze metrics like resource utilization, latency and cost anomalies.
Amazon CloudWatch provides real-time monitoring and actionable insights to optimize cloud performance, automate maintenance and control costs.
Optimization ensures that your cloud adoption strategies deliver value. Use analytics to understand your cloud usage patterns and adjust your cloud investments accordingly. This could include rightsizing instances, automating workflows, switching to reserved pricing models or even exploring machine learning tools to predict and scale based on demand.
An organization should foster a culture of continuous improvement. Document and share optimization successes across teams and stay informed about your cloud provider’s new features.
As the business grows, implement regular cloud infrastructure strategy reviews to assess whether your deployment models, service providers and tools still align with your organizational goals.
Final Thoughts
A comprehensive cloud computing strategy is essential for organizations looking to modernize operations and remain competitive. A strategic road map helps you avoid pitfalls like unexpected costs, security gaps and failed migrations while maximizing the benefits of cloud computing, such as enhanced agility, flexibility and cost efficiency.
The cloud adoption journey does not end at migration. Ongoing optimization, cost management and security monitoring are critical for long-term success. Organizations should stay flexible, measure performance, and adapt as technology and business needs evolve.
Thank you for taking the time to explore this guide with us. We hope it provides clear and actionable steps for your cloud adoption journey. Which part of the cloud strategy framework are you excited to implement? Share your thoughts in the comments section below. We would love to hear about your challenges and successes.
FAQ: Cloud-First Strategy
-
A cloud strategy is a road map that guides how an organization adopts and uses cloud technologies to meet business goals. It defines priorities, deployment models and governance for effective cloud implementation.
-
The three cloud strategies are Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). They offer varying levels of control, flexibility and management over your cloud infrastructure.
-
The five pillars of cloud computing are operational excellence, security, reliability, performance efficiency and cost optimization. They help organizations build cloud solutions that are scalable, resilient, secure and cost-effective.