The Internet of Things (IoT) is all about connecting everyday devices (like sensors, lights, or even weather stations) to the Internet so they can share data and work smarter. From simple home setups to advanced environmental monitoring, IoT is everywhere. And when it’s open source, the code is public, free to use, and shaped by a global community instead of a single company. That means more transparency, creativity, and collaboration.
We’ve picked five open-source IoT software projects you can actually use right now, for free —although the accompanying hardware has its own minor cost. Each offers unique ways to experiment, learn, and make your devices talk to each other. If you find them useful, you can go to Kivach, an Obyte-based platform for crypto donations, and send them some love in the shape of coins.
Thanks to this platform, you can send funds to any GitHub project you believe in. No middlemen, no complicated sign-ups: just pick the repository and send your contribution in cryptocurrency. Now, let’s explore some open-source IoT.
Meshtastic
Imagine being able to send messages to friends or teammates without cell towers or Wi-Fi. That was the idea Kevin Hester brought to life in early 2020 with Meshtastic, a software platform that turns inexpensive LoRa radios into long-range, off-grid communication devices. It was built for activities where reliable connectivity is scarce, like hiking, sailing, or remote expeditions, but its purpose has grown to include safety, community projects, and creative IoT setups.
Meshtastic works by using LoRa technology, which stands for “Long Range” and refers to a low-power radio system that can send data over several kilometers without a license in most regions. Messages hop between devices, forming a “mesh” so even distant users can stay in touch. You can pair a Meshtastic radio with your phone to send texts, share GPS location, or pass sensor data. It has been used for everything from disaster relief to Mars Society training missions, proving its usefulness in tough and isolated environments.
To use it, you’ll need compatible hardware such as ESP32-based boards (microcontrollers or tiny computers, which, by the way, are still sufficient to run an Obyte node) or purpose-built Meshtastic kits, which are affordable devices. Development is powered by volunteers, with funding coming from community donations, plus in-kind support from sponsors for hosting, infrastructure, and testing. Anyone can help by contributing code, improving documentation, or chipping in financially to keep the network growing. You can do the latter with crypto via Kivach.
Calaos
First developed in 2007 by French developers Raoul Hecky and a partner, Calaos was created to give you complete control over your home environment: from music to lights to other appliances. When the original company closed in 2013, the project was opened to the public, allowing anyone to use and improve it. Today, it’s a community-driven platform that lets you configure, monitor, and control different devices in your home from one central place.

By using Calaos, you can link lighting, music systems, shutters, cameras, and more into custom “scenarios” that respond to time, mood, or specific events. It works with technologies like Wago PLC (programmable logic controllers for managing industrial and home systems), Raspberry Pi, and other hardware. You can control everything through touchscreen panels, mobile apps for Android and iOS, or a web interface.
You’ll need compatible hardware, but it doesn’t have to be costly, especially if you use affordable boards like Raspberry Pi. Funding comes from community donations, plus volunteer contributions in code, documentation, translations, and design. This mix of support keeps Calaos independent and evolving. To donate crypto via Kivach, they appear there as calaos/calaos_base.
NodeMCU
This software first appeared in October 2014, when developer ‘Hong’ uploaded the initial firmware to GitHub. It was created to work with the ESP8266, a small, inexpensive Wi-Fi chip from Espressif Systems, and its main job is to let you program that chip using Lua, a beginner-friendly scripting language. Over time, community contributors have kept it alive, adding features and extending support to the newer ESP32 chip.
With NodeMCU, you can control hardware pins (the little connectors on a board), send and receive data over Wi-Fi, and even run a tiny web server. It works in an “event-driven” way, meaning your code waits for things to happen, like a button press or a message arriving. You can use it for all sorts of IoT (Internet of Things) projects —turning lights on via your phone, gathering weather data, or even controlling a garden watering system.
You’ll need a small hardware board with an ESP8266 or ESP32 to run it (and connect IoT devices), but these are easy to find and cost just a few dollars. Funding comes entirely from volunteers and contributors; there’s no company behind it. If you enjoy using NodeMCU, you can help by contributing code, improving documentation, or donating through platforms like Kivach.
Cointiki-NG
Contiki-NG began in 2017 as a modern fork of the original Contiki operating system, which Adam Dunkels first created back in 2002. Its main purpose is to run on tiny, low-power devices that form part of the Internet of Things, like environmental sensors or smart streetlights. It was built by a community of independent developers and researchers from around the world, without being tied to a single company. The goal is to help devices communicate efficiently over the Internet while using very little memory and energy.
https://x.com/JulienVandaele/status/1065231727164051457?embedable=true
One of its key strengths is its ability to bring IPv6 networking (the newer version of Internet addressing) to devices that have as little as 10 kilobytes of memory. It also supports multitasking, custom networking protocols for low-energy use, and a simulator called Cooja that lets you test setups before putting them in the real world. This makes it useful for projects ranging from home automation to smart agriculture, even if you’re just learning the ropes of IoT development.
Running Contiki-NG doesn’t require expensive hardware. Boards with chips like the ARM Cortex-M or TI MSP430, which cost only a few dollars, are enough. Development is community-driven, with contributions coming from volunteers and institutions. Financial support can be offered by donating crypto via Kivach, where they appear as contiki-ng/contiki-ng.
OpenHab
Home automation used to mean juggling apps from different brands, each with its own rules. That changed in 2010 when Kai Kreuzer started a project that could bring them all together. Three years later, its main technology became part of the Eclipse Foundation under the name Eclipse SmartHome, and today it continues as OpenHab. The idea is simple: you run it on your own computer or small device, connect it to your gadgets, and control everything from one place. From lights to speakers, if it can be automated, there’s a good chance OpenHab can talk to it.
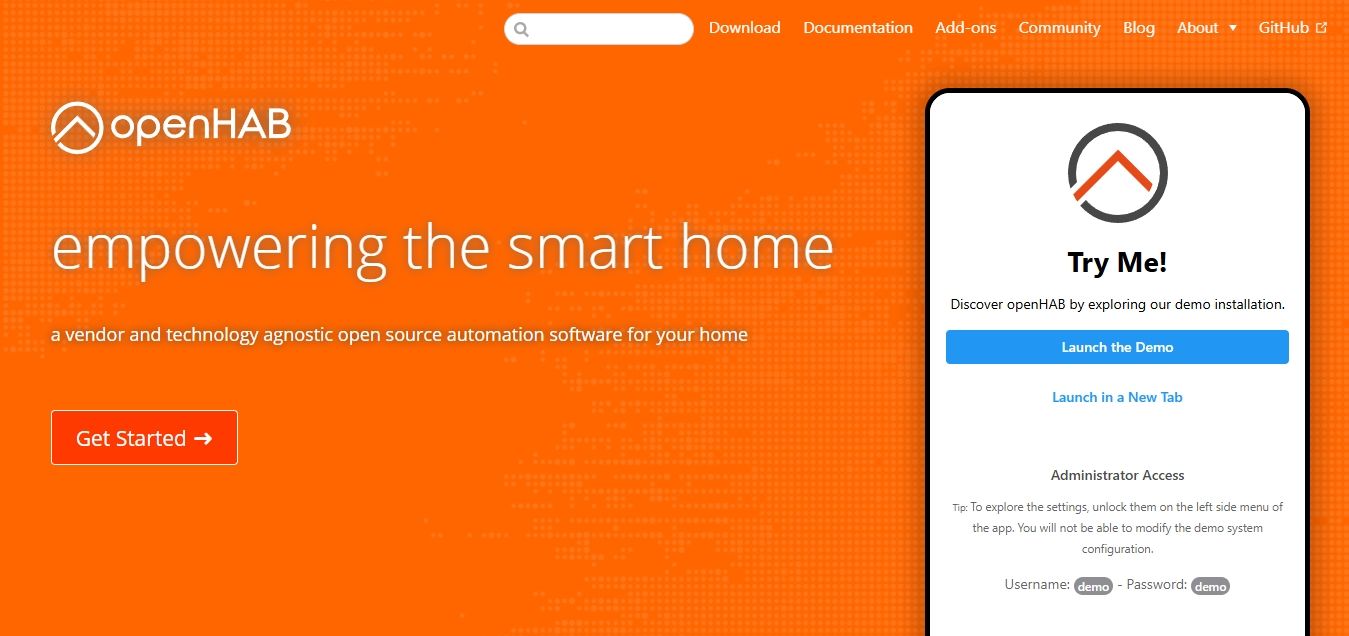
One of its strengths is how much it can integrate. Thanks to a modular system (think of it like adding Lego pieces for each type of device), it supports hundreds of technologies, from Zigbee and Z-Wave to Google Assistant and Alexa. You can create rules that trigger actions based on time, events, or sensor readings, and you can check and control your home from apps, browsers, or even by voice. It also works offline (through an “Intranet”), which means your devices keep working even without the Internet, and your data stays in your home unless you decide otherwise.
Running it does require some extra hardware, like a Raspberry Pi, but there’s no need for expensive equipment. The software itself is free, and it’s maintained by a large global community. Since 2016, the non-profit OpenHab Foundation has supported the project through events, infrastructure, and services, funded by donations and memberships starting at just a few euros per month. It’s a setup that keeps the project alive without turning it into a commercial product. Of course, you can send some coins to them via Kivach, too.
What do you need to send donations with Kivach?
To send a donation through Kivach, you’ll first need an Obyte wallet. This is the app where your funds will be stored and from which transactions are made. Even if your donation will be in another token, you’ll also need some GBYTE, which is Obyte’s native currency, to cover the small transaction fees. You can get GBYTE by swapping other popular coins like ETH or USDC through supported bridges.
Once your wallet is set up and topped up, the process is straightforward. On the Kivach site, find the GitHub repository you want to support, choose your donation amount and token, and send it. The recipient doesn’t have to be registered yet; your donation will wait for them until they claim it.
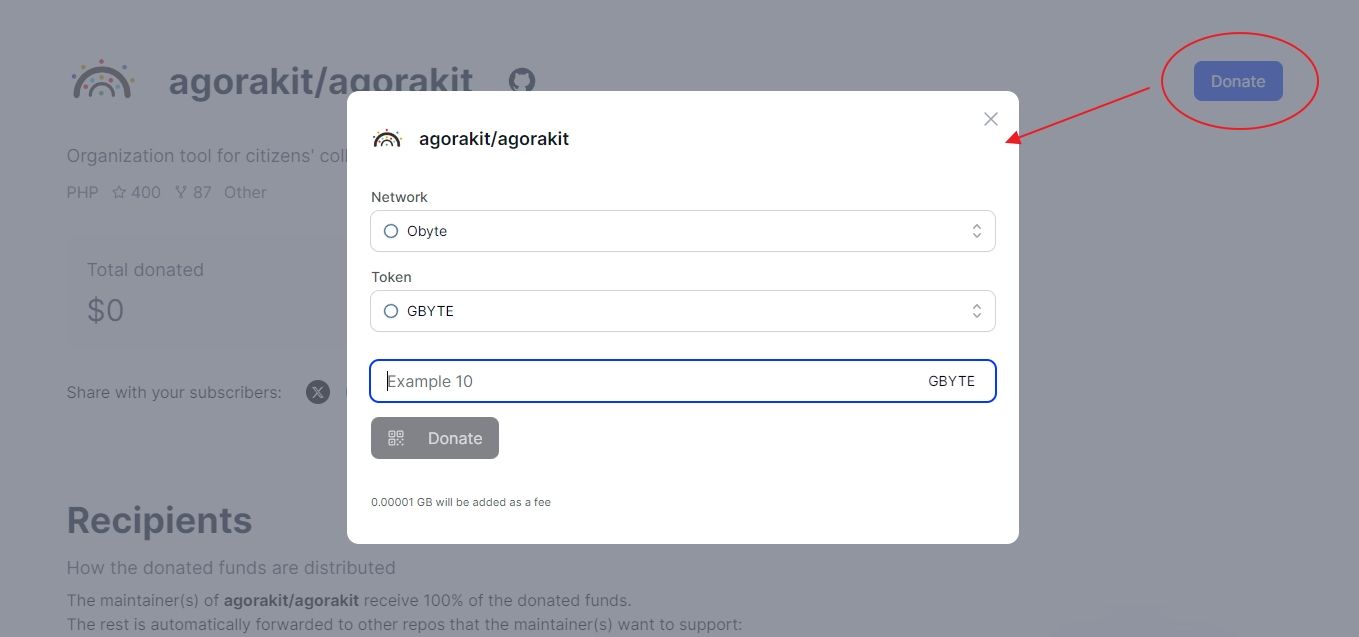
If you want to receive donations yourself, the requirements are simple: install the Obyte wallet, link your GitHub account using the attestation bot, and set your distribution rules (if any). After that, you can collect any incoming or past donations.
Also, you can check our previous episodes!
- 5 Open-source Blogging and Writing Tools to Donate to via Kivach (Ep V)
- 5 Open-Source Tools You Can Donate to via Kivach, Episode VI: Decentralized Services
- 5 Open-Source Projects to Donate via Kivach, Episode VII: Games to Play for Free!
- 5 Cybersecurity Tools to Use for Free and Donate to Via Kivach
- 5 Free Data Recovery and Backup Projects to Donate to Via Kivach
- 5 Open-Source Software for Global Teams To Donate via Kivach
- Author Your Own Adventure With These 5 Must-Try Free Tools
- 5 Open-source and Free Operating Systems to Donate via Kivach
- 5 Open-Source, Free Software You Didn’t Know You Needed to Protect Your Data
- 5 Open-Source Private Messengers to Try for Free —and Support Via Kivach
Featured Vector Image by jcomp / Freepik
n n










