Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Our Contribution
1.2 Setting
1.3 The algorithm
-
Related Work
-
Algorithm
3.1 The Structural Decomposition Phase
3.2 The Routing Phase
3.3 Variants of WormHole
-
Theoretical Analysis
4.1 Preliminaries
4.2 Sublinearity of Inner Ring
4.3 Approximation Error
4.4 Query Complexity
-
Experimental Results
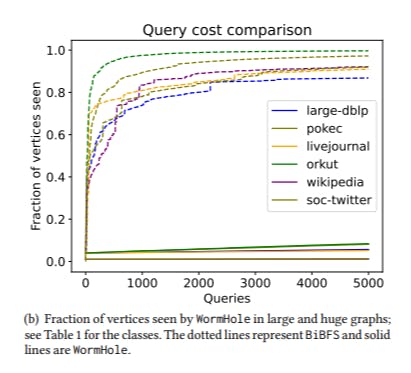
5.1 WormHole𝐸, WormHole𝐻 and BiBFS
5.2 Comparison with index-based methods
5.3 WormHole as a primitive: WormHole𝑀
References
1.2 Setting
We consider the problem of constructing a data structure for approximately answering shortest-path inquiries between pairs
of vertices (𝑠,𝑡) in an undirected graph𝐺, given limited query access to the graph.
Query model. Access to the network is given through the standard node query model [10, 14], where we start with an arbitrary seed vertex as the “access point” to the network, and querying a node 𝑣 reveals its list of neighbors Γ(𝑣). Unlike existing index-based solutions, which perform preprocessing on the whole graph, we aim for a solution that queries and stores only a small fraction of the nodes in the network.
Objective. Following the initialization of the data structure, the task is to answer multiple shortest path inquiries, where each inquiry SP(𝑠,𝑡) needs to be answered with a valid path 𝑝0𝑝1 …𝑝ℓ between 𝑠 = 𝑝0 and 𝑡 = 𝑝ℓ , and the objective is to minimize the mean additive error measured over all inquiries. The additive error for an inquiry SP(𝑠,𝑡) is the difference between the length of the returned𝑠–𝑡 path and the actual shortest distance between 𝑠 and 𝑡 in 𝐺. Depending on the specific application, one would like to minimize (a subset of) the additive error, running time, memory and/or node queries.
Core-periphery structure. The degree distribution in social and information networks often follows a power-law distribution with exponent 2<𝛽 <3, which results in a core-periphery structure [9, 43, 50, 52, 63], where the core is a highly connected component with good expansion properties, consisting of higher degree nodes, while the periphery is a collection of small, poorly connected components of low degree.
Our data structure is designed for networks exhibiting these structural characteristics. It takes advantage of the structure by first performing a preprocessing step to acquire (parts of) the core of the network, and then answering approximate shortest path inquiries by routing through the core. The working hypothesis is that pairs of nodes that are sufficiently far apart will typically have the shortest path between them (or close to it) routed through the higher degree parts of the network. This is somewhat reminiscent of approaches based on the highway dimension [1–3] for routing in road networks, although the structural characteristics of these network types differ considerably
1.3 The algorithm
WormHole builds an explicit hierarchical core-periphery type structure with a sublinear inner ring and provides a framework which uses this structure to answer shortest path inquiries. There are two phases:
• A preprocessing step where we decompose the graph into three partitions, storing only the smallest one: a highly dense subgraph of sublinear size.
• The phase where we answer inquiries: here the algorithm (approximately) answers shortest path inquiries of the form SP(𝑠,𝑡) for arbitrary vertex pairs (𝑠,𝑡).
We elaborate on the two phases.
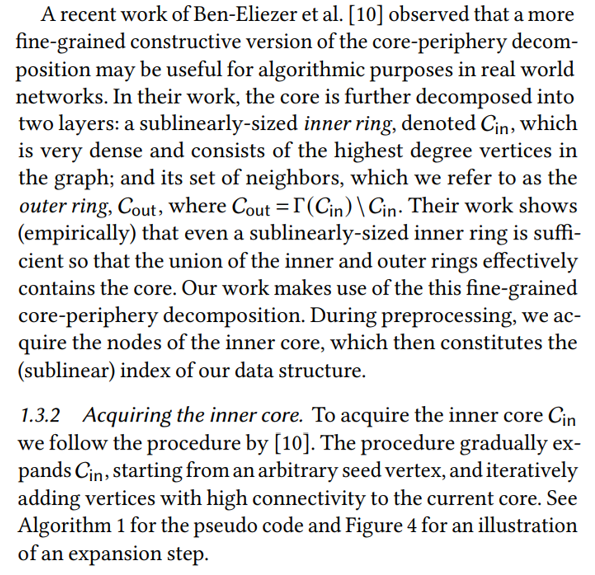
1.3.1 The decomposition. It is well-documented that social networks exhibit a core-periphery structure; see, e.g., [43, 50, 52, 63] and the many references within. The core is a highly-connected component with good expansion properties and smaller effective diameter. The periphery, denoted P, consists of smaller isolated communities that connect to the core, but are sparsely connected internally, and whose union is of linear size [16]. Therefore, when answering shortest path inquiries, it is reasonable to first check if the two vertices are in the same peripheral community, and otherwise route through the core.
1.3.3 Answering shortest-path queries. In the second phase, given a query SP(𝑠,𝑡), WormHole does the following. First, it checks if the two vertices are in the same peripheral component, by performing a truncated BiBFS from both 𝑠 and 𝑡 up to depth two. If the two trees collide, it returns the shortest path between 𝑠 and 𝑡. Otherwise, WormHole continues both BFS traversals until it reaches the outer ring (from both 𝑠 and 𝑡). From here, it takes a single step to reach the inner ring, and then performs a restricted BiBFS on the subgraph induced by the inner ring vertices. We note that the choice of BiBFS here is arbitrary, and we can use any shortest-path algorithm (including modern index-based approaches, initialized only on the inner core) as a black-box to find a shortest path in the inner ring.
Figure 3 illustrates a few typical cases encountered by the algorithm; in the first two cases the algorithm returns a true shortest path, and in the third case the returned path is not a shortest path (thus incurring a nonzero additive error).
We stress that a single decomposition is subsequently used to answer all shortest path queries. Theorem 1.1 provides a strong theoretical guarantee on the performance of WormHole. It is worth emphasizing that our notion of approximation is inspired by practical relaxations, and is distinct from the one usually considered in theoretical works.
:::info
Authors:
(1) Talya Eden, Bar-Ilan University ([email protected]);
(2) Omri Ben-Eliezer, MIT ([email protected]);
(3) C. Seshadhri, UC Santa Cruz ([email protected]).
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::