Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Our Contribution
1.2 Setting
1.3 The algorithm
-
Related Work
-
Algorithm
3.1 The Structural Decomposition Phase
3.2 The Routing Phase
3.3 Variants of WormHole
-
Theoretical Analysis
4.1 Preliminaries
4.2 Sublinearity of Inner Ring
4.3 Approximation Error
4.4 Query Complexity
-
Experimental Results
5.1 WormHole𝐸, WormHole𝐻 and BiBFS
5.2 Comparison with index-based methods
5.3 WormHole as a primitive: WormHole𝑀
References
5.3 WormHole as a primitive: WormHole𝑀
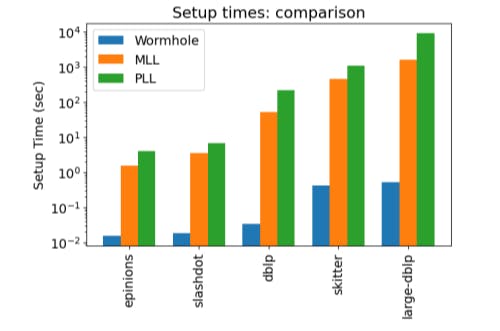
We conduct similar experiments for WormHole𝑀 . Remarkably, while MLL fails to complete setup on most of the graphs, WormHole𝑀 successfully runs it on the core in all cases. Moreover, as noted in Table 6, the cost in both time and space is orders of magnitude smaller than for the full graph, though still significantly larger than the default WormHole𝐻. We note about two orders of magnitude of improvement in time per inquiry over WormHole𝐻 , but at the same time, the setup cost is also about two orders of magnitude higher in both time and space. Notably, even in cases where MLL does complete on the full graph, we are able to answer inquiries in roughly the same time (see Figure 1) at a fraction of the setup cost (Figure 7). We leave a more systematic investigation of this approach of combining WormHole with existing methods on the core to future work.
REFERENCES
[1] Ittai Abraham, Daniel Delling, Amos Fiat, Andrew V. Goldberg, and Renato F. Werneck. 2011. VC-Dimension and Shortest Path Algorithms. In Automata, Languages and Programming (ICALP ’11).
[2] Ittai Abraham, Daniel Delling, Amos Fiat, Andrew V. Goldberg, and Renato F. Werneck. 2016. Highway Dimension and Provably Efficient Shortest Path Algorithms. J. ACM 63, 5, Article 41 (2016).
[3] Ittai Abraham, Daniel Delling, Andrew V. Goldberg, and Renato F. Werneck. 2011. A Hub-Based Labeling Algorithm for Shortest Paths in Road Networks. In Experimental Algorithms, Panos M. Pardalos and Steffen Rebennack (Eds.).
[4] D. Aingworth, C. Chekuri, P. Indyk, and R. Motwani. 1999. Fast Estimation of Diameter and Shortest Paths (Without Matrix Multiplication). SIAM J. Comput. 28, 4 (1999).
[5] Takuya Akiba, Yoichi Iwata, and Yuichi Yoshida. 2013. Fast Exact Shortest-Path Distance Queries on Large Networks by Pruned Landmark Labeling (SIGMOD ’13).
[6] Takuya Akiba, Christian Sommer, and Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi. 2012. Shortest-Path Queries for Complex Networks: Exploiting Low Tree-Width Outside the Core (EDBT ’12).
[7] Réka Albert, Hawoong Jeong, and Albert-László Barabási. 1999. Diameter of the World-Wide Web. Nature 401, 6749 (1999).
[8] Noga Alon, Allan Grønlund, Søren Fuglede Jørgensen, and Kasper Green Larsen. 2023. Sublinear Time Shortest Path in Expander Graphs. arXiv:2307.06113 [cs.DS]
[9] Igor Artico, I Smolyarenko, Veronica Vinciotti, and Ernst C Wit. 2020. How rare are power-law networks really? Proceedings of the Royal Society A 476, 2241 (2020).
[10] Omri Ben-Eliezer, Talya Eden, Joel Oren, and Dimitris Fotakis. 2022. Sampling Multiple Nodes in Large Networks: Beyond Random Walks (WSDM ’22). 37–47.
[11] Thomas Bläsius, Cedric Freiberger, Tobias Friedrich, Maximilian Katzmann, Felix Montenegro-Retana, and Marianne Thieffry. 2022. Efficient Shortest Paths in Scale-Free Networks with Underlying Hyperbolic Geometry. ACM Trans. Algorithms 18, 2, Article 19 (mar 2022).
[12] Michele Borassi and Emanuele Natale. 2019. KADABRA is an ADaptive Algorithm for Betweenness via Random Approximation. ACM J. Exp. Algorithmics 24, Article 1.2 (feb 2019).
[13] Arthur Brady and Lenore Cowen. 2006. Compact Routing on Power Law Graphs with Additive Stretch. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Algorithm Engineering and Experiments (ALENEX ’06).
[14] Flavio Chiericetti, Anirban Dasgupta, Ravi Kumar, Silvio Lattanzi, and Tamás Sarlós. 2016. On Sampling Nodes in a Network. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW ’16).
[15] Fan Chung and Linyuan Lu. 2002. Connected components in random graphs with given expected degree sequences. Annals of combinatorics 6, 2 (2002).
[16] Fan Chung and Linyuan Lu. 2004. The average distance in a random graph with given expected degrees. Internet Mathematics 1, 1 (2004).
[17] Fan Chung and Linyuan Lu. 2006. The volume of the giant component of a random graph with given expected degrees. SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics 20, 2 (2006).
[18] Andrea Costa, Ana M. Martín González, Katell Guizien, Andrea M. Doglioli, José María Gómez, Anne A. Petrenko, and Stefano Allesina. 2019. Ecological networks: Pursuing the shortest path, however narrow and crooked. Scientific Reports 9, 1 (Nov. 2019).
[19] Mingyang Deng, Yael Kirkpatrick, Victor Rong, Virginia Vassilevska Williams, and Ziqian Zhong. 2022. New Additive Approximations for Shortest Paths and Cycles (ICALP ’22, Vol. 229).
[20] Jörg Derungs, Riko Jacob, and Peter Widmayer. 2007. Approximate Shortest Paths Guided by a Small Index. In Algorithms and Data Structures, 10th International Workshop, WADS (Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 4619).
[21] E. W. Dijkstra. 1959. A Note on Two Problems in Connexion with Graphs. Numer. Math. 1, 1 (dec 1959).
[22] Michal Dory, Sebastian Forster, Yael Kirkpatrick, Yasamin Nazari, Virginia Vassilevska Williams, and Tijn de Vos. 2023. Fast 2-Approximate All-Pairs Shortest Paths. CoRR abs/2307.09258 (2023).
[23] Michalis Faloutsos, Petros Faloutsos, and Christos Faloutsos. 1999. On Power-Law Relationships of the Internet Topology (SIGCOMM ’99).
[24] John A Fitch III and Lance J Hoffman. 1993. A shortest path network security model. Computers & Security 12, 2 (1993), 169–189.
[25] Michael L. Fredman and Robert Endre Tarjan. 1987. Fibonacci Heaps and Their Uses in Improved Network Optimization Algorithms. J. ACM 34, 3 (jul 1987).
[26] Peng Gao, Xusheng Xiao, Zhichun Li, Kangkook Jee, Fengyuan Xu, Sanjeev R. Kulkarni, and Prateek Mittal. 2019. A Query System for Efficiently Investigating Complex Attack Behaviors for Enterprise Security. Proc. VLDB Endow. 12, 12 (2019).
[27] Patrice Godefroid, Nils Klarlund, and Koushik Sen. 2005. DART: Directed Automated Random Testing. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM SIGPLAN conference on Programming language design and implementation (PLD ’05).
[28] Andrew V. Goldberg and Chris Harrelson. 2005. Computing the Shortest Path: A Search Meets Graph Theory (SODA ’05).
[29] Ruoming Jin, Zhen Peng, Wendell Wu, Feodor Dragan, Gagan Agrawal, and Bin Ren. 2020. Parallelizing Pruned Landmark Labeling: Dealing with Dependencies in Graph Algorithms (ICS ’20). Article 11.
[30] Xin Jin, Charalampos Katsis, Fan Sang, Jiahao Sun, Elisa Bertino, Ramana Rao Kompella, and Ashish Kundu. 2023. Prometheus: Infrastructure Security Posture Analysis with AI-generated Attack Graphs. CoRR (2023). arXiv:2312.13119
[31] Siddharth Kaza, Jennifer Xu, Byron Marshall, and Hsinchun Chen. 2009. Topological Analysis of Criminal Activity Networks: Enhancing Transportation Security. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems 10, 1 (2009).
[32] Masahiro Kimura and Kazumi Saito. 2006. Tractable Models for Information Diffusion in Social Networks. In Knowledge Discovery in Databases: PKDD 2006.
[33] Maksim Kitsak, Alexander Ganin, Ahmed Elmokashfi, Hongzhu Cui, Daniel A. Eisenberg, David L. Alderson, Dmitry Korkin, and Igor Linkov. 2023. Finding shortest and nearly shortest path nodes in large substantially incomplete networks by hyperbolic mapping. Nature Communications 14, 1 (2023).
[34] Jérôme Kunegis. 2013. KONECT: The Koblenz Network Collection (WWW ’13 Companion).
[35] Andrey Kutuzov, Mohammad Dorgham, Oleksiy Oliynyk, Chris Biemann, and Alexander Panchenko. 2019. Learning Graph Embeddings from WordNet-based Similarity Measures. In Proceedings of the Eighth Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics (*SEM 2019).
[36] Jure Leskovec and Andrej Krevl. 2014. SNAP Datasets: Stanford Large Network Dataset Collection. http://snap.stanford.edu/data.
[37] Wentao Li, Miao Qiao, Lu Qin, Ying Zhang, Lijun Chang, and Xuemin Lin. 2020. Scaling up distance labeling on graphs with core-periphery properties (SIGMOD ’20). 1367–1381.
[38] Wentao Li, Miao Qiao, Lu Qin, Ying Zhang, Lijun Chang, and Xuemin Lin. 2020. Scaling Up Distance Labeling on Graphs with Core-Periphery Properties (SIGMOD ’20).
[39] Wentao Li, Miao Qiao, Lu Qin, Ying Zhang, Lijun Chang, and Xuemin Lin. 2022. Distance labeling: on parallelism, compression, and ordering. The VLDB Journal 31 (01 2022).
[40] Ye Li, Leong Hou U, Man Lung Yiu, and Ngai Meng Kou. 2017. An Experimental Study on Hub Labeling Based Shortest Path Algorithms. Proc. VLDB Endow. 11, 4 (dec 2017). [
41] Linyuan Lincoln Lu. 2002. Probabilistic methods in massive graphs and Internet computing. Ph. D. Dissertation. University of California, San Diego.
[42] Amgad Madkour, Walid G Aref, Faizan Ur Rehman, Mohamed Abdur Rahman, and Saleh Basalamah. 2017. A survey of shortest-path algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.02044 (2017).
[43] Fragkiskos D. Malliaros, Christos Giatsidis, Apostolos N. Papadopoulos, and Michalis Vazirgiannis. 2019. The Core Decomposition of Networks: Theory, Algorithms and Applications. The VLDB Journal 29, 1 (nov 2019).
[44] M. E. J. Newman. 2003. The Structure and Function of Complex Networks. SIAM Rev. 45, 2 (2003).
[45] Ali Pinar, C. Seshadhri, and Vaidyanathan Vishal. 2017. ESCAPE: Efficiently Counting All 5-Vertex Subgraphs (WWW ’17).
[46] Ira Pohl. 1969. Bi-directional and heuristic search in path problems. Ph. D. Dissertation. Stanford University, USA.
[47] Jianzhong Qi, Wei Wang, Rui Zhang, and Zhuowei Zhao. 2020. A Learning Based Approach to Predict Shortest-Path Distances (EBDT’20).
[48] Fatemeh Salehi Rizi, Joerg Schloetterer, and Michael Granitzer. 2020. Shortest Path Distance Approximation Using Deep Learning Techniques (ASONAM ’18).
[49] Liam Roditty. 2023. New Algorithms for All Pairs Approximate Shortest Paths (STOC ’23).
[50] M. Puck Rombach, Mason A. Porter, James H. Fowler, and Peter J. Mucha. 2014. Core-Periphery Structure in Networks. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 74, 1 (2014).
[51] Barna Saha and Christopher Ye. 2023. Faster Approximate All Pairs Shortest Paths. CoRR abs/2309.13225 (2023). [52] Stephen B. Seidman. 1983. Network structure and minimum degree. Social Networks 5, 3 (1983).
[53] Sandeep Sen. 2009. Approximating shortest paths in graphs.In International Workshop on Algorithms and Computation. 32–43.
[54] Matteo Serafino, Giulio Cimini, Amos Maritan, Andrea Rinaldo, Samir Suweis, Jayanth R. Banavar, and Guido Caldarelli. 2021. True scale-free networks hidden by finite size effects. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 118, 2 (2021).
[55] Christian Sommer. 2014. Shortest-path queries in static networks. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR) 46, 4 (2014).
[56] Chi Wang, Wei Chen, and Yajun Wang. 2012. Scalable Influence Maximization for Independent Cascade model in Large-scale Social Networks. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Journal 25, 3 (2012).
[57] YeWang, QingWang, Henning Koehler, and Yu Lin. 2021. Query-by-Sketch: Scaling Shortest PathGraph Queries onVery LargeNetworks(SIGMOD’21).
[58] Jennifer J Xu and Hsinchun Chen. 2004. Fighting organized crimes: using shortest-path algorithms to identify associations in criminal networks. Decision Support Systems 38, 3 (2004).
[59] Xiaolong Xu, Yuancheng Li, Tao Huang, Yuan Xue, Kai Peng, Lianyong Qi, and Wanchun Dou. 2019. An energy-aware computation offloading method for smart edge computing in wireless metropolitan area networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications (2019).
[60] Zhiqiang Xu, Pengcheng Fang, Changlin Liu, Xusheng Xiao, Yu Wen, and Dan Meng. 2022. DEPCOMM: Graph Summarization on System Audit Logs for Attack Investigation. In IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP).
[61] Hongyang Zhang, Huacheng Yu, and Ashish Goel. 2019. Pruning Based Distance Sketches with Provable Guarantees on Random Graphs (WWW ’19).
[62] Junhua Zhang, Wentao Li, Long Yuan, Lu Qin, Ying Zhang, and Lijun Chang. 2022. Shortest-Path Queries on Complex Networks: Experiments, Analyses, and Improvement. Proc. VLDB Endow. 15, 11 (2022).
[63] Xiao Zhang, Travis Martin, and M. E. J. Newman. 2015. Identification of core-periphery structure in networks. Physical Review E 91, 3 (mar 2015). [64] Xiaohan Zhao, Alessandra Sala, Christo Wilson, Haitao Zheng, and Ben Y. Zhao. 2010. Orion: Shortest Path Estimation for Large Social Graphs (WOSN’10).
[65] Xiaohan Zhao, Alessandra Sala, Haitao Zheng, and Ben Y. Zhao. 2011. Efficient shortest paths on massive social graphs. In 7th International Conference on Collaborative Computing: Networking, Applications and Worksharing (CollaborateCom).
[66] Uri Zwick. 2001. Exact and Approximate Distances in Graphs — A Survey. In Algorithms — ESA 2001.
[67] Uri Zwick. 2002. All pairs shortest paths using bridging sets and rectangular matrix multiplication. Journal of the ACM (JACM) 49, 3 (2002), 289–317.
:::info
Authors:
(1) Talya Eden, Bar-Ilan University ([email protected]);
(2) Omri Ben-Eliezer, MIT ([email protected]);
(3) C. Seshadhri, UC Santa Cruz ([email protected]).
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::