Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Related Work
2.1. Motion Reconstruction from Sparse Input
2.2. Human Motion Generation
-
SAGE: Stratified Avatar Generation and 3.1. Problem Statement and Notation
3.2. Disentangled Motion Representation
3.3. Stratified Motion Diffusion
3.4. Implementation Details
-
Experiments and Evaluation Metrics
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Quantitative and Qualitative Results
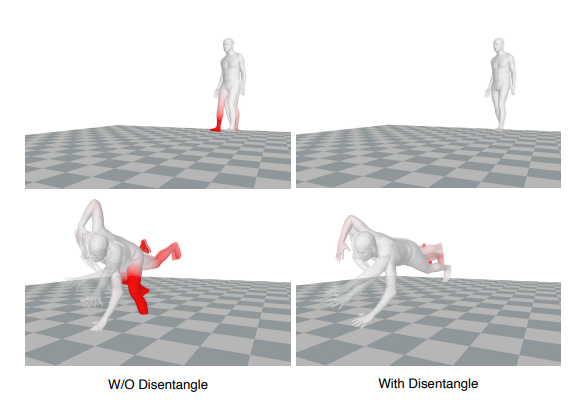
4.3. Ablation Study
-
Conclusion and References
Supplementary Material
A. Extra Ablation Studies
B. Implementation Details
4.2. Quantitative and Qualitative Results
For a fair comparison, we follow two settings used in previous works [5, 10, 11, 18, 34, 54] for quantitative and qualitative assessment. Moreover, we propose a new setting in this paper for a more comprehensive evaluation on current methods.
In the first setting, as previous works [7, 11, 18, 54], subsets CMU [6], BMLrub [41], and HDM05 [28] datasets are randomly divided into 90% for training and 10% for testing. Besides sparse observations of three joints, we also evaluate the performance of all compared methods by using four joints as input, including the root joint as an additional input, the same as in [18]. We term this setting as S1 in the following.
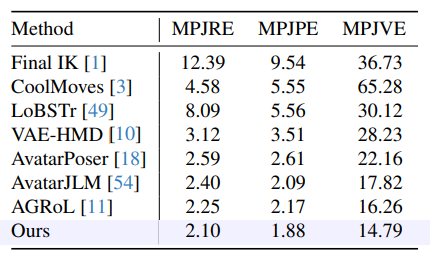
Tabs. 1 and 2 show that our method outperforms existing methods on most evaluation metrics, confirming its effectiveness. For the MPJVE metric, only AGRoL [11] surpasses our method when employing an offline strategy. In this scenario, specifically, AGRoL processes the entire sparse observation sequence in one pass and outputs the predicted full-body motions simultaneously. This enables each position in the sequence to utilize the information from both preceding and subsequent time steps, offering an advantage in this particular metric. However, it’s important to note that, despite being competitive in metric numbers, offline inference has limited practical applicability in real-world scenarios where online processing capability is most important.
The second setting follows [5, 10, 11, 34, 54], where we evaluate the methods on a larger benchmark from AMASS [25]. The subsets [2, 4, 6, 12, 21, 23, 26, 26, 28, 41–43, 43] are for training, and Transition [25] and HumanEva [37] subsets are for testing. We term this setting as S2 in the following.
![Table 3. Evaluation result under setting S2. † indicates that these methods use additional inputs of pelvis location and rotation for training and inference, which are not directly comparable methods. The results of AvatarPoser [18] is provided by [11].](https://cdn.hackernoon.com/images/fWZa4tUiBGemnqQfBGgCPf9594N2-6f332f9.png)
As shown in Tab. 3, our method achieves comparable performance with previous works on S2. However, we observe that the testing set of S2 is disproportionately small (i.e., only 1% of the training set). Such a small fraction cannot represent the overall data distribution of the large dataset and may not include sufficiently diverse motions to evaluate the models’ scalability, causing unconvincing evaluation results. We introduce a new setting, S3, which adopts
the same training and testing splitting ratio used in S1. In this setting, we randomly select 90% of the samples from the 15 subsets of S2 for training, while the remaining 10% are for testing. We train and evaluate the compared methods with this new setting. Table 4 reveals that under S3, the performance differences between the compared methods are more significant than S1 and S2. Since the test set has more diverse motions in S3, this benchmark evaluates the models’ scalability in a more objective way. In this context, our method outperforms existing methods in most metrics, especially in the critical metric of Lower PE, highlighting the superiority of our stratified design for lower-body modeling and inference.
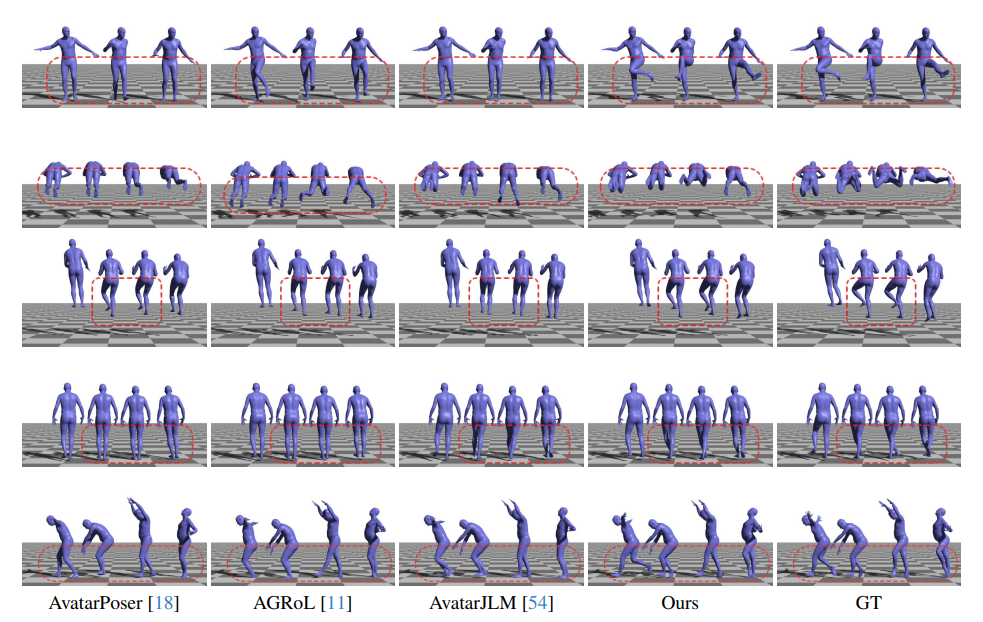
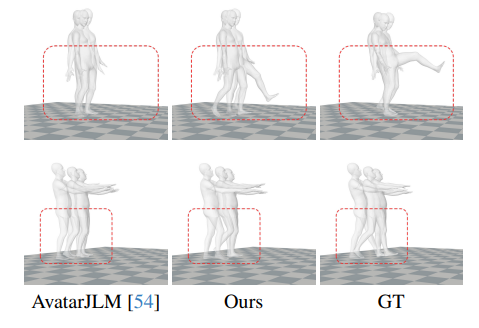
Fig. 3 presents a visual comparison between our SAGE Net and baseline methods, all trained under the S1 protocol, which is commonly used by baselines for releasing their trained checkpoints. These visualizations demonstrate the significant improvements that our model offers in reconstructing the lower body. For example, in the first row of samples, baseline methods typically reconstruct the feet too close to the ground, restricting the avatar’s leg movements. Our model, however, overcomes this limitation, enabling more flexible leg movements. In the third row, for a subject climbing a ladder, the baseline methods often result in avatars with floating feet, failing to capture the detailed motion of climbing. In contrast, our SAGE Net accurately replicates complex foot movements, resulting in more realistic and precise climbing animations. We also evaluate our model on the real data, and for fair comparison, we directly use the real data release by [54]. As shown in Fig. 4, our method also achieves better reconstruction results on the real data.
:::info
Authors:
(1) Han Feng, equal contributions, ordered by alphabet from Wuhan University;
(2) Wenchao Ma, equal contributions, ordered by alphabet from Pennsylvania State University;
(3) Quankai Gao, University of Southern California;
(4) Xianwei Zheng, Wuhan University;
(5) Nan Xue, Ant Group ([email protected]);
(6) Huijuan Xu, Pennsylvania State University.
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 DEED license.
:::