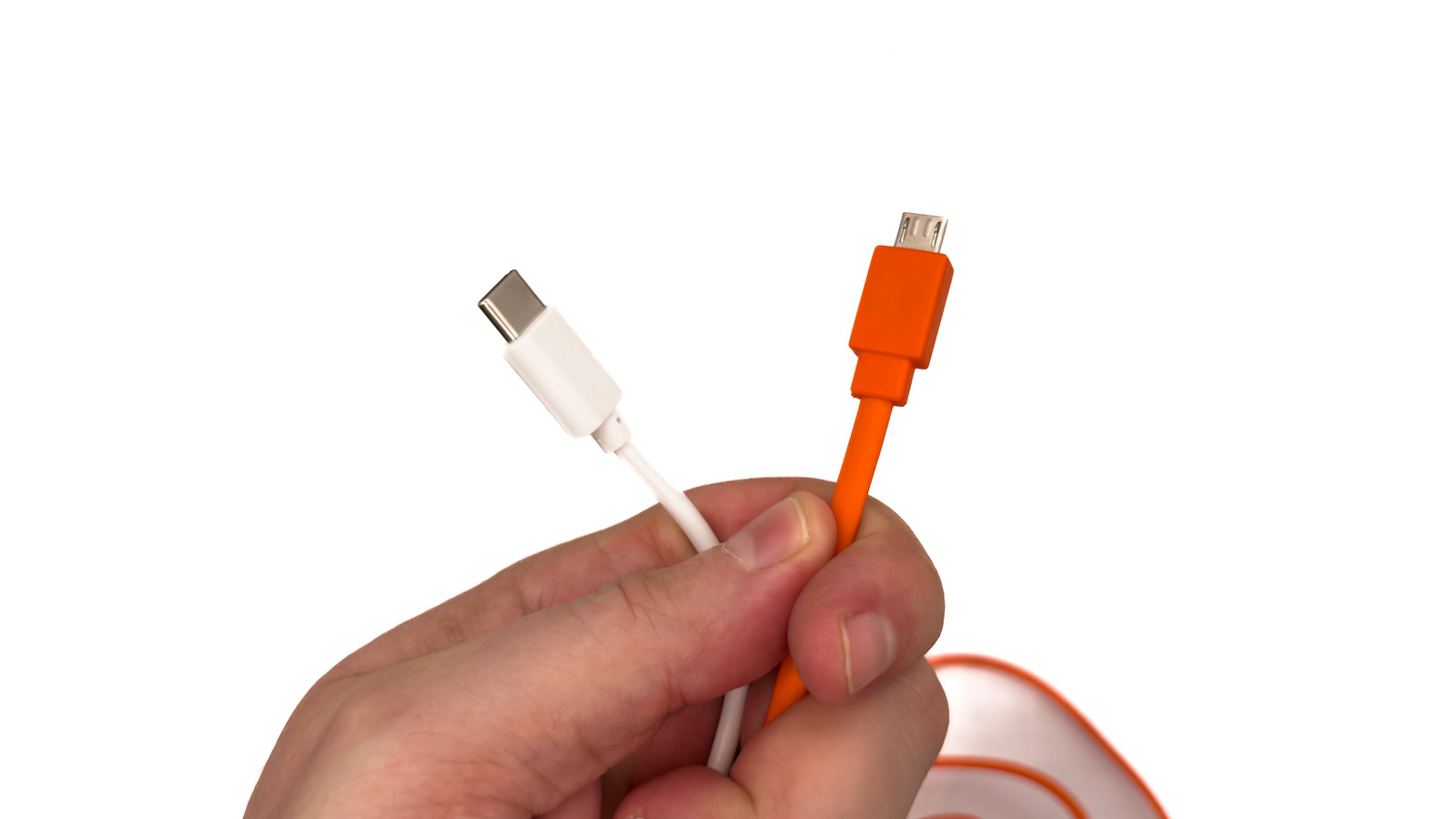
If you’ve ever wondered why so many gadgets made before the mid-2010s used the slim, tapered Micro-USB connector, and why almost everything today has moved to the oval-shaped USB-C port, the answer comes down to speed, convenience, and versatility. Micro-USB was once the default choice for cellphones, tablets, e-readers, headphones, and power banks because it was small and relatively cheap to implement. But as our devices demanded faster charging, quicker data transfer, and more durable connectors, the older standard couldn’t keep up anymore, and USB-C has been the replacement.
USB-C first arrived in 2014 as a modern, universal replacement. It introduced a reversible design that eliminates the frustration of plugging cables in the wrong way. It supports data transfer rates of up to 40 Gbps and can deliver far more power, making it enough to charge not just smartphones but also laptops and even your computer monitor. It can also carry video and audio signals, allowing a single cable to handle multiple tasks that Micro-USB could never.
So when comparing Micro-USB to USB-C, the differences aren’t just cosmetic. USB-C is faster, stronger, more flexible, and better future-proofed, which is why it has become the universal port for nearly every modern gadget.
Micro-USB: the older and more limited standard
For most of the 2010s, Micro-USB reigned as the go-to charging and data port for various gadgets. Its recognizable tapered shape made it easy to tell which way the plug needed to face — but also easy to plug in wrong, since it only fit one way. While it was a big step forward from the older Mini-USB connectors in both size and durability, Micro-USB showed its age as devices demanded faster charging and speedier data transfers.
Typical Micro-USB 2.0 connections top out at 480 Mbps for data transfer, which is fine if all you are doing is syncing music or small files, but it’s sluggish when compared to today’s needs, like moving 4K video files or high-resolution photos. Charging speeds also varied widely, as early implementations of Micro-USB stuck to 5 V/1-2 A power delivery, while later revisions like Qualcomm’s Quick Charge improved performance somewhat; the underlying design of Micro-USB limited just how fast devices could charge and how much power could be delivered safely.
Another drawback of the Micro-USB port was durability. The connector’s thin internal tongue and one-sided insertion meant that repeated stress, such as plugging in and unplugging daily, led to loose ports and was known to sometimes break cables. As batteries grew larger and mobile devices more powerful, these shortcomings became difficult to ignore. That’s why most new smartphones, laptops, and even accessories have abandoned Micro-USB altogether in favor of the newer, more versatile USB-C connector.
USB-C: the modern, reversible, and far more capable connector
USB-C, first introduced in 2014 and widely adopted by mid-decade, was designed to replace Micro-USB and older USB types entirely. The most obvious difference is the connector’s symmetrical oval shape, which works no matter which side is facing up; a seemingly small but hugely convenient upgrade that eliminates the frustration of fumbling with cables in the dark.
Beyond convenience, USB-C is dramatically more capable. Depending on the version it supports, from USB 2.0 to USB 4 and Thunderbolt 4, a single USB-C port can move data at speeds ranging from 480 Mbps to 40 Gbps. It also supports higher-wattage power delivery, with USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) delivering up to 240W. That means the same cable that charges your phone can power a full-size laptop or even some gaming monitors.
Another leap forward in its versatility. USB-C isn’t just for charging and data: it can handle video and audio output via standards like DisplayPort Alt Mode. That’s why many laptops and tablets now use USB-C for external displays, and why some phones can output a full desktop-style interface when plugged into a monitor.
Durability has also improved. The lack of a fragile internal tongue and the reversible design mean that USB-C ports typically last longer under frequent use. However, this flexibility can cause some confusion. Not every USB-C cable or port supports every feature, so it’s worth checking specs if you need high-speed data or 4K video output.
Altogether, USB-C delivers faster data transfer, more power, and broader functionality, which is why it has become the universal port standard across devices. Compared to Micro-USB, it’s more future-proof and far better suited for the demands of modern devices.