Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Related Work
-
Low Rank Adaptation
3.1 LoRA and 3.2 Limitation of LoRA
3.3 ReLoRA*
-
Sparse Spectral Training
4.1 Preliminaries and 4.2 Gradient Update of U, VT with Σ
4.3 Why SVD Initialization is Important
4.4 SST Balances Exploitation and Exploration
4.5 Memory-Efficient Implementation for SST and 4.6 Sparsity of SST
-
Experiments
5.1 Machine Translation
5.2 Natural Language Generation
5.3 Hyperbolic Graph Neural Networks
-
Conclusion and Discussion
-
Broader Impacts and References
Supplementary Information
A. Algorithm of Sparse Spectral Training
B. Proof of Gradient of Sparse Spectral Layer
C. Proof of Decomposition of Gradient of Weight
D. Proof of Advantage of Enhanced Gradient over Default Gradient
E. Proof of Zero Distortion with SVD Initialization
F. Experiment Details
G. Singular Value Pruning
H. Evaluating SST and GaLore: Complementary Approaches to Memory Efficiency
I. Ablation Study
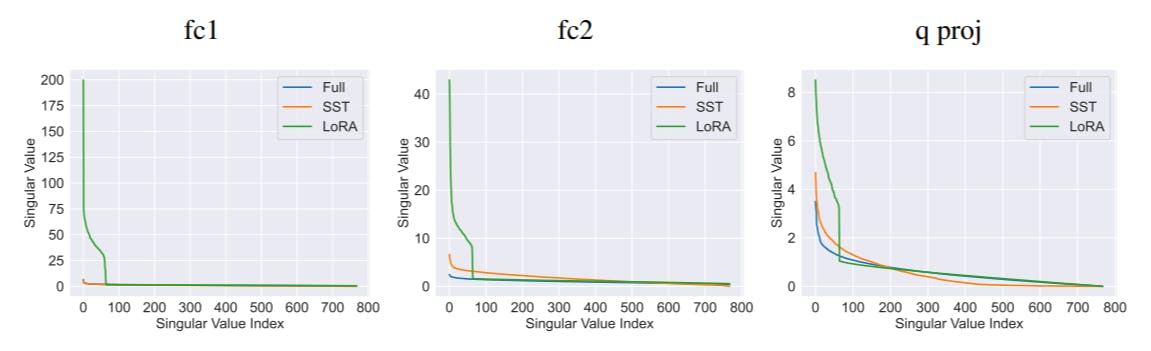
G Singular Value Pruning
We further conduct an analysis study of the potential for using SST model for further compression. The results, as shown in Figure 3, indicate that the SST model retains lower perplexity across a wider range of pruning ratios compared to the full-rank model. This suggests that the SST method effectively concentrates the informational content of the weights into fewer singular values, making it more suitable for further compression.
This enhanced performance underscores the potential of SST in maintaining essential model characteristics even under significant compression, making it a promising approach for developing lightweight yet powerful language models for inference.
H Evaluating SST and GaLore: Complementary Approaches to Memory Efficiency
Recently, a new approach named Gradient Low-Rank Projection (GaLore) has been proposed to address the memory challenges associated with training large language models. GaLore, by implementing a memory-efficient gradient projection method, enhances training efficiency without compromising the training dynamics as traditional low-rank adaptation methods, like LoRA, often do.
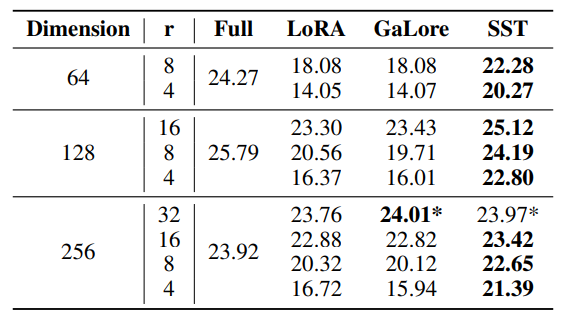
Using the released code of GaLore[2], we conducted comparative experiments on the IWSLT’14 dataset with Transformer models, employing the same configurations as other low-rank methods. We set the scale factor α = 1 in these experiments because α = 0.25, which is used in the article, performs much worse than α = 1. As illustrated in Table 9, SST method consistently outperformed GaLore across various model dimensions and ranks, except for d = 256, r = 32.
In addition, we evaluated validation perplexity on the OpenWebText dataset with OPT-125M models. We tested GaLore with scale factor α = 0.25 (used in the article) and α = 1. As shown in Table 10, SST surpassed GaLore at both settings of α.


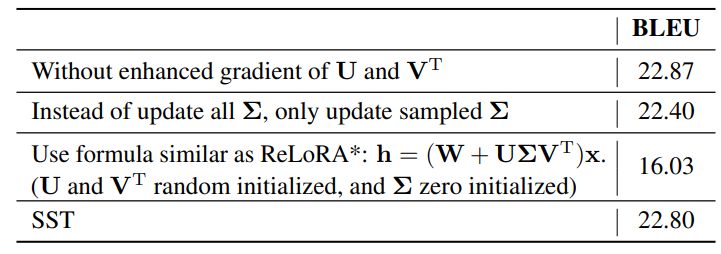
I Ablation Study
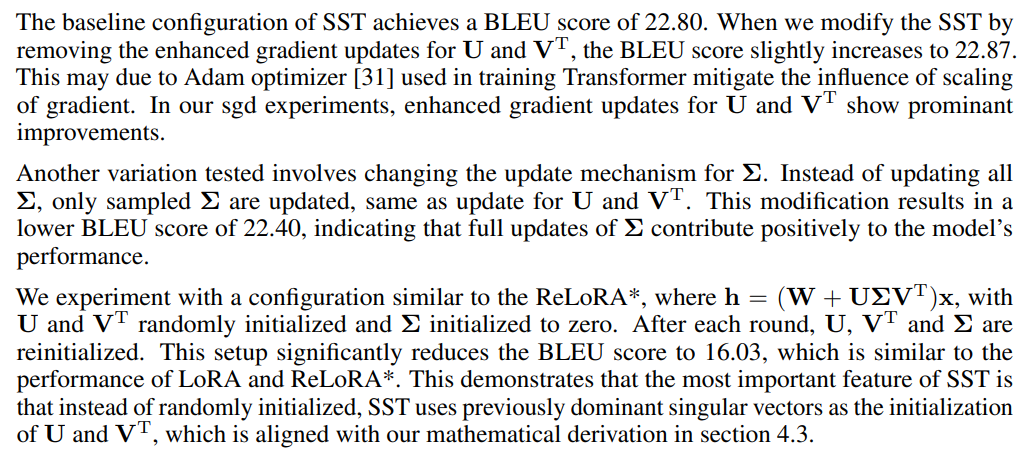
We conduct an ablation study to evaluate the impact of various components and configurations within SST on the IWSLT’14 using a Euclidean Transformer with a dimension of 128 and rank r of 4. The results of this study are summarized in Table 11, which highlights the contributions of specific elements to the overall performance measured in BLEU score.
:::info
Authors:
(1) Jialin Zhao, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI) and Department of Computer Science;
(2) Yingtao Zhang, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI) and Department of Computer Science;
(3) Xinghang Li, Department of Computer Science;
(4) Huaping Liu, Department of Computer Science;
(5) Carlo Vittorio Cannistraci, Center for Complex Network Intelligence (CCNI), Tsinghua Laboratory of Brain and Intelligence (THBI), Department of Computer Science, and Department of Biomedical Engineering Tsinghua University, Beijing, China.
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::