Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
1.1 Syllogisms composition
1.2 Hardness of long compositions
1.3 Hardness of global reasoning
1.4 Our contributions
-
Results on the local reasoning barrier
2.1 Defining locality and auto-regressive locality
2.2 Transformers require low locality: formal results
2.3 Agnostic scratchpads cannot break the locality
-
Scratchpads to break the locality
3.1 Educated scratchpad
3.2 Inductive Scratchpads
-
Conclusion, Acknowledgments, and References
A. Further related literature
B. Additional experiments
C. Experiment and implementation details
D. Proof of Theorem 1
E. Comment on Lemma 1
F. Discussion on circuit complexity connections
G. More experiments with ChatGPT
2 Results on the local reasoning barrier
Prior literature. Much work in the learning literature has been devoted to obtaining complexity measures for the sample/time complexity of learning. The largest portion is devoted to target classes in PAC settings, e.g., with the VC dimension measures [18], and some to statistical query (SQ) settings with the statistical dimension measures [14, 19]. Here, we are however interested in measures that are relevant to (1) regular Transformers (or related models) trained by (S)GD, and (2) data distribution fixed by a task. Some recent literature has studied complexity measures for (S)GD-trained neural networks. Various settings and measures have been used, such as the noise sensitivity [20, 6, 21], the cross-predictability [12, 15], the NTK alignment [22, 23], the INAL [24], the G-alignment [13], the information and generative exponents [25, 26, 27] and the leap [28]; we refer to Appendix A.2 for discussions on these.
However, despite this significant body of work, finding a simple measure giving a tight proxy for Transformer weak learning (i.e., the first non-trivial learning requirement) on a given data distribution, remains unsettled. We next propose such a measure.
2.1 Defining locality and auto-regressive locality
We define now the notion of distribution locality, which in turn will quantify the notion of locality (or local reasoning) barrier.
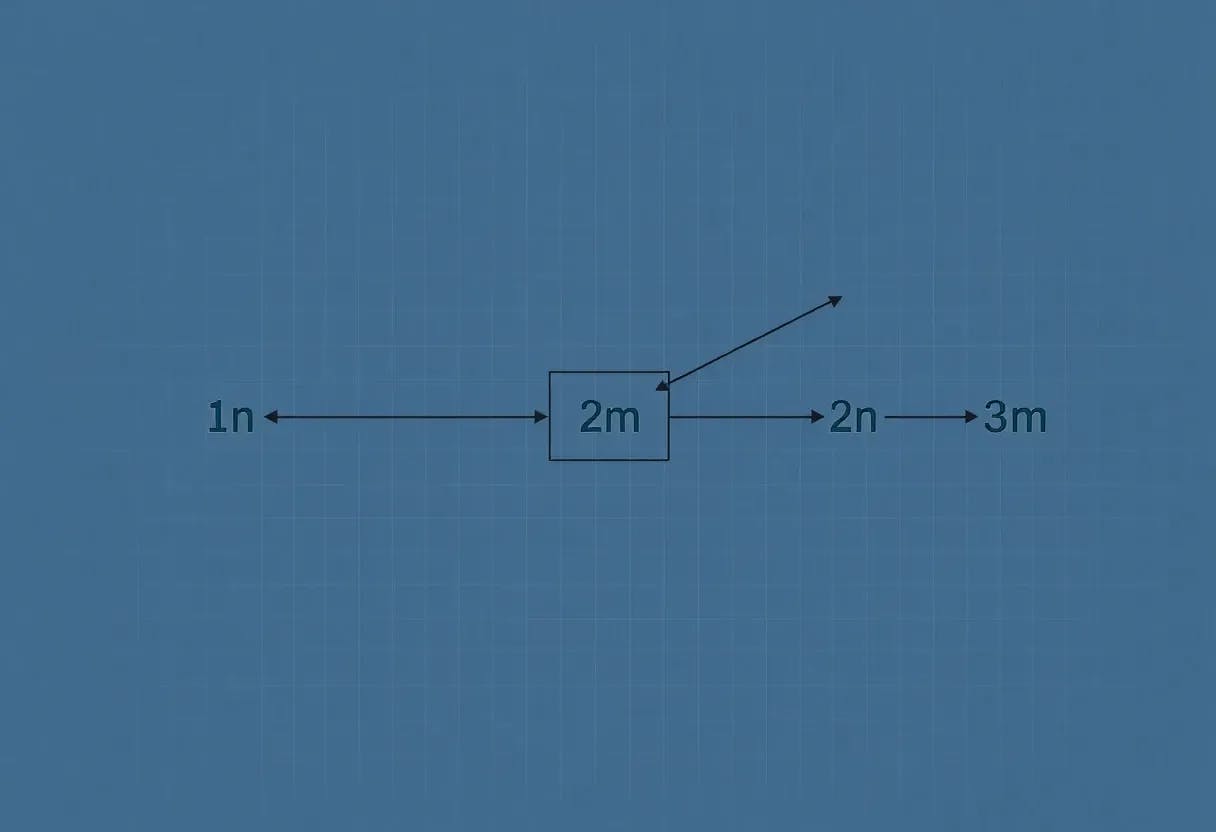
We now define the globality in the autoregressive setting.
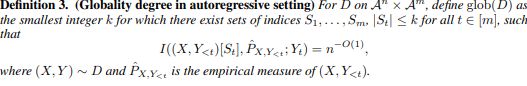
In the auto-regressive setting, the locality is mostly relevant when weak learning gives strong learning, in order to let the scratchpad learn each step.
As we will see in the next section, the locality is put forward as a tight proxy to understand efficient weak learning of regular Transformers for arbitrary data distributions. We first present the operational advantages of the definition, going back to the running example of the cycle task.
Attributes of glob and some examples. The locality has the attributes that of being (i) a fairly explicit measure, (ii) applicable to any data distribution on tokens without having to infer a distribution class from the model invariances to estimate the distribution complexity, (iii) not limited to i.i.d. inputs but any input distribution, (iv) relevant to current models of interest such as Transformers.
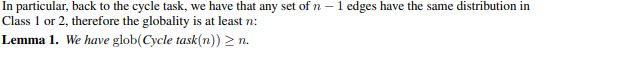
As discussed in the next section, this explains why the cycle task is hard to learn. In contrast, the example at the beginning of Section 1.2 has a much lower locality, as being connected correlates to query nodes having large enough degrees, and thus it can be expected for the model to learn with non-trivial accuracy (e.g., using degree shortcuts).
2.2 Transformers require low locality: formal results

We now state the general conjecture putting forward the globality barrier for learning.

Remark 3. (1) An important property of the learning model for the above conjecture is that the probability distribution of the function computed by the model is invariant under permutations of the inputs, and if it is trained in a reasonable way on samples drawn from a probability distribution drawn from a class that is symmetric under permutations of the inputs, its probability distribution will retain its symmetry under permutations of the inputs. For MLPs, we expect most of the results in this paper to apply, with the modification of

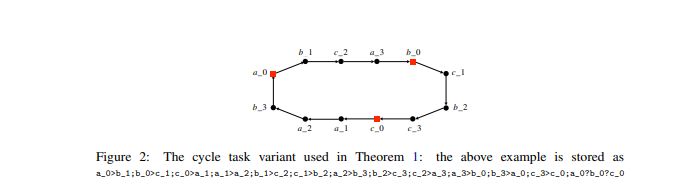

We prove the negative side of Conjecture 1 for a variant of the cycle task

The proof of Theorem 1 is presented in Appendix F.
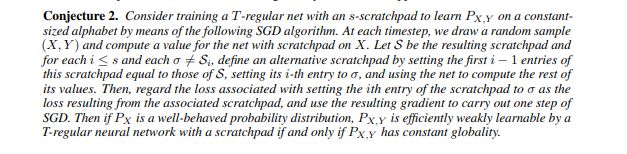
2.3 Agnostic scratchpads cannot break the globality
Next, we put forward a conjecture that agnostic scratchpads (scratchpads without direct supervision on the scratchpad tokens) cannot break the globality barrier.
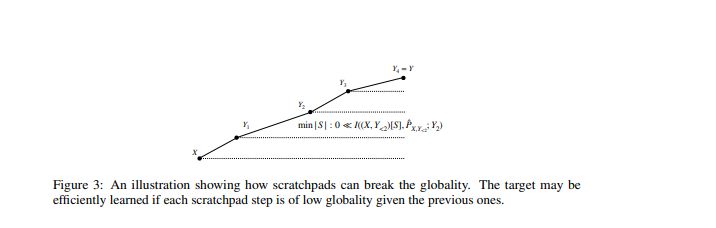
A natural counterpart of Theorem 1 holds for the previous conjecture (see Theorem 2). In order to define the Transformer’s loss on any given input it takes the expectation over every possible value of the scratchpad it might generate, and its proof is essentially identical to that of Theorem 1.

:::info
Authors:
(1) Emmanuel Abbe, Apple and EPFL;
(2) Samy Bengio, Apple;
(3) Aryo Lotf, EPFL;
(4) Colin Sandon, EPFL;
(5) Omid Saremi, Apple.
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC BY 4.0 license.
:::