Standard RAG pipelines are hitting a wall. Here is how to break through by combining Vector Search with Knowledge Graphs.
If you have built a “Chat with your Data” bot using standard RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation), you know the problem: Vector databases are great at finding keywords, but they are terrible at understanding relationships.
If I ask, “How do I reset the password?”, a vector search finds the password reset page perfectly. n But if I ask, “How does the backup configuration in Server A affect the latency in Region B?”, a vector search will return a chunk about backups and a chunk about latency, but it will fail to connect the dots.
To solve this, we need a Hybrid RAG approach. We need to combine the speed of Vector Search with the relational intelligence of a Knowledge Graph, and we need to run it locally to keep data secure.
In this guide, based on recent research into high-stakes global support systems, we will build an architecture that dynamically switches between Vector and Graph indexes to slash support response times.
Architecture: The “Smart Switch”
Most RAG tutorials force every query through the same pipeline. That is inefficient. We are going to build a system that classifies the intent first.
- Closed Questions (Fact-based): Route to Vector Search.
- Open Questions (Relational/Complex): Route to Knowledge Graph.
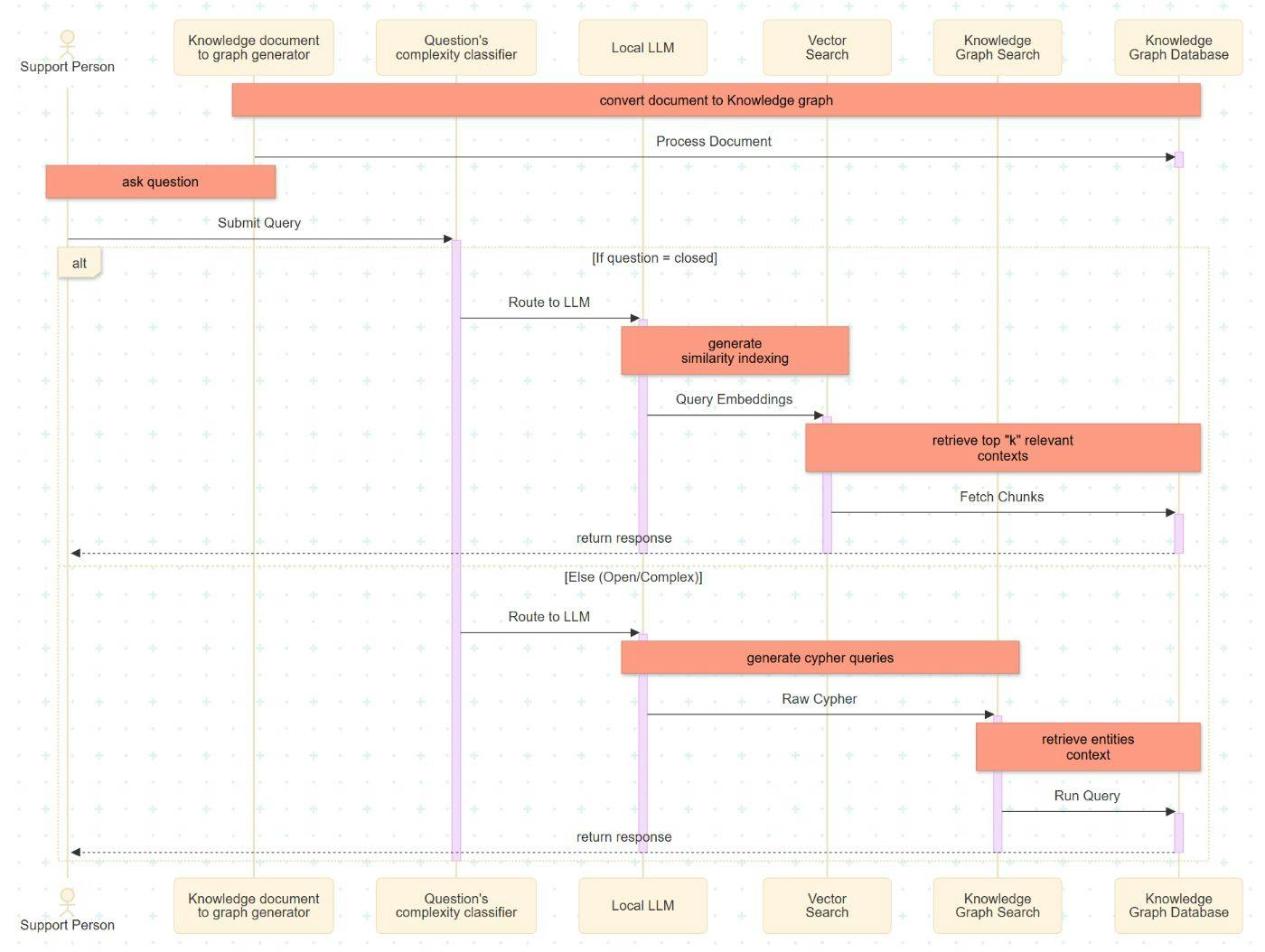
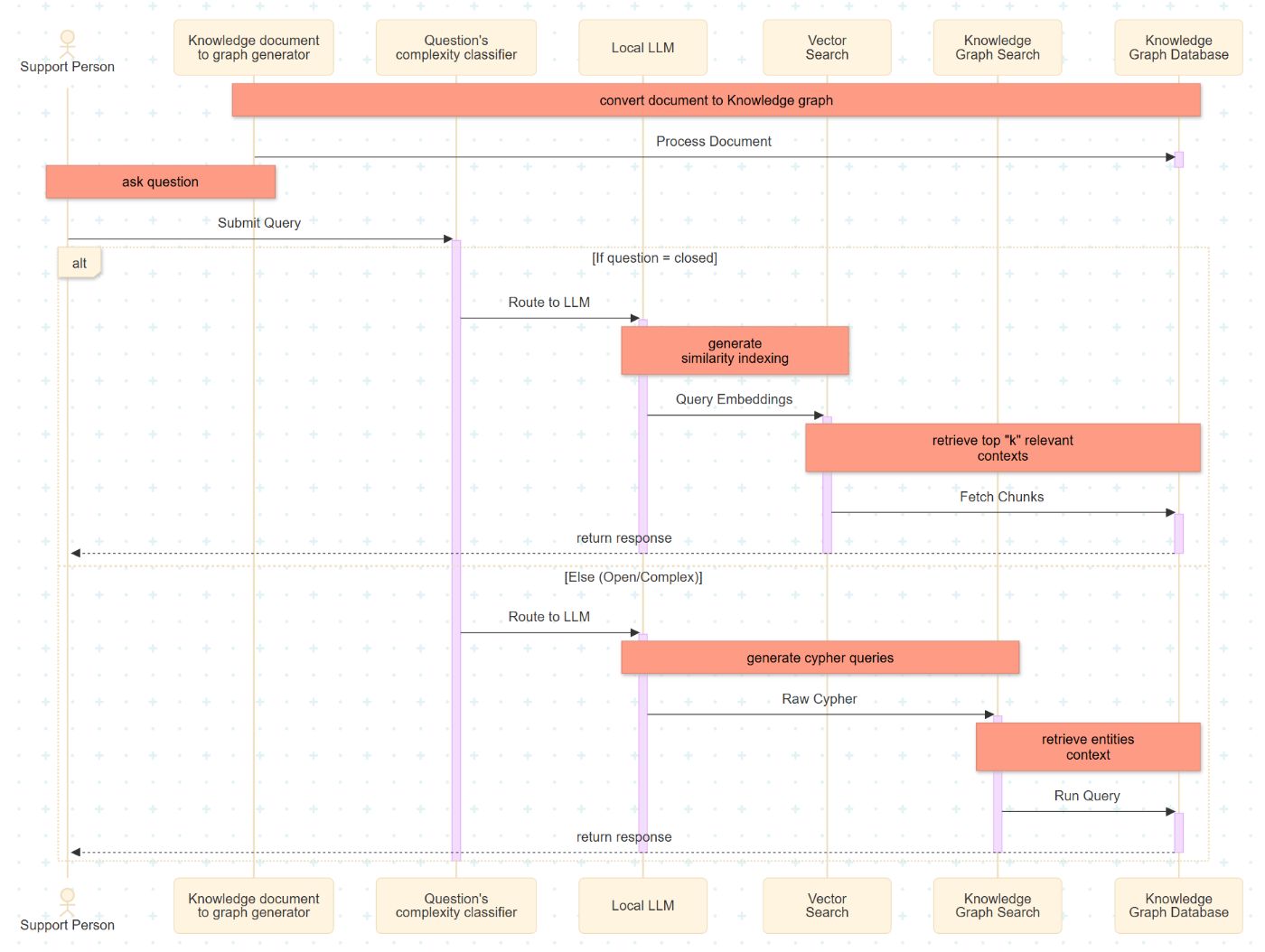
Here is the logic flow we are implementing:
Enhanced Global Support System Process Using Hybrid RAG Architecture
This section details the implementation sequence of the enhanced support process for a global system using a Hybrid RAG architecture. This architecture integrates a dual-path retrieval mechanism comprising a Vector Index and a Knowledge Graph.
-
Document Ingestion: The process begins with data ingestion, where source documents are divided into smaller, fixed-size segments. These segments are transformed into nodes and edges to populate a local Knowledge Graph database.
-
Intent Classification: Upon receiving a user query, the Complexity Classifier evaluates the input. The query is categorized as either “closed” (fact-retrieval) or “open” (relational reasoning), determining the subsequent retrieval strategy.
-
LLM Execution & Embedding: The locally implemented Large Language Model (LLM) serves as the semantic bridge between natural language and the backend system. For vector-based retrieval, the LLM generates high-dimensional embeddings to represent the query semantically.
-
Vector Search Retrieval: For closed queries, the system executes a similarity search. It identifies and retrieves the top-k document segments that share the highest cosine similarity with the query embedding.
-
Knowledge Graph Traversal: For open or complex queries, the LLM translates the natural language intent into Cypher queries. These queries define specific traversal patterns within the graph database to extract relevant entities and their interrelationships.
-
Response Generation: The final step aggregates the retrieved context (from either the Vector Index or Knowledge Graph) and passes it to the LLM to generate a coherent, context-aware response for the support personnel.
Let’s build this phase by phase.
Phase 1: The Local Setup
For a global enterprise support, privacy is paramount. We aren’t sending customer logs to OpenAI. We are using Local LLMs. We will use Llama-2-13B (or Llama-3 for newer setups) for both the classification and the generation.
The Stack
-
Model: Llama-2-13B (via llama.cpp or Ollama)
-
Vector DB: FAISS or ChromaDB
-
Graph DB: Neo4j (using Cypher query language)
-
LangChain: To glue it all together.
# Basic setup command
pip install langchain langchain-community neo4j faiss-cpu llama-cpp-python
Phase 2: The Classifier (The Brain)
We need a function that looks at a user prompt and decides: “Do I need a simple lookup, or do I need to think?”
In the research, questions like “Is it possible to perform a backup using pg_dump?” are closed. Questions like “What settings should I make to use Enterprise Postgres?” are Open.
Here is how we code the Classifier Agent:
from langchain.llms import LlamaCpp
# Initialize Local LLM
llm = LlamaCpp(
model_path="./llama-2-13b-chat.gguf",
temperature=0.1, # Low temp for deterministic classification
n_ctx=2048
)
def classify_query(user_query):
prompt = f"""
You are a support routing assistant. Classify the following query into one of two categories:
1. 'CLOSED': The question asks for a specific fact, a Yes/No answer, or a simple command.
2. 'OPEN': The question asks for a process, a relationship between components, or an explanation.
Query: "{user_query}"
Return ONLY the category name.
"""
response = llm(prompt)
return response.strip().upper()
# Test it
print(classify_query("Can I use pg_dump for backups?"))
# Output: CLOSED
print(classify_query("How does the new update impact legacy database replication?"))
# Output: OPEN
Phase 3: The Knowledge Graph Strategy
This is where the magic happens. While Vector stores text chunks, the Graph stores Entities and Relationships.
To build the graph from unstructured documentation (like PDF manuals), we use the LLM to extract nodes. We want to convert text into Cypher Queries (the SQL of Graph DBs).
The Extraction Logic
When the document ingestion runs, the LLM analyzes chunks and generates relationships.
Input Text: “The pg_dump utility is part of the Backup Module. It requires read access to the Database Cluster.”
Generated Cypher Query:
from neo4j import GraphDatabase
uri = "bolt://localhost:7687"
username = "neo4j"
password = "your_password"
driver = GraphDatabase.driver(uri, auth=(username, password))
cypher_query = """
MERGE (u:Utility {name: "pg_dump"})
MERGE (m:Module {name: "Backup Module"})
MERGE (d:Component {name: "Database Cluster"})
MERGE (u)-[:PART_OF]->(m)
MERGE (u)-[:REQUIRES_ACCESS]->(d)
"""
with driver.session() as session:
session.run(cypher_query)
driver.close()
The Retrieval Logic
When an OPEN query comes in, we don’t scan for keywords. We generate a Cypher query to traverse the graph.
def query_knowledge_graph(question):
# Ask the LLM to convert natural language to Cypher
cypher_generation_prompt = f"""
You are an expert in Neo4j. Convert the following question into a Cypher query
to find relevant nodes and relationships.
Question: {question}
"""
generated_cypher = llm(cypher_generation_prompt)
# Execute against database (Pseudo-code)
# results = graph_db.execute(generated_cypher)
return results
Why this matters: If the user asks about “Access issues,” the Vector DB might return 50 random chunks containing the word “Access.” The Graph DB will return exactly the nodes connected to “Access” via the [:REQUIRES_ACCESS] relationship.
Phase 4: The Hybrid Execution
Now we stitch the logic together. This “Enhanced Global Support System Process” allows the system to fail gracefully.
def generate_support_response(user_query):
# Step 1: Classify
category = classify_query(user_query)
print(f"Detected Category: {category}")
context = ""
# Step 2: Route
if category == "CLOSED":
print("Routing to Vector Search...")
context = vector_db.similarity_search(user_query, k=3)
else:
print("Routing to Knowledge Graph...")
# If Graph fails or returns empty, fall back to Vector (Hybrid Safety Net)
try:
context = query_knowledge_graph(user_query)
except:
context = vector_db.similarity_search(user_query, k=5)
# Step 3: Generate Answer
final_prompt = f"""
Use the following context to answer the user's support question.
Context: {context}
Question: {user_query}
"""
return llm(final_prompt)
Results: Does it actually work?
Let’s look at the data. In a controlled study involving complex Middleware support tickets, this hybrid approach was compared against a standard manual support workflow.
The Time Savings:
- Manual Investigation: ~180 minutes per ticket.
- Hybrid AI Investigation: Reduced significantly, leading to a total ticket resolution drop of ~28 minutes (8%) per complex case.
Reality Check (Accuracy): The accuracy of the Local Llama-2 model in this specific experiment hovered around 25% for complex open-ended questions.
Wait, only 25%?
Yes. This is the reality of Local LLMs on complex proprietary data. While it is an improvement over the baseline, it highlights the current challenge: Hallucinations.
The system is designed not to replace the Support Engineer, but to function as a “Tier 0” analyst. Even if the answer is imperfect, retrieving the specific relationship between document chunks saves the engineer hours of reading.
Conclusion
Building a “Production” RAG system means moving beyond simple embeddings. By implementing a Classifier-Based Router, you ensure that simple questions get fast answers, and complex questions get deep, relational context.
Your Next Steps:
- Don’t dump everything into Vectors. Identify your domain’s “Entities” (Product names, Error codes, Configuration files).
- Start Local. Use Llama-3 or Mistral locally to test your graph extraction without leaking IP.
- Build the Router. The single most effective optimization for RAG is knowing when not to use it.