Beyond being a cliché, “artificial intelligence” and its associated automation technologies have driven major developments in security, signifying that important changes have occurred in this field. In the field of cybersecurity, artificial intelligence refers to systems that acquire data, trace patterns, and forecast trends. Typically, this application is performed using machine learning, neural networks, or other high-performance data processing algorithms. There are limited domains in which an AI-driven system is more effective than humans or conventional security systems, such as detecting security threats, connecting unrelated incidents across various geographical or logistical contexts, and examining large datasets for subtle attack indicators that are often missed by humans or conventional security systems.
While traditional automation is constrained to predefined instructions, intelligent automation leverages artificial intelligence through playbooks and reasoning processes. This enables systems to analyze the outcomes they receive, make suitable decisions, or perform a series of predetermined tasks beyond simple ‘if-then’ rules. A simple example is a system that detects a malicious device and, if appropriate, isolates the bad actors by isolating the device. Such devices can suggest removing the malicious endpoint from the network or implementing a specific set of controls without the manual approval of security personnel.
AI, in combination with intelligent automation, plays a significant role in changing the operation of security functions. To ensure security, system architectures must incorporate preventive measures that shift security responsiveness toward flexible prediction and continuous defense strategies. This method improves how organizations identify, manage, and address security concerns, thereby promoting a more proactive security strategy.
Why AI and Automation Matter: The State of Security Operations
Modern security teams face several key challenges:
- Alert overload and burnout: Security systems generate a large number of alerts, most of which are either low-risk or false alarms. Operational teams find it challenging to identify the initial tasks on which to focus.
- Sophisticated attacks: Attackers use AI to probe networks, avoid detection, and automate their activities.
- Talent shortage: There are insufficient skilled cybersecurity professionals to meet the growing demands.
- Expanding attack surfaces: Cloud, remote work, IoT, and hybrid systems create complex environments that are hard to secure manually.
When automated attacks are considered, the speed and scale of the offence even exceed those of the best security teams. Thus, an AI and automation framework that can help in detecting and responding to such attacks at all times within the suggested time is deemed necessary.
AI and Automation Frameworks for Cybersecurity
Frameworks such as Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR), User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA), and Zero Trust are important for addressing current security challenges, as noted in the previous section. When SOAR is operational, response times improve, crime decreases, and rapid actions are taken without requiring physical intervention. UEBA employs AI to analyze user behaviour to detect deviations from normal patterns, such as internal threats or stolen credentials. With Zero Trust, each individual and device is authenticated continuously, regardless of location, ensuring that only authorised access is granted.
It should be noted that the power of AI-based threat intelligence is sufficient to provide discerning attention to emerging threats, thereby enabling their prevention. Security teams can rely on AI to manage vulnerability scanning, enabling them to identify risks and remediate them promptly, thereby reducing the attack surface.
Here’s a simple Python example for automating incident response with SOAR integration:
import requests
import os
API_TOKEN = os.getenv("API_TOKEN")
BASE_URL = os.getenv("API_URL")
# Example function to isolate a compromised endpoint
def isolate_endpoint(endpoint_ip):
url = f"{BASE_URL}/isolate"
payload = {"ip": endpoint_ip}
headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {API_TOKEN}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
response = requests.post(url, data=payload, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"Endpoint {endpoint_ip} isolated successfully.")
else:
print("Failed to isolate endpoint.")
# Trigger isolation for an identified compromised system
# isolate_endpoint(ip_address)
This framework simplifies and accelerates security operations, enabling faster responses to threats.
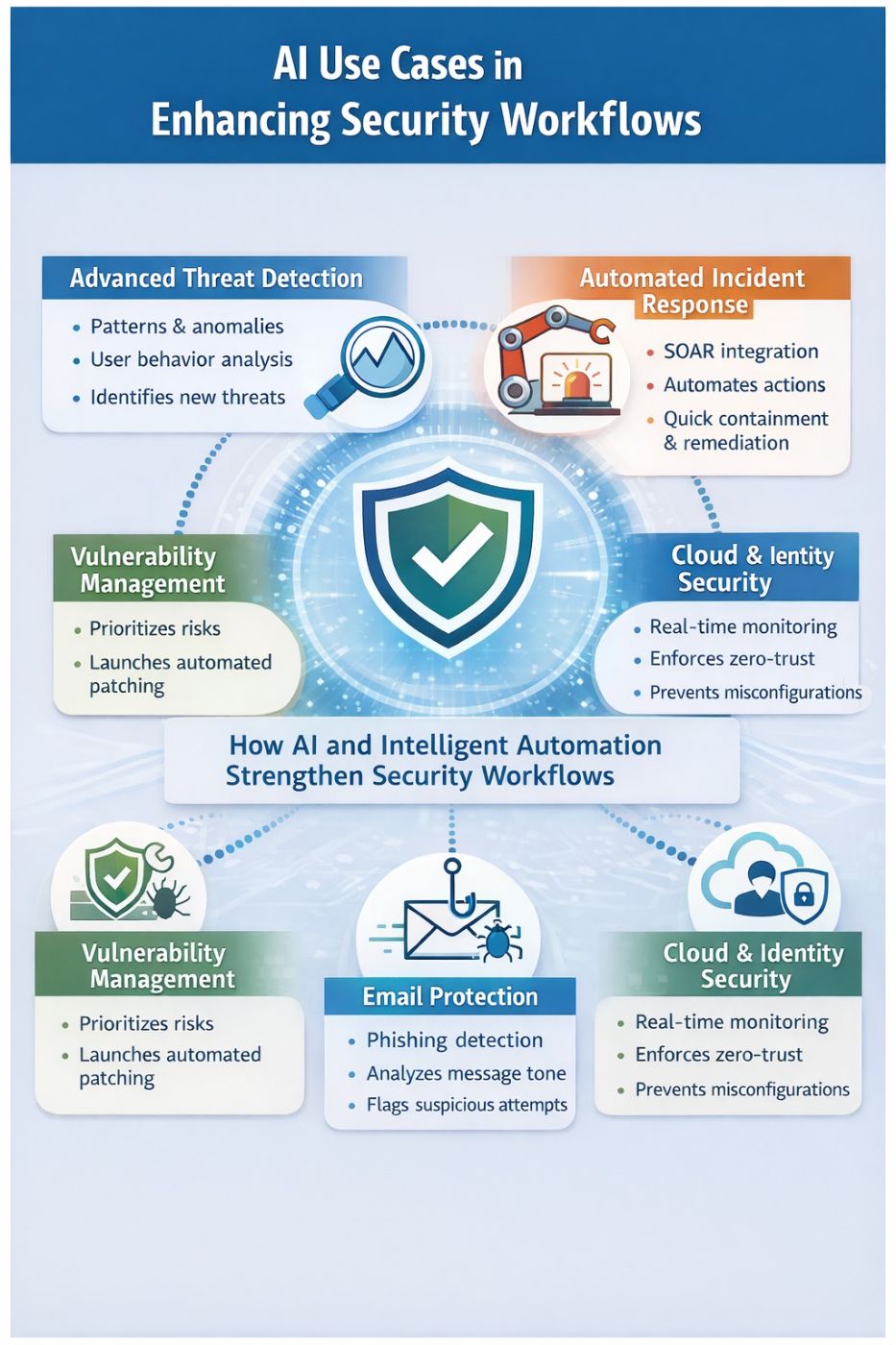
Core Use Cases: How AI + Intelligent Automation Strengthen Security Workflows
Here are practical, real‑world ways that AI and intelligent automation are being used today:
i. Advanced Threat Detection and Pattern Recognition
Machine learning-powered systems examine extensive log data to identify diverse behaviours on multiple endpoints, such as the reactions of different victims when subjected to particular network events. Some of these algorithms employ hierarchical learning rather than signature‑based methods and examine how certain activities change and evolve.
For instance, User and Entity Behavior Analytics uses machine learning to identify normal activity patterns and to detect anomalies and abnormal behavior by employees or third parties. Alerts from such Work are based solely on differences when the deviation confidence is in milliseconds.
ii. Automated Incident Response and SOAR Integration
SOAR platforms are designed to integrate additional tools, such as AI, that can receive observations and act on them, rather than requiring analyst intervention. For example:
- A programmable AI can determine sophisticated phishing events.
- Once a phishing playbook is created, the AI quarantines the affected assets.
- Moreover, content with appropriate orchestration capabilities will inform playbook tasks to perform risk reduction when intrusions are detected in near-real time.
This reduces the Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) and mitigates the incident without exacerbating it.
iii. Vulnerability and Exposure Management
One reason AI is fundamentally distinct is that it helps you understand vulnerability data, the probability of certain attacks, and how they occur. Instead of focusing on adjusting the basic Common Vulnerability Scoring System, the analysis focuses on the risk contributed by the estimated vulnerabilities. Machines can conduct patch-lift and patch-shift campaigns and apply configuration changes in accordance with pre‑approved policies.
iv. Cloud and Identity Security
Cloud environments are a source of large volumes of data. AI identifies compliance statuses, network traffic, user behaviors, and indirect invasions, all of which occur in real time, assesses associated risks, and prevents configurations from directly resulting in breaches. AI‑driven aspect administrators and authentication ensure prospective cyber-attack prevention by employing zero-trust best practices: they identify suspicious network activity in real time and issue a multifactor authentication request.
v. Email Protection and Phishing Defense
Today, advanced email filtering is powered by artificial intelligence. Various systems utilize sentiment analysis, email sender statistics, read-on ratios, email click rates, and other factors to provide such protection, enabling them to outperform even static rule-based content filters vastly.
Human + AI Collaboration in Cybersecurity
AI has powerful capabilities; however, its effectiveness is enhanced by human participation in governance processes and in interpreting critical risk issues. One strategy used in a human-in-the-loop (HITL) setup is widely practised in domains where human operators control and assist AI systems, with the level of risk determining the degree of human involvement. Hence, in such arrangements, AI is used to support rather than replace decision-making in critical situations.
Here, AI is responsible for routine tasks, such as pattern recognition and process automation, thereby increasing productivity. Conversely, people assume greater responsibilities, such as making moral or ethical judgments and understanding the relevant context. This makes such consolidation possible without time loss and is unbreakable because the system is centralized.
Challenges in AI-Enabled Cybersecurity: Actionable Steps with Automation
- Adversarial Attacks: Automate adversarial testing to detect vulnerabilities. n Example: Use Python to test AI models for prompt injection risks.
- Data Quality and Bias: Automate data audits and retraining pipelines. n Example: Set up scripts to pull clean data and retrain models automatically.
- Exploitability: Automate decision-logging to enhance transparency. n Example: Use scripts to log AI decisions and store them for compliance.
- Anomaly Detection: Automate anomaly detection and response actions. n Example: Script to disconnect a device when a threat is detected.
- Threat Intelligence: Automate threat intelligence gathering and defense updates. n Example: Set scripts to pull threat feed data and adjust security rules automatically.
These actions help strengthen AI systems and improve security responses.
Here is a Python code snippet that shows how AI and human oversight can work together to automate security-centric activities and make better decisions in terms of security
import requests
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import IsolationForest
import logging
import os
API_TOKEN = os.getenv("SOAR_API_TOKEN")
API_BASE_URL = os.getenv("BASE_API_URL")
# Example: Adversarial testing for model vulnerabilities
def test_adversarial_model(model, test_data):
adversarial_data = generate_adversarial_data(test_data)
predictions = model.predict(adversarial_data)
if any(pred == -1 for pred in predictions): # Checking for misclassifications
print("Adversarial vulnerability detected!")
else:
print("Model is secure.")
def generate_adversarial_data(data):
# Scafolding function for generating adversarial data (to be implemented)
return data
# Example: Automating data retraining pipeline
def retrain_model(model, data):
model.fit(data)
print("Model retrained with new data.")
# Example: Automated anomaly detection with Isolation Forest
def detect_anomalies(data):
model = IsolationForest()
model.fit(data)
predictions = model.predict(data)
anomalies = data[predictions == -1]
if len(anomalies) > 0:
print(f"Anomalous behavior detected: {anomalies}")
return True
return False
# Example: Automating response action (disconnecting device)
def automated_response(action, ip_address):
if action == "disconnect":
# Example API request to disconnect a device
url = f"{API_BASE_URL}/disconnect"
payload = {"ip": ip_address}
response = requests.post(url, data=payload)
if response.status_code == 200:
print(f"Device {ip_address} disconnected successfully.")
else:
print(f"Failed to disconnect device {ip_address}.")
# Example: Logging AI decision for transparency
def log_decision(action, details):
logging.basicConfig(filename="ai_decisions.log", level=logging.INFO)
logging.info(f"Action: {action}, Details: {details}")
# Example: Automating threat intelligence gathering
def gather_threat_intelligence():
response = requests.get(API_BASE_URLh)
threat_data = response.json()
# Process and update security systems based on new threat data
print("Threat intelligence gathered:", threat_data)
# Main execution
data = pd.DataFrame({'login_time': [8, 9, 10, 16, 17, 3]}) # Sample data for anomaly detection
model = IsolationForest()
# 1. Adversarial testin
test_adversarial_model(model, data)
# 2. Data retraining
retrain_model(model, data)
# 3. Anomaly detection
if detect_anomalies(data):
# 4. Automate response action if an anomaly is detected
# with sample private address
automated_response("disconnect", "192.170.1.111")
# 5. Logging the decision
log_decision("Disconnect", "Malicious activity detected from 192.170.1.111")
# 6. Gather threat intelligence
gather_threat_intelligence()
The purpose of this code is to detect the time of login that does not fit in a sequence where the next login time is that of the current. It also has a defined internal control. An analyst will manually investigate all such events (i.e., flagged suspicious activities) to determine whether they are false positives or genuine issues.
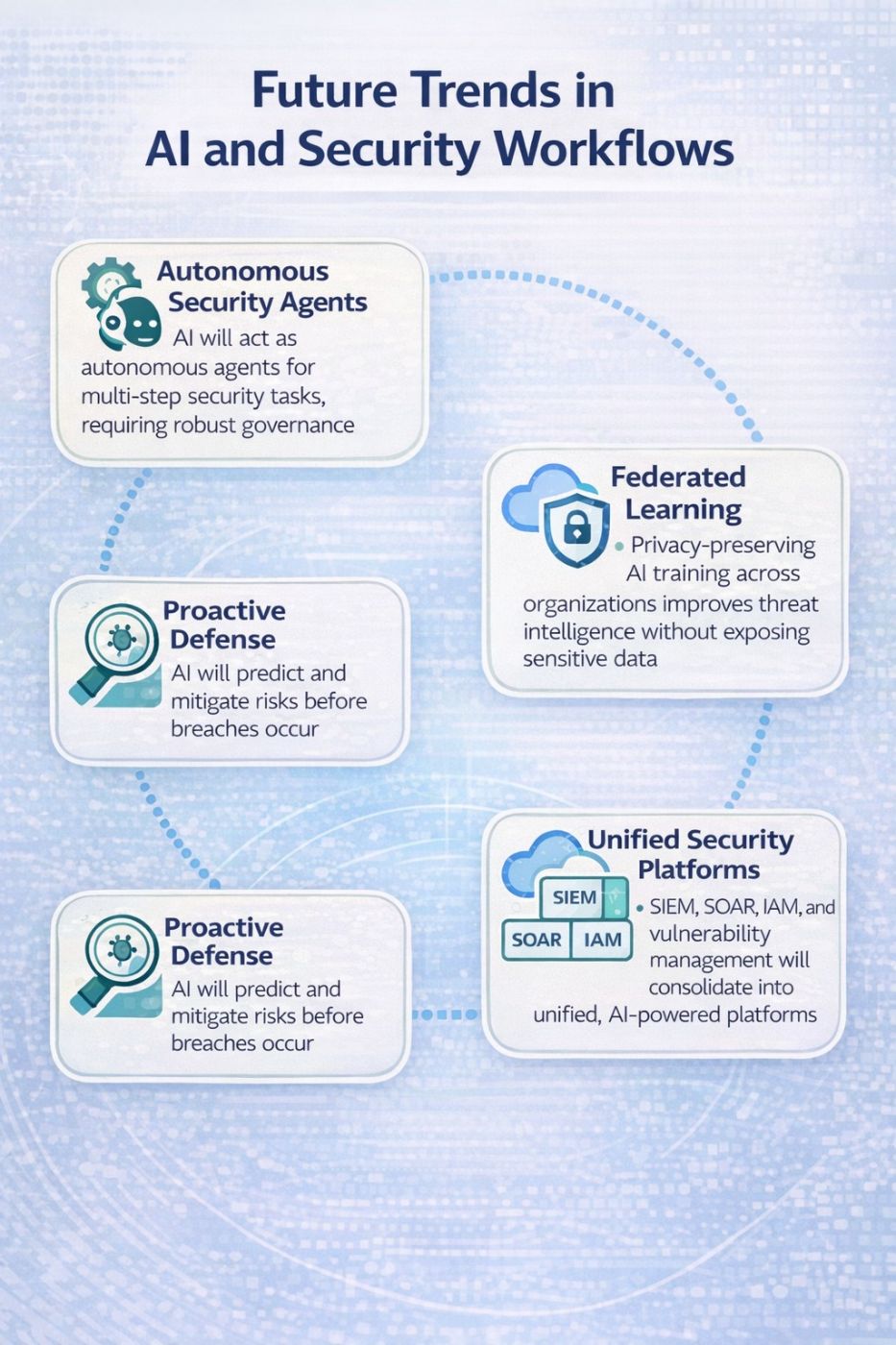
Future Trends in AI and Security Workflows
As AI evolves, key trends are shaping the future of cybersecurity:
Autonomous Security Agents
AI systems will operate as independent agents that make decisions through multi-step processes and manage emergencies by using current data. The systems will execute automated security responses, including isolating infected endpoints, but will require human supervision to verify compliance with established policies.
Federated Learning and Collaborative Threat Intelligence
Federated learning enables organizations to train their AI models without sharing sensitive data by allowing them to collaborate. This approach enhances security threat intelligence by collecting data from diverse sources and employing advanced predictive functions.
Proactive and Predictive Defense
The defense system will shift from reactive to proactive methods, employing predictive modelling to identify emerging threats. AI analyses historical attack patterns to identify security vulnerabilities, thereby determining which weaknesses should be addressed first.
Unified Security Platforms
Integrated security platforms combine SIEM, SOAR, IAM, and vulnerability management into unified systems that operate through artificial intelligence. The system achieves three benefits through its automated response capability, which links data from various platforms.
These trends point to smarter, more efficient, and proactive security systems.
Applying AI for Predictive Defense
This can be accomplished by developing a model to infer the presence of network vulnerabilities in anticipation of arising attacks using Python snippets:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn. ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# Historical attack data (vulnerability score, patch status, success)
data = pd.DataFrame({
'vulnerability_score': [0.8, 0.6, 0.9, 0.4, 0.7],
'patch_available': [1, 1, 0, 0, 1],
'successful_attack': [1, 0, 1, 0, 0]
})
# Train RandomForest model
X = data[['vulnerability_score', 'patch_available']
y = data['successful_attack']
model = RandomForestClassifier().fit(X, y)
# Predict risk for new vulnerability
new_vul = pd.DataFrame({'vulnerability_score': [0.85], 'patch_available': [1]})
prediction = model.predict(new_vul)
# Print result
print("High risk. Prioritize patching." if prediction == 1 else "Low risk. Monitor.")
The RandomForestClassifier in this code predicts the probability of attack success by analyzing two factors: the vulnerability score and patch status. The system enables security teams to priorities which vulnerabilities to patch first by identifying the most dangerous threats.
Best Practices for Adopting AI and Intelligent Automation
To maximize value and manage risks, organizations should follow these key practices:
Define Clear Objectives
Start with critical use cases that include alert triage, threat hunting and incident response. Select automation areas that will deliver immediate benefits while increasing the team’s operational productivity.
Ensure Data Quality and Governance
AI models should be trained on reliable, representative data, and their performance should be continuously monitored to ensure accuracy. To be successful, organizations must implement strong data governance practices.
Balance Automation with Human Oversight
A Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) framework should be implemented to enable artificial intelligence to assist human decision-making while allowing human experts to handle emergencies.
Invest in Training
Develop hybrid skills by combining cybersecurity knowledge with AI expertise. The system enables teams to manage artificial intelligence tools while efficiently assessing their operational impact.
Monitor and Adapt
AI models and workflows must be modified as new threats emerge. Security systems require frequent updates to maintain protection against emerging threats while security controls remain operational.
Organizations that follow these practices will achieve better security through AI and automation technologies.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Cybersecurity defense operations have achieved a new level of effectiveness through AI and intelligent automation, as these technologies enable defenders to operate at machine speed while improving threat detection and enabling faster, more accurate threat responses. Although these technologies are beneficial to defense systems, they introduce new security risks, ethical challenges, and organizational difficulties that must be managed with caution.
The integration of human expertise and intelligent systems will enable advanced security systems that protect against future cybersecurity threats. Organizations need to move away from their current security methods, which only respond to incidents, by adopting new security systems that combine AI and automation through strategic design and management to protect against emerging security threats while maintaining their protection capacity.










