Table of Links
Abstract and I. Introduction
II. Background
III. Method
IV. Experiments
V. Conclusion and References
III. METHOD
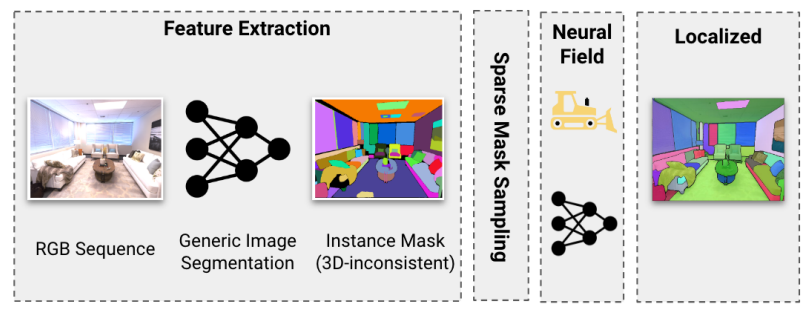
Given a sequence of N posed RGB images, (Ii , Ti) where I denotes the image and T pose, we first extract viewinconsistent instance masks Mi using a generic instance segmentation model such as Mask2Former or SAM.
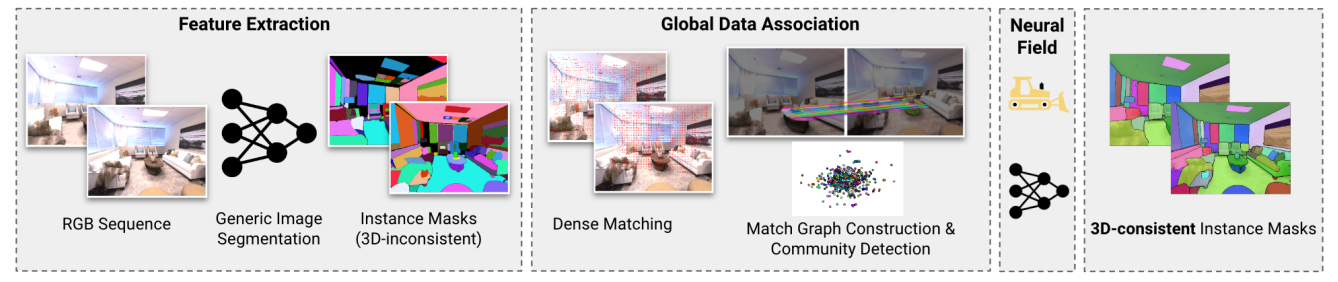
A. Mask Association
We first generate pseudolabel masks with InstanceMap. Formally, define ϕ(M, r) to map a mask M and region r to a consistent label for the same 3D object across different masks and regions. We extend the popular hLoc [16] framework for scalable 3D reconstruction to mask association as follows:
Since NetVLAD and LoFTR don’t have 3D information, 3DIML only performs well if each image in the scan sequence contains enough context for these models. We observe empirically a good rule of thumb is to have at least one other recognizable landmark for frames containing near-identical objects.
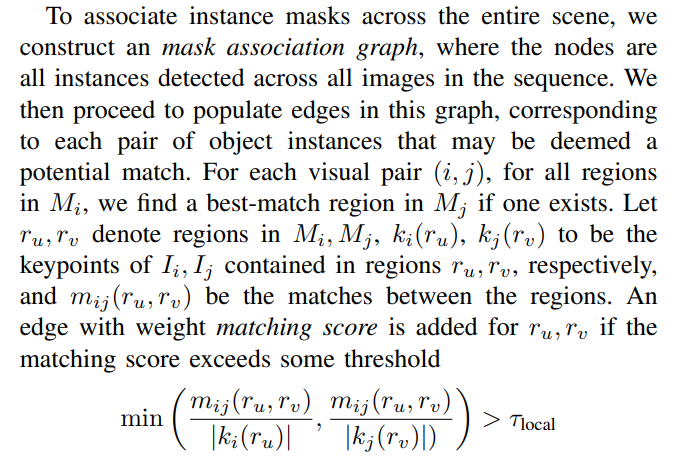
Mask Association Graph: Insofar, our approach produces instance masks and dense pixel correspondences among images that share a visual overlap. However, segmentation models such as SAM [2] suffer multiple issues: (a) segmentations of the same object need not be consistent across images, owing to viewpoint and appearance variations; and (b) owing to over-segmentation of objects, there isn’t usually a one-one correspondence among masks.
B. Mask Refinement
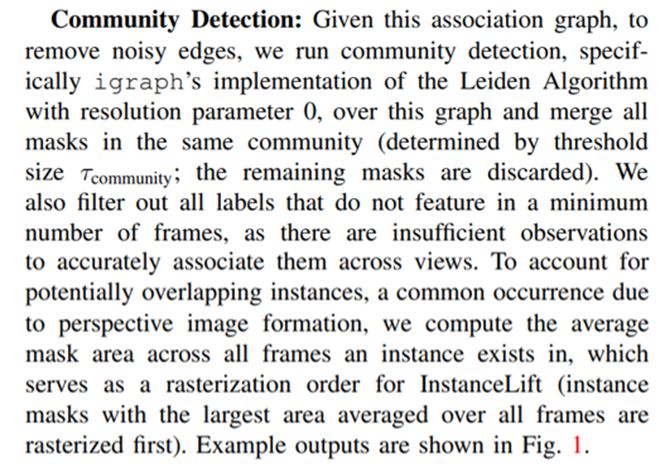
ϕ(M, r) is inherently noisy due to varying segmentation hierarchies for different instance masks due to differing viewpoints as well as design specifics. To address this, in InstanceLift we feed the pseudolabel masks to a label NeRF, which resolves some ambiguities. Still, NeRF cannot handle extreme cases of label ambiguity, to which we devise a fast post-processing method that determines and merges colliding labels based on random renders from the label NeRF. The few remaining, if any, ambiguities can be corrected via sparse human annotation.
Post graph construction, we merge labels a, b if
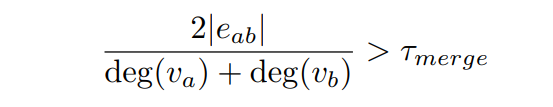
Since we only need coarse information i.e. instance mask noise, we render images downsampled by a factor of 2.
C. Fast Instance Localization and Rendering
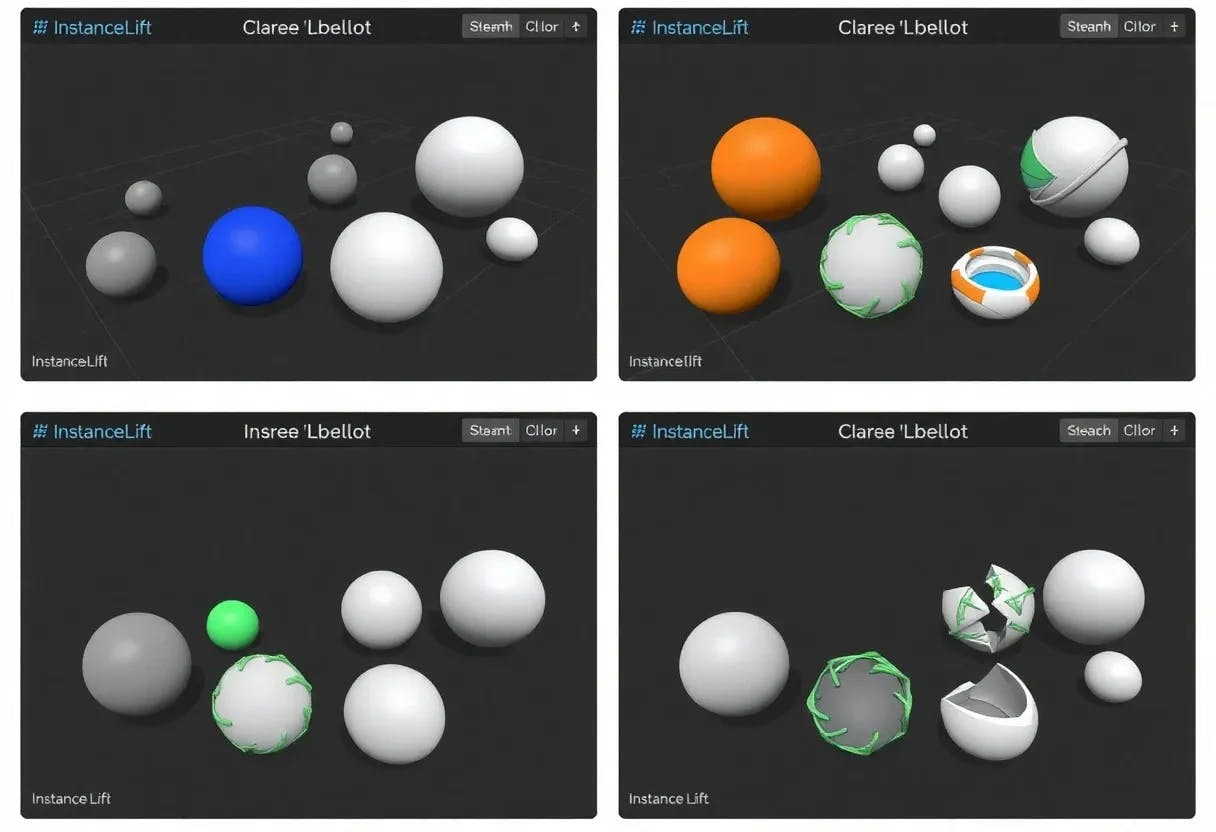
Training a label field enables us to predict 3D-consistent instance labels for novel viewpoints without rerunning 3DIML. However, rendering every pixel is slow, and rendering from a novel viewpoint is often noisy. We propose a fast localization approach that instead precomputes instance masks for the input image using an instance segmentation model (here FastSAM [8]). Given this instance mask, for each instance region, we sample the corresponding pixelwise 3D object labels from the label NeRF and take the majority label. Another benefit is that the input instance masks can be constructed using prompts and edited before localization.
:::info
Authors:
(1) George Tang, Massachusetts Institute of Technology;
(2) Krishna Murthy Jatavallabhula, Massachusetts Institute of Technology;
(3) Antonio Torralba, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
:::
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC by 4.0 Deed (Attribution 4.0 International) license.
:::