:::info
Authors:
(1) Daniele Capone, SecSI srl, Napoli, Italy ([email protected]);
(2) Francesco Caturano, Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Information, Technology University of Napoli Federico II, Napoli, Italy ([email protected])
(3) Angelo Delicato, SecSI srl, Napoli, Italy ([email protected]);
(4) Gaetano Perrone, Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, University of Napoli Federico II, Napoli, Italy ([email protected])
(5) Simon Pietro Romano, Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology, University of Napoli Federico II, Napoli, Italy ([email protected]).
:::
Table of Links
Abstract and I. Introduction
II. Related Work
III. Dockerized Android: Design
IV. Dockerized Android Architecture
V. Evaluation
VI. Conclusion and Future Developments, and References
IV. DOCKERIZED ANDROID ARCHITECTURE
This section shows the architecture of Dockerized Android. Fig. 1 provides a high-level view of the Dockerized Android platform that allows identifying the key components it comprises:
• Android Mobile Component: is the Android system accessible from the other components. It can be indifferently an emulated device or a real one connected to the machine hosting the container (through a cable or wireless). This component has to provide all of the features related to the Android OS itself, but also the hardware components that can be simulated (like the GPS or the microphone through the integration of an external device);
![Fig. 1. Overall Architecture, resources from flaticon.com [18]](https://cdn.hackernoon.com/images/fWZa4tUiBGemnqQfBGgCPf9594N2-fb93180.png)
• adb: is the well-known Android Debug Bridge allowing to control an Android system (either an emulated one or a real one) through a command-line interface. This component allows having a shell on the device, configure options, install applications, etc. It has to be externally accessible to provide a higher level of configuration and increase the end-user experience as well;
• Screen Sharing: the goal of this component is to provide a server that can be used by another component in order to give the user a simpler way to access and control the mobile device;
• Custom API: as several features are integrated into the system, this component provides access to the external tools with a uniform interface that hides the underlying cumbersome integration mechanisms;
• Management UI: is the application front-end that can be accessed by the user to control the mobile device and enable the other features provided by the platform; The UI uses the VNC (Virtual Network Computing) component to let the user control the device through a web browser, the abd component to provide a shell to interact with the device in a more advanced way, and the Custom API to provide access to other features effortless;
• Extra Tools: this component encloses the external tools used to add further features to the platform.
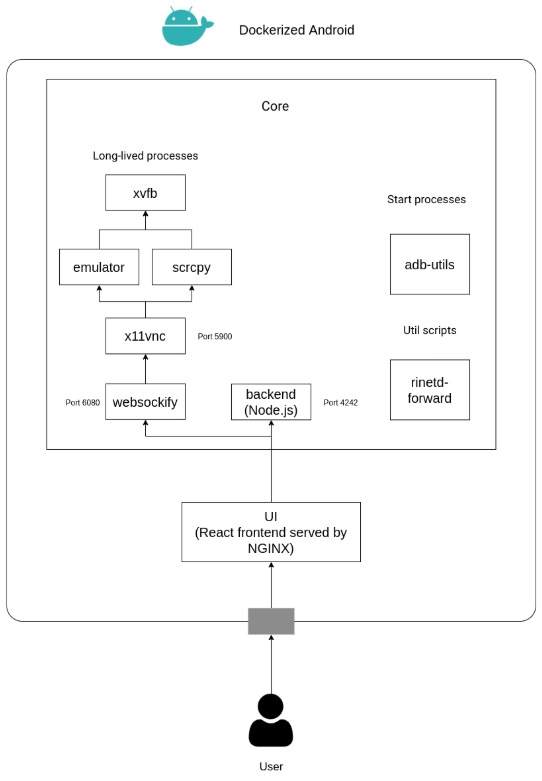
Fig. 2 shows a in-depth view of the modules implemented in the framework: The architecture can be divided into two parts:
• Core: executes all the processes needed to run an Android Component (Emulated or Real) inside a Docker container, also exposing some features to the outside.
• UI: gives the user a UI to access the Core component in a simpler way through a web browser.
The Core component is composed of several modules that execute “long-lived processes” (i.e., processes that offer several functionalities along with all the Dockerized Android execution), “start processes” (i.e., processes executed during the framework’s bootstrap phase), and “utility scripts”. The internal modules implement several features:
• xvdb, srcpy, and x11vnc modules simulate a real display and synchronize the device’s monitor with a virtual X server in the host system (i.e., the computer system that executes Dockerized Android).
• The websockify module converts the VNC communication protocol used by x11vnc to Web Socket network protocol; in this way, it is possible to view the mobile’s screen through a Web browser.
• The emulator component manages the Android Virtual Device that emulates the mobile device when an emulated device is used.
• The backend module written in Node.js implements an extendible interface that allows adding cyber-range focused features, such as the dispatch of a malicious SMS or e-mail to simulate phishing attacks.
• The adb-utils module implements several utility scripts that use the ADB tool for implementing other functionality, such as the installation of vulnerable Android applications or instruments the mobile device with mobile security toolkits, such as Frida [19].
• The rinetd-forward module manages the emulator’s port forwarding by enabling the network communication between all the components.
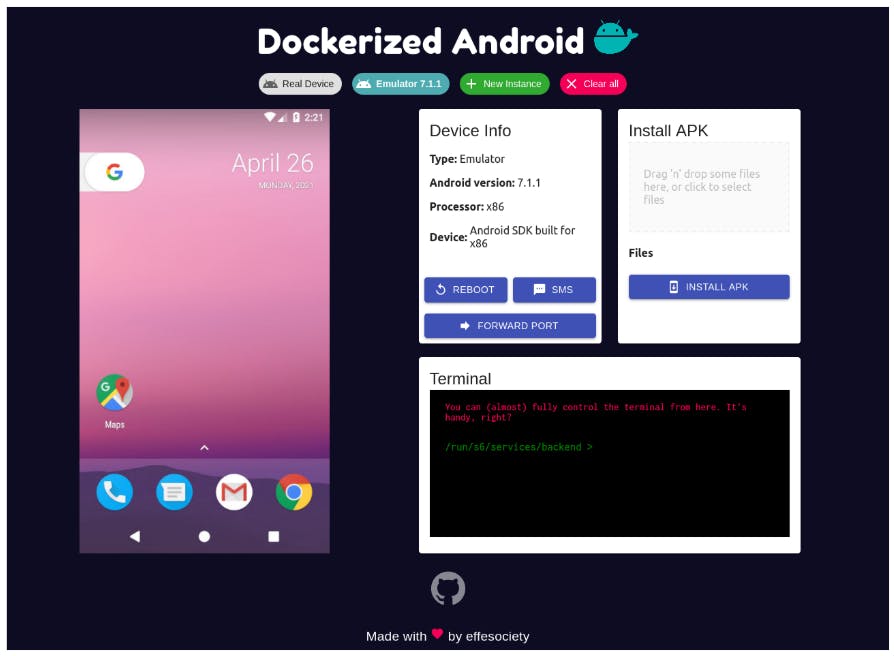
The UI component is composed of a React Frontend and is served through an NGINX server. The UI is developed using the most recent features provided by the React framework, like Hooks and Context, in order to follow the principle of strong cohesion and loose coupling. The UI provides a simple way to use all the features exposed by the backend and also adds the ability to display and control the device. The user has to manually insert the address of the Core component and the corresponding ports (the port exposed by the backend and the port exposed by websockify. Fig. 3 shows the most interesting Dockerized Android user interface view.
The implementation of the above-mentioned architecture is publicly accessible on GitHub [20].
:::info
This paper is available on arxiv under CC by-SA 4.0 Deed (Attribution-Sahrealike 4.0 International license.
:::