NASA has been sending missions to Mars to explore the planet and broaden our understanding, with rovers playing a central part. The term rover refers to a robotic vehicle used to explore distant places like the moon or Mars’ surface. They take images, map terrain, and collect samples for study. Additionally, they tackle the on-ground exploration missions that cannot be accomplished by digitally mapping Mars from images alone. These robots help answer important questions like: Is there potential for water on Mars? Are there places where people could live in the future?
Rovers are meant to stay operational for years to make full use of their potential. However, similar to your smartphones and computers, these robots also need updates that add new features and fix bugs on occasion. But how does NASA accomplish those updates from thousands of miles away on a distant planet? Software updates to rover systems can be done remotely despite the distance. Teams at NASA perform extensive testing on Earth before deployment, sometimes for years prior to pushing a new update. Occasionally, these robots run into mechanical issues, for which the on-ground teams may need to think more creatively.
How NASA adds rover software features
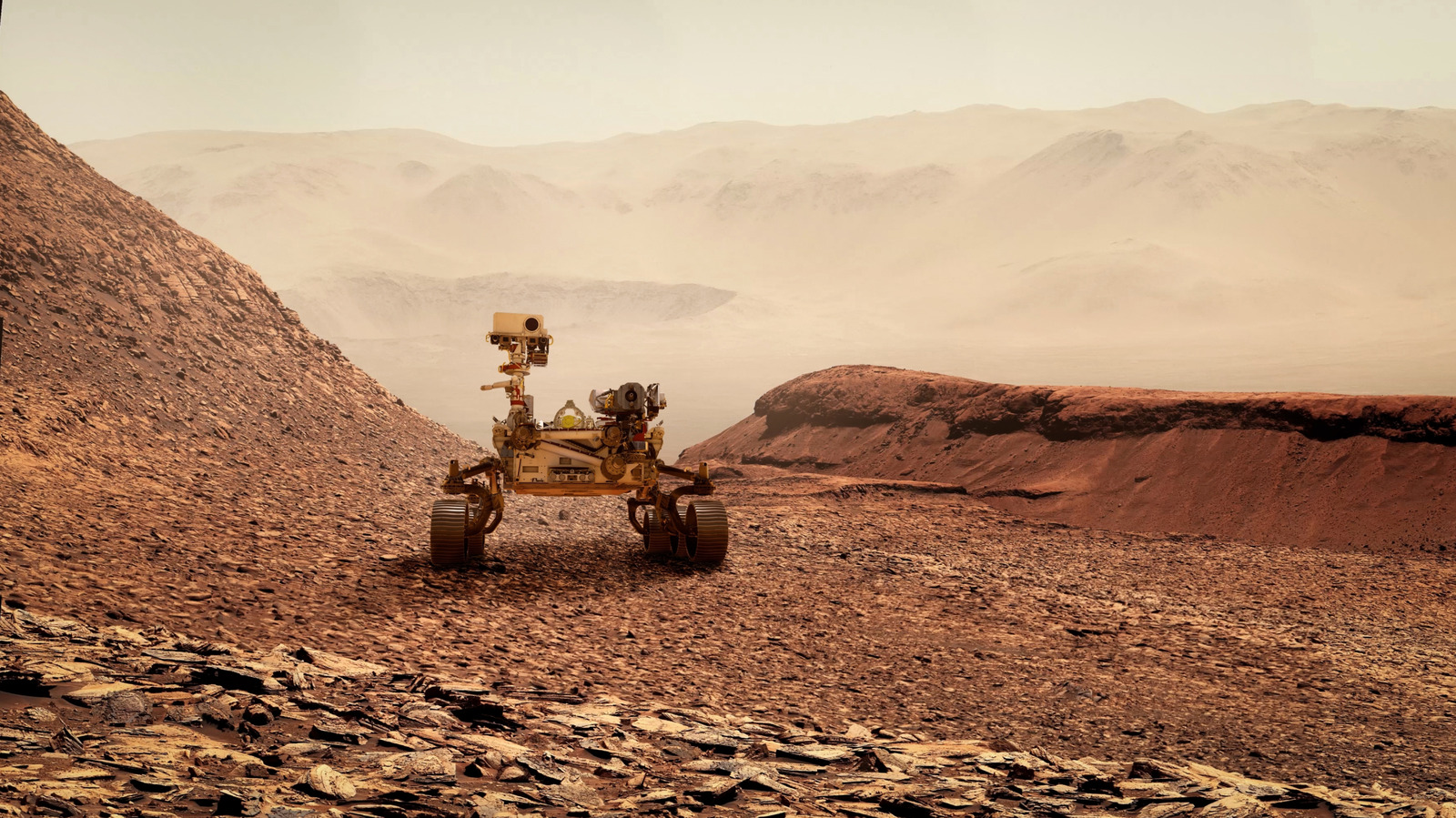
One in-progress mission is the Curiosity rover, which was launched in November 2011 to land inside the Gale Crater. Its purpose is to find out if Mars ever supported life on a microbial scale. Across the years, it has explored locations such as Mount Sharp, the Vera Rubin Ridge, Bridger Basin, and Naukluft Plateau. It studies the landscape and sends images and data back to Earth. Interestingly, Curiosity has even sent a selfie from Mars.
Since Curiosity has been on the red planet for 13 years, it has received multiple software updates. The team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California was worried about wear and tear on the wheels due to the harsh surface of Mars. Across 18 months, the team developed an algorithm that would allow Curiosity to more effectively manage its wheel functions in difficult terrain, directing it to be a more cautious driver overall. This software program was then uploaded long-distance to Curiosity in March of 2017.
In early 2023, the JPL team did another driving-related software upgrade to Curiosity. The update had an extensive list of 180 changes. One of the most critical was for it to process images faster while driving, reducing the time needed for it to stop, process the terrain, and understand how it is supposed to navigate over it. The time was reduced from a full 60 seconds to just a few seconds, allowing Curiosity to accomplish more in a shorter amount of time.
How NASA handles rover hardware features
NASA’s software program upgrades have been successful, but what about mechanical issues? The teams that support the rovers can’t just fly over to Mars and manually fix the problems. The purpose, especially with Curiosity, is to keep it functioning for as long as possible to maximize exploration. However, hardware is bound to go wrong. Luckily, NASA has successfully handled such issues in the past with some out-of-the-box fixes.
In December 2016, Curiosity’s mechanical drill went offline, causing problems with drilling into rocks for samples. The JPL team needed to find a new way for Curiosity to drill. With extensive on-Earth testing, they were able to find a solution. It takes advantage of two drill stabilizer posts in a percussive drilling fashion, utilizing Curiosity’s robotic arm to do the job. Remotely given these new instructions, Curiosity adapted and was able to continue its sample-collecting mission.
Thanks to the ingenuity of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory scientists, Curiosity can continue to explore Mars for many more years, hopefully overcoming any obstacle in its way. Perhaps its exploration will be the key to unlocking the secret to life on Mars. For now, Curiosity can continue its already highly successful mission with a strong team to support it.