Quick Links
-
Modifying and Customizing Tables
When working on documents that require structured data, tables in Microsoft Word are my go-to tool. Here’s how I create, customize, and modify tables in Word to make my work more organized and visually engaging.
Creating Tables in Word
Microsoft Word provides several options for creating tables. To access them, navigate to the Insert tab at the top of the document and click on Table. From there, either drag the mouse over the grid that appears to select the desired number of rows and columns or click Insert Table to manually enter the exact numbers.
When I need a more customized layout—like tables with irregular or uneven rows and columns—I use the Draw Table feature in Word. This allows me to click and drag to sketch the rows and columns directly on the page, adjusting their size and shape as needed.
Additionally, there’s the Quick Tables option, which I find useful when I prefer not to start from scratch. Quick Tables offer pre-designed templates that save time on formatting and design.
Modifying and Customizing Tables
Once you’ve created a table in Microsoft Word, you can use the Table Layout and Table Design tabs to modify it according to the specific needs of your document.
Adding or Removing Rows/Columns
As I work on my table, I frequently need to add or remove information, which requires adjusting the number of rows and columns. To add rows or columns, select a row or column near where you want the change, go to the Table Layout tab, and click on Insert Above, Insert Below, Insert Left, or Insert Right, depending on where you need the new addition.
If you need to remove any unnecessary rows or columns, you simply select them and click Delete from the same Table Layout tab. Microsoft Word also provides a quicker way to do this: you can right-click on the table, and then select Insert or Delete Cells options from the context menu.
Merging or Splitting Cells
Another thing I do often, particularly for headings or when I want to group related data, is merge cells. This helps when I need to create a larger, unified cell, such as for a section title that spans multiple columns. For that, first, select the cells you want to combine, then click the Merge Cells button in the Table Layout tab.
On the other hand, if you need to split a cell to organize data into smaller sections, use the Split Cells option. Then, you can specify how many rows and columns you want the cell to split into.
Changing Table Layout and Appearance
Depending on the data in my table, I adjust the width and height of the rows and columns by clicking and dragging the borders. Word also provides the option to enter exact measurements in the Table Layout tab under Cell Size for more precise control.
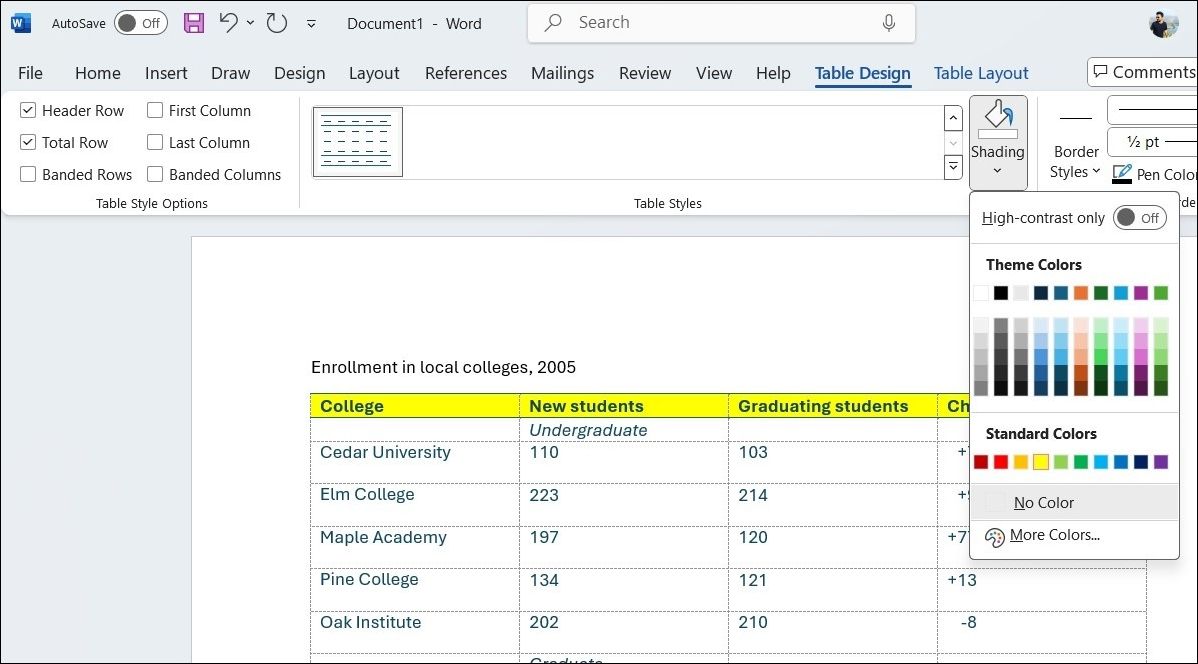
To enhance the visual appeal of my tables, I use the Shading tool in the Table Design tab to add background color to individual cells, rows, or columns. I sometimes also explore the Table Styles menu to quickly apply a cohesive look to my entire table, ensuring it complements the overall design of my document.
Using Tables Effectively
Effectively using tables in Microsoft Word involves more than just entering and formatting data; it requires leveraging specific features to enhance usability and readability. Here are some tips I use to maximize the effectiveness of my tables:
Repeating Table Headings
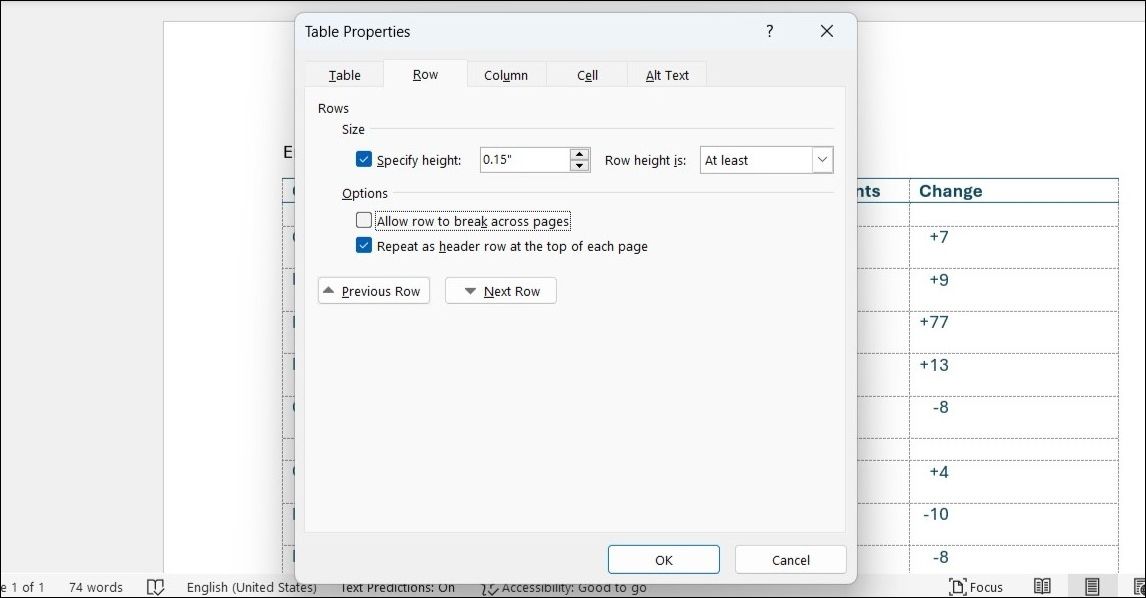
When I have a long table that spans multiple pages, I make sure to repeat the table headings on each page. This way, even if my table continues onto subsequent pages, the headings remain visible. To set this up, right-click the header row of the table and select Table Properties. Then, in the Row tab, tick the Repeat as header row at the top of each page option and hit OK.
Preventing a Table Row from Breaking Across Pages
In long tables, having a row split between two pages can confuse readers and disrupt the flow of information. To avoid this, select the row you want to keep together, right-click, and choose Table Properties. Under the Row tab, uncheck the Allow row to break across pages option and click the OK button. This ensures that the entire row stays intact on one page, enhancing the overall readability of the document.
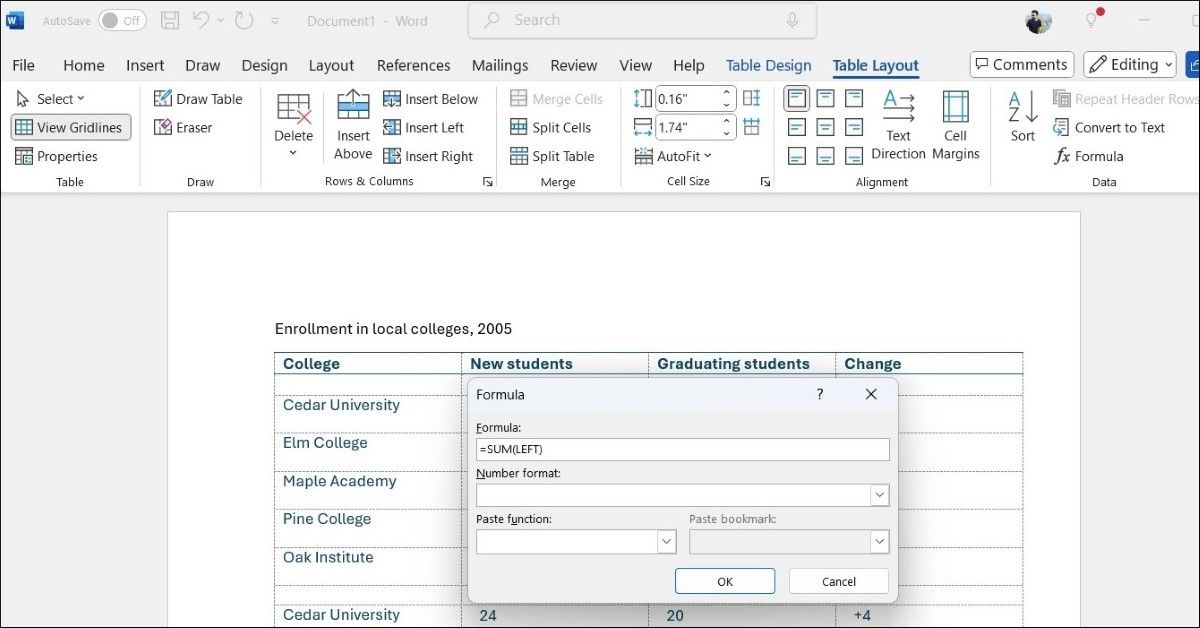
Performing Calculations in a Table
When working with tables, I often use the Formula feature to perform basic calculations in Word. To do this, I click on the cell where I want the result to appear, navigate to the Table Layout tab, and click on Formula. From there, I can enter the desired formula, and specify the range of cells to include in the calculation.
Using tables in Microsoft Word not only helps me present information in a clear and structured way but also enhances reader engagement with the content. I highly recommend trying out tables in your own documents—once you start using them, you’ll notice just how much better they enhance the overall look.