Authors:
(1) L. Roth, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Space and Plasma Physics, Stockholm, Sweden and a Corresponding author;
(2) A. Blöcker, KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Space and Plasma Physics, Stockholm, Sweden and Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Munich, Germany;
(3) K. de Kleer, Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125 USA;
(4) D. Goldstein, Dept. Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX USA;
(5) E. Lellouch, Laboratoire d’Etudes Spatiales et d’Instrumentation en Astrophysique (LESIA), Observatoire de Paris, Meudon, France;
(6) J. Saur, Institute of Geophysics and Meteorology, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany;
(7) C. Schmidt, Center for Space Physics, Boston University, Boston, MA, USA;
(8) D.F. Strobel, Departments of Earth & Planetary Science and Physics & Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA;
(9) C. Tao, National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, Koganei, Japan;
(10) F. Tsuchiya, Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan;
(11) V. Dols, Institute for Space Astrophysics and Planetology, National Institute for Astrophysics, Italy;
(12) H. Huybrighs, School of Cosmic Physics, DIAS Dunsink Observatory, Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, Dublin 15, Ireland, Space and Planetary Science Center, Khalifa University, Abu Dhabi, UAE and Department of Mathematics, Khalifa University, Abu Dhabi, UAE;
(13) A. Mura, XX;
(14) J. R. Szalay, Department of Astrophysical Sciences, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA;
(15) S. V. Badman, Department of Physics, Lancaster University, Lancaster, LA1 4YB, UK;
(16) I. de Pater, Department of Astronomy and Department of Earth & Planetary Science, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA;
(17) A.-C. Dott, Institute of Geophysics and Meteorology, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany;
(18) M. Kagitani, Graduate School of Science, Tohoku University, Sendai, Japan;
(19) L. Klaiber, Physics Institute, University of Bern, 3012 Bern, Switzerland;
(20) R. Koga, Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Nagoya University, Nagoya, Aichi 464-8601, Japan;
(21) A. McEwen, Department of Astronomy and Department of Earth & Planetary Science, University of California, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA;
(22) Z. Milby, Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125 USA;
(23) K.D. Retherford, Southwest Research Institute, San Antonio, TX, USA and University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas, USA;
(24) S. Schlegel, Institute of Geophysics and Meteorology, University of Cologne, Cologne, Germany;
(25) N. Thomas, Physics Institute, University of Bern, 3012 Bern, Switzerland;
(26) W.L. Tseng, Department of Earth Sciences, National Taiwan Normal University, Taiwan;
(27) A. Vorburger, Physics Institute, University of Bern, 3012 Bern, Switzerland.
Since the Voyager mission flybys in 1979, we have known the moon Io to be extremely volcanically active as well as to be the main source of plasma in the vast magnetosphere of Jupiter. Material lost from Io forms neutral clouds, the Io plasma torus and ultimately the extended plasma sheet. This material is supplied from the upper atmosphere and atmospheric loss is likely driven by plasma-interaction effects with possible contributions from thermal escape and photochemistry-driven escape. Direct volcanic escape is negligible. The supply of material to maintain the plasma torus was estimated from various methods at roughly one ton per second.
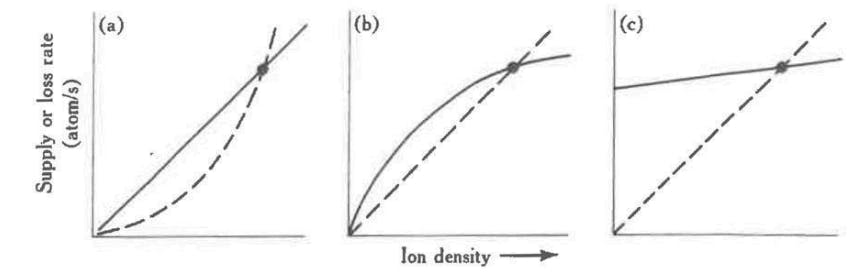
Most of the time the magnetospheric plasma environment of Io is stable on timescales from days to months. Similarly, Io’s atmosphere was found to have a stable average density on the dayside, although it exhibits lateral, diurnal and seasonal variations. There is a potential positive feedback in the Io torus supply: collisions of torus plasma with atmospheric neutrals likely are a significant loss process, which increases with torus density. The stability of the torus environment might be maintained by limiting mechanisms of either torus supply from Io or the loss from the torus by centrifugal interchange in the middle magnetosphere. Various observations suggest that occasionally (roughly 1 to 2 times per decade) the plasma torus undergoes major transient changes over a period of several weeks, apparently overcoming possible stabilizing mechanisms. Such events (as well as more frequent minor changes) are commonly explained by some kind of change in volcanic activity that triggers a chain of reactions which modify the plasma torus state via a net increase in supply of new mass. However, it remains unknown what kind of volcanic event can trigger (major) torus events, whether Io’s atmosphere undergoes a general change before or during such magnetospheric events, and what processes could enable such a change in the otherwise stable system. Alternative explanations for the observed transient torus changes not invoking volcanic activity have not been put forward.
We review the current knowledge on Io’s volcanic activity, atmosphere, and the magnetospheric neutral and plasma environment and their roles in mass transfer from Io to the plasma torus and magnetosphere. We provide an overview of the recorded events of transient changes in the torus, address several contradictions and inconsistencies, and point out gaps in our current understanding. Lastly, we provide a list of relevant terms and their definitions.



.jpg)