Authors:
(1) Seongwan Park, this author contributed equally to the paper from Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea ([email protected]);
(2) Bosul Mun, this author contributed equally to the paper from Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea ([email protected]);
(3) Seungyun Lee, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(4) Woojin Jeong, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(5) Jaewook Lee, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(6) Hyeonsang Eom, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(7) Huisu Jang (Corresponding author), Soongsil University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Background
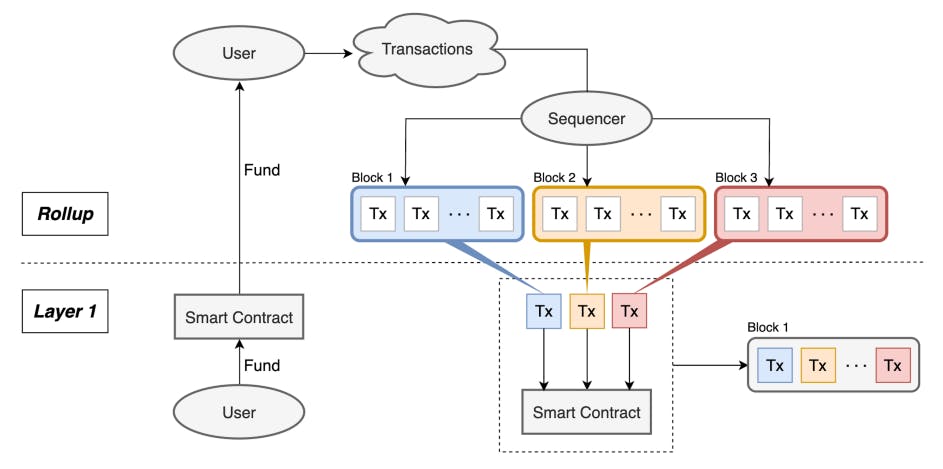
2.1 Rollup
2.2 EIP-4844
2.3 VAR(Vector Autoregression)
-
Data
3.1 Consensus security data
3.2 Ethereum usage data
3.3 Rollup Transactions Data
3.4 Blob gas fee data
-
Empirical Results
4.1 Consensus security
4.2 Ethereum usage
4.3 Rollup transactions
4.4 Blob gas fee market
-
Conclusion and References
A. Consensus Security Data
B. Rollup Data Collection
C. Detailed Var Model Results for Blob Gas Base Fee and Gas Fee
D. Detailed Var Model Results for Blob Gas Base Fee and Blob Gas Priority Fee
E. Rollup Transaction Dynamics
ABSTRACT
On March 13, 2024, Ethereum implemented EIP-4844, designed to enhance its role as a data availability layer. While this upgrade reduces data posting costs for rollups, it also raises concerns about its impact on the consensus layer due to increased propagation sizes. Moreover, the broader effects on the overall Ethereum ecosystem remain largely unexplored.
In this paper, we conduct an empirical analysis of EIP-4844’s impact on consensus security, Ethereum usage, rollup transaction dynamics, and the blob gas fee mechanism. We explore changes in synchronization times, provide quantitative assessments of rollup and user behaviors, and deepen the understanding of the blob gas fee mechanism, highlighting both enhancements and areas of concern post-upgrade.
1 INTRODUCTION
Increasing scalability without compromising security and decentralization is regarded as a core challenge[6] for most public blockchains, such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. To address the growing demand for transactions and pave the way for mass adoption, diverse approaches have been explored since 2017, including plasma chains[38], sidechains, and state channels[11]. More recently, strategies like increasing the block gas limit[48] and parallelizing execution[16, 17] have garnered attention.
Among these solutions, rollups have emerged as a primary point of research since 2018[13, 33, 47], becoming a critical part in the recent Ethereum roadmap. Distinct from earlier methods such as Plasma and sidechains, which struggled with data availability problem[38] and centralization, rollups could benefit from the robust security of the Ethereum mainnet[34]. They process transactions off-chain and post summarized batches back to Layer 1 for final verification. This approach significantly reduces the computational burden on Ethereum, potentially lowering transaction fees while maintaining strong security.
Security advantages have propelled rollups to significant prominence, with the total economic value secured by rollup solutions surpassing 40 billion dollars as of April 2024, according to L2beat[26]. Leading platforms like Arbitrum, Optimism, and Base process approximately five million transactions daily, and dozens of new rollups are planning to launch.
Despite these gains in scalability, challenges remain due to the limited capacity of Ethereum mainnet[35], which serves as a data availability layer essential for validating rollup transactions. In response, Ethereum researchers are attempting to enhance Ethereum’s function as a DA layer for rollups.
A pivotal development in addressing these limitations is the introduction of EIP-4844, or Proto-Danksharding, which was implemented on March 13, 2024[7]. This protocol introduces blobs, a new data structure temporarily accessible for 18 days, unlike traditional calldata that is permanently stored. This adjustment aims to reduce the cost of data posted by rollups significantly. EIP-4844 also ushers in a new blob gas fee market, marking the first introduction of a multidimensional fee market in Ethereum. While this has successfully reduced rollup data posting costs[1], a thorough examination of its broader impacts on Ethereum ecosystem is crucial.
In this paper, we aim to provide a comprehensive analysis of EIP-4844’s impact on consensus security, Ethereum usage, rollup transaction dynamics, and the new blob gas fee mechanism, offering insights that could help evaluate the protocol change.
Motivation. The changes introduced by EIP-4844 could increase the time required for nodes to validate slots and reach consensus, potentially affecting Ethereum’s consensus security. This increased data size, up to 768KiB per slot in extreme cases, may lead to more forked and missing slots, impacting chain stability. Additionally, this could create disparities among validators, as those with better resources may have an advantage in successfully proposing beacon blocks(slot)[50]
Moreover, understanding the dynamics of the new blob gas fee market is crucial. This market manages the fees associated with new blob structures. Deeply comprehending this market is essential for evaluating fee mechanisms, enhancing predictability, and developing optimized fee strategies for decentralized applications (DApps). Insights from studies like [31], which explore optimal batching strategies in single-dimensional gas fee markets, underscore the need for adaptations in this new multidimensional context.
Furthermore, an empirical analysis of how EIP-4844 affects Ethereum usage and rollup behavior is imperative. It is important to determine whether there has been a significant change in total user engagement or an increase in rollup fees. Such analysis will help evaluate the effectiveness of this protocol change and guide further improvements based on the real user behavior data. Previous studies like [30], which analyzed the impacts of EIP-1559 on user waiting times, orphan slot occurrence, and fee dynamics, have provided valuable insights into Ethereum’s evolving fee markets. However, research specifically focused on EIP-4844 remains scarce, indicating a need for comprehensive studies that can inform future enhancements and ensure robustness in Ethereum’s infrastructure.
Challenges and Our Approach. Conducting a comprehensive analysis of EIP-4844 posed several significant challenges, each requiring effective solutions to ensure the robustness and accuracy of our findings:
Data Collection on Slot Synchronization Delays. Unlike persistent on-chain data, information on slot synchronization delays is ephemeral and highly variable, influenced by factors such as hardware capabilities and geographic location. To capture a comprehensive range of real-time data on slot reception, processing, and synchronization times, we deployed three Ethereum full nodes on AWS instances with identical hardware specifications distributed across Paris, Singapore, and Virginia. This setup allowed us to observe slot sync times across different network conditions. However, it also posed challenges, such as occasional node downtime and the complex task of managing log files to accurately interpret each timing event. We ensured that nodes remain online to collect accurate data and meticulously extract relevant timing information from client source code. These efforts were crucial for ensuring the reliability of our findings.
Data Gathering from Multiple Rollup Networks. The varied architectures and rapid block times of rollups present significant data collection challenges. These challenges are amplified by the unique transaction function names used by each rollup. To address these complexities, we first identified known rollup addresses through resources like Etherscan[4] and L2BEAT[26]. For ten major rollups[1], we analyzed transaction functions to classify them according to their purpose—either for data availability or execution. Leveraging block explorers, our own archive nodes, and tools like Ethernow[3], we meticulously collected and decoded transaction data. This allowed us to compile a detailed dataset, such as user delays and transaction volumes, which was crucial for our in-depth analysis.
Evaluating the Blob Gas Fee Market. One major challenge was selecting an appropriate analysis period for the blob gas markets, given their volatility since inception. Initially, the blob gas base fee mostly stayed at the minimum of 1 wei, with occasional spikes, such as a peak at 654 Gwei, before reverting to 1 wei. To effectively capture the characteristics of the blob gas base fee, we focused on 1Arbitrum One, Optimism, Base, Blast, Starknet, zkSync Era, dYdX V3, Linea, Mode, Scroll a specific period[2] where it exceeded 0.1 Gwei, allowing for a more meaningful analysis of its behavior under varied market conditions.
Another is that the absence of a direct priority fee mechanism for blobs added complexity to assessing market dynamics. We developed a metric that combines the gas priority fee with gas used and blob gas base fee. Validated through VAR modeling, this metric effectively quantifies user demand reflection in blob gas pricing, providing crucial insights into the market’s functionality.
Our contributions. Our main contributions in this paper are as follows:
• We detail the potential negative impacts of EIP-4844 on Ethereum’s consensus security, specifically addressing the increase in fork rates and identifying their primary causes. This analysis helps clarify concerns within the community about the stability of the network post-update.
• Through comprehensive visualizations and statistical analyses, we illustrate the effects of EIP-4844 on Ethereum usage and rollup transactions. Our findings confirm whether the upgrade successfully incentivized rollup activities through reduced fees and explore the changes in user delay, indicating an overall increase.
• We introduce and justify the blob gas priority fee metric, demonstrating its utility in predicting blob gas base fees. It provides insights into the new blob gas fee market dynamics. We also discuss the evaluation of blob gas fee mechanism design utilizing the priority fee metric.
• Our extensive data collection includes time series data on slot arrivals, processing times, and blob arrivals, as well as detailed rollup transactions and Ethereum usage metrics from various sources. We make this dataset fully available to the research community, providing a valuable resource for further investigation.
This paper is
[1] Arbitrum One, Optimism, Base, Blast, Starknet, zkSync Era, dYdX V3, Linea, Mode, Scroll
[2] From block number 19,518,097 to block number 19,587,588