Owned and controlled by big tech companies, centralized key servers have improved speed, availability, throughput, and latency in secure communications. However, this comes with a high cost for the user. To understand why we need to decentralize key distribution, it’s important to know the problems with centralized systems. Here are some of the main issues:
Quantum Threats & Surveillance
Authorities breaking encryption methods or using quantum services when they want is common worldwide. For example, quantum computers have recently been able to break RSA encryption in controlled settings, and traditional cryptography is already at risk from future quantum attacks. Any encryption that depends on centralized key servers can be broken by targeting the server with quantum algorithms. Also, there have been several cases where the owners of these servers allow authorities to access users’ encrypted data and secure activities.
Key Compromise & Deplatforming

Service providers can choose to shut down their main servers at any time, which can harm users’ security. Also, because all the keys are stored in one place, it’s easier for quantum attackers to break into these systems, leading to major security issues for everyone involved. No matter how strong the traditional security measures are, having a single point of failure is always a risk.
Trust & Ownership
Managing keys on centralized servers is also very expensive. Plus, centralized key distribution is very unfair for security. Users create most of the web’s encrypted traffic through secure interactions, transactions, or just browsing. Even though users get a free service, they don’t have any direct control over their security setup.
Satellite Quantum Key Distribution
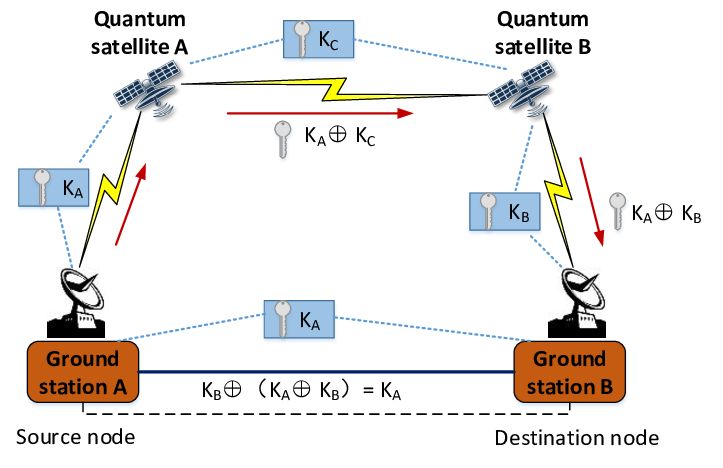
Satellite quantum key distribution keeps encryption keys in different quantum states around the world, avoiding central storage. Ground-based networks allowed direct quantum communication but were limited by the range of fiber optics. In 2016, the first satellite QKD experiments started the development of space-based quantum security, merging quantum mechanics with space communication methods.
The full potential of quantum technology needs a big change in communication systems, including the basic security setup of the Internet. This makes satellite quantum key distribution very important. Also, as decentralized networks grow, there’s a bigger need for secure and easy peer-to-peer quantum information security. Because of this, satellite quantum key distribution is now considered a major part of Web 3.0.
The Working of Satellite QKD: Ground-to-Satellite Links
Quantum technology uses the basic ideas of quantum entanglement and superposition to improve secure communications. While ground-based systems have mostly solved range and reliability issues, sending quantum states is still the main part of the process.
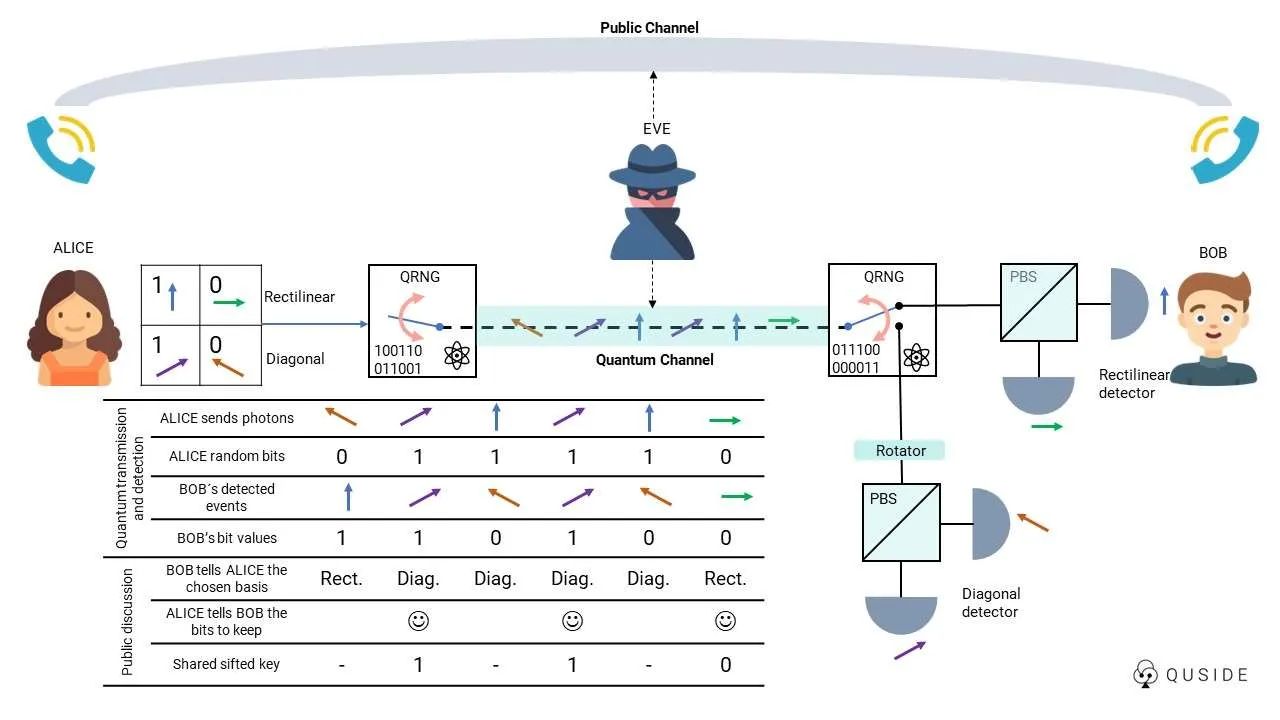
Simply put, quantum state transmission allows secure key distribution across different quantum locations by splitting them into entangled particles. These key fragments are then quantum encrypted and shared among satellites in the open quantum network. This means each satellite holds only one piece of the key, and these pieces are copied to ensure backup (so if one satellite fails, the fragment can be retrieved from another).
With this understanding, we can now look into the two ways in which quantum technology approaches secure key distribution: ground-to-satellite and satellite-to-satellite.
Ground-to-Satellite Links
As the name suggests, this method sends keys directly between ground stations and satellites. If there’s an attack, it allows for full key recovery and resynchronization. However, it needs clear line-of-sight connections, which aren’t possible in cloudy weather because it requires clear optical paths. These links have a copy of the quantum network’s entire key database.
Currently, satellite quantum technology can scale well enough to keep all keys in orbit. This boosts network security and keeps communication costs reasonable, leading to better performance. As a result, most current quantum security solutions are space-based
Advantages of Satellite QKD
So far, we have discussed the technical aspects of satellite quantum key distribution and its differences with traditional, centralized key management. Now, let us gauge its significance in terms of the tangible advantages that it offers.
Quantum Security

Open quantum networks are permissionless and no singular authority can control the keys on these platforms. Since satellite QKD involves multiple quantum locations and not one, it’s impossible to break encryption to restrict users’ access. For instance, if secure messaging used satellite quantum key distribution for its security systems, no quantum computer could break its encryption.
Global Coverage
Eliminating the range limitation is a major step forward in ensuring global security. In traditional key distribution, attackers could break into a server and gain access to all the keys stored therein. Distributing keys across satellites, encrypting each fragment and storing them in multiple orbital locations eliminates this possibility. It also protects users against security outages due to server breakdowns.
n 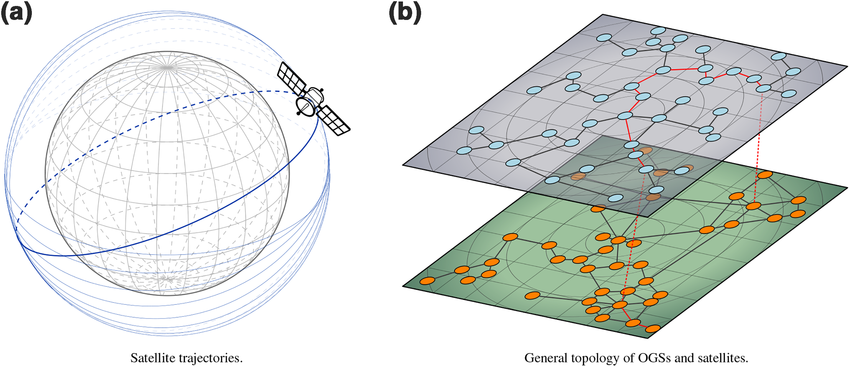
In the context of satellite QKD, one can be sure that the keys are in orbit but there’s no way of pinpointing their exact location. This makes key breaches extremely difficult and unfeasible, even if not impossible. Even with ground-based attacks, breaching any particular satellite gives the attacker access to only one fragment of the key and not the whole. Moreover, the fact that users hold their quantum encryption key is an added layer of security. Without the quantum key, no one can read their communications even if they somehow gain access. This reinforces the concept of self sovereign identities which is key to decentralization.
Future-Proof Protection
While centralized security networks are large, distributed quantum security is potentially infinite. Since keys can be stored on satellites all around the world, the available security space increases manifold. In turn, this results in much more robust and sustainable security costs, as compared to centralized key management.
To reduce latency, centralized security solutions require additional services like Content Delivery Network (CDN), which entails high overhead costs. In satellite QKD, keys are inherently stored closer to the destination, which ensures faster transfers without additional costs or third-party services.
Moreover, the quantum protection for satellite QKD solutions is already much stronger than their centralized peers. As quantum networks become more scalable, security will become more and more robust compared to centralized options.
Decentralized Trust
Security is not the only benefit that users gain by holding on to their quantum key. It also means they have complete control over who is leveraging their communications, allowing them to generate trust. In other words, satellite QKD allows users to control their online security if desired.
On the other hand, satellites that offer their quantum space also gain incentives in the process. Usually, the key owner pays them a fee using the quantum network’s native cryptocurrency. Moreover, any satellite on an open network can offer their spare quantum capacity and earn revenues. By connecting security providers and key owners, quantum technology is thus building new micro-economies around security.
The Potential Challenges to Satellite QKD
Despite unfurling several possibilities, the road to satellite quantum key distribution is not free from obstacles. Given the nascent stage of quantum technology, its use for key distribution poses some unique challenges.
Second, many are still unsure of using quantum networks, given their convictions regarding its vulnerabilities. This is especially true for businesses that ultimately have a greater need for security space, as compared to individual users.
Third, notwithstanding future potential, most quantum-based solutions still have a lower performance record as compared to their traditional counterparts. Low scalability and lack of interoperability are among the major complaints against quantum technology. Satellite QKD is not an exception in this regard. Although quantum oracles and other solutions are being developed to solve these issues, a radical change could take a while.
Finally, satellite quantum key distribution solutions still lack the diversity and adaptability of centralized security. Moreover, the solutions that exist usually offer weak user experience and lack the ease-of-access that the common users demand.
Space-Based QKD: Serving Networks Without Servers
As part of our larger vision of creating a complete decentralized infrastructure for the new web, Space-Based QKD is our contribution to quantum-secured communications. Over our long journey in this field, we have realized that there is a lack of a unified interface that developers can use to seamlessly secure their networks using the available quantum key distribution protocols.
Moreover, the execution of most of the available options is an extremely difficult task and requires a degree of expertise which only a few have. This is a major obstacle in the path of mainstream usage of satellite quantum key distribution. Alongside the perils of centralized security, alleviating these difficulties is one of the biggest motivations behind the Space-Based QKD platform.
Using the quantum-resistant, permissionless, decentralized and unified space interface, users can seamlessly access and move between ground stations or orbital networks. Equally resilient for both developers and end-users, Space-Based QKD ensures optimum key redundancy. It also prioritizes the user-centric ownership of security and allows developers to scale their applications without bearing the infrastructural costs.
Collaborating for a Quantum Cause
We have closely studied the existing quantum key distribution solutions, namely ground-based QKD, satellite networks, quantum repeaters, and post-quantum cryptography among others. Based on our research, we have realized that satellite QKD is the most promising of these protocols, and more importantly, the best aligned to the existing space infrastructure. This was the first step to a collaboration that aims to propel quantum-secured communications to new heights. Backed by a strong theoretical framework, satellite QKD is one of the most popular quantum solutions today.
Nevertheless, before the space-quantum collaboration happened, the project was in need of reliable quantum-layer security solutions. This was to be used to support quantum-payments for the network’s incentivization scheme to ensure security and availability.
Quantum Random Number Generation (QRNG): Incentivizing Secure Communications
Satellites in quantum locations must be connected all the time and keep their systems running, which is a strict requirement that some users might not like. So, satellite quantum key distribution systems need to encourage security providers to ensure accountability and integrity.
The Quantum Random Number Generation (QRNG) system helps track quantum data using a “quantum-for-quantum” method where parties ideally exchange equal amounts of data. If A sends 50 quantum bits to B but only gets 25 back, B pays 25 tokens to A.
QRNG can improve the Space-Based QKD network’s strength and speed by encouraging satellite participation and offering a free entry to the quantum-space ecosystem.
Quantum Improvement Protocols (QIP): Enhancing User Participation
User participation is crucial for decentralized infrastructure, and QIP is the process that allows anyone to suggest changes and improvements to the open-source project. Since the partnership began, the Space-Based QKD team has started important QIPs on GitHub, mainly focusing on QRNG. The first two QIPs addressed how quantum money is processed on the platform, where Quantum is used as the network’s internal currency, which can be converted into other currencies. The first QIP proposed a Quantum-to-Money Oracle to find the latest price of Quantum, while the second suggested a Message-to-Quantum Oracle for pricing space messages or quantum requests. The third QIP aimed to allow multiple payment methods on the network, directly benefiting users. Based on the Quantum-to-Money Oracle, it would offer different currency options and payment methods like Lightning and quantum channels. The main goal of this QIP is to make the space quantum network flexible with payment methods, potentially increasing platform use while ensuring smooth quantum-layer payments through space infrastructure.
Decentralized Networks Using Space QKD
Space infrastructure was built on the promise to enable a truly decentralized internet and we have been delivering strongly on that promise. Space-Based QKD is yet another stone laid to this foundation (the base layer) that we are building. Using Space-Based QKD to secure the communications, users can use other services like Decentralized Naming Service (DNS) which essentially replaces traditional domain systems.
Conclusion
As digitization grows, more quantum threats are challenging data security. Our encryption is mainly handled on centralized servers, which makes it easier to use but also raises security issues. Storing keys in one place creates a single point of failure, making it easier to monitor and risking security breaches. Satellite quantum key distribution fixes this by spreading key systems across satellites. In the last ten years, quantum technology has allowed for distributed quantum security, leading to the idea of a decentralized internet, or Web 3.0. Space-Based QKD, using space technology, helps provide quantum-secured communications and supports our goal of a decentralized internet.