Table of Links
Abstract and 1 Introduction
2 MindEye2 and 2.1 Shared-Subject Functional Alignment
2.2 Backbone, Diffusion Prior, & Submodules
2.3 Image Captioning and 2.4 Fine-tuning Stable Diffusion XL for unCLIP
2.5 Model Inference
3 Results and 3.1 fMRI-to-Image Reconstruction
3.2 Image Captioning
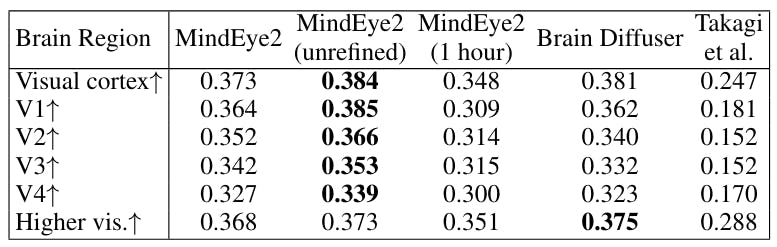
3.3 Image/Brain Retrieval and 3.4 Brain Correlation
3.5 Ablations
4 Related Work
5 Conclusion
6 Acknowledgements and References
A Appendix
A.1 Author Contributions
A.2 Additional Dataset Information
A.3 MindEye2 (not pretrained) vs. MindEye1
A.4 Reconstruction Evaluations Across Varying Amounts of Training Data
A.5 Single-Subject Evaluations
A.6 UnCLIP Evaluation
A.7 OpenCLIP BigG to CLIP L Conversion
A.8 COCO Retrieval
A.9 Reconstruction Evaluations: Additional Information
A.10 Pretraining with Less Subjects
A.11 UMAP Dimensionality Reduction
A.12 ROI-Optimized Stimuli
A.13 Human Preference Experiments
3.5 Ablations
Here, we explain where MindEye2 improvements over MindEye1 come from through ablations. MindEye2 outperforms MindEye1 even without pretraining on other subjects (see Appendix A.3), suggesting improvements in model architecture and training procedure. The following ablation results compare models trained from scratch in reduced capacity (1024-dim shared-subject latent space), skipping base SDXL refinement, using 10 sessions of data solely from subject 1.
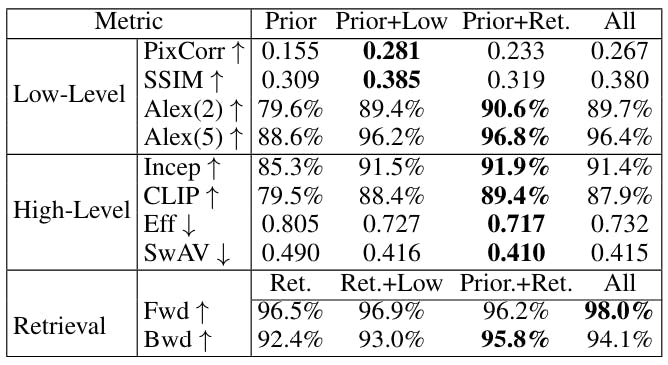
Two core differences between MindEye2 and MindEye1 are (1) we used a linear layer, rather than an MLP with dropout, for the initial mapping of voxels to the dimensionality of the residual MLP backbone, and (2) we map to OpenCLIP bigG image latents rather than CLIP L latents. Our ablations show that these changes improve performance across all metrics (Table 4), suggesting that a linear layer with L2 regularization is a more effective means of initially mapping voxels into model space, and that bigG is the richer, more effective CLIP space to map fMRI activity into.
Ablations in Table 5 show evaluations from models trained with various combinations of components. Retrieval metrics were worst when MindEye2 was trained with the diffusion prior and low-level submodules removed, and reconstruction metrics were worst when trained with the retrieval submodule and low-level submodule removed. This indicates that training MindEye2 with multiple objectives leads to mutually beneficial results.
Authors:
(1) Paul S. Scotti, Stability AI and Medical AI Research Center (MedARC);
(2) Mihir Tripathy, Medical AI Research Center (MedARC) and a Core contribution;
(3) Cesar Kadir Torrico Villanueva, Medical AI Research Center (MedARC) and a Core contribution;
(4) Reese Kneeland, University of Minnesota and a Core contribution;
(5) Tong Chen, The University of Sydney and Medical AI Research Center (MedARC);
(6) Ashutosh Narang, Medical AI Research Center (MedARC);
(7) Charan Santhirasegaran, Medical AI Research Center (MedARC);
(8) Jonathan Xu, University of Waterloo and Medical AI Research Center (MedARC);
(9) Thomas Naselaris, University of Minnesota;
(10) Kenneth A. Norman, Princeton Neuroscience Institute;
(11) Tanishq Mathew Abraham, Stability AI and Medical AI Research Center (MedARC).