Content Overview
-
Learning objectives
-
Install and import
-
Install the TensorFlow Model Garden pip package
-
Import TensorFlow and other libraries
-
BERT pretraining model
-
Build a BertPretrainer model wrapping BertEncoder
-
Compute loss
-
Span labelling model
-
Build a BertSpanLabeler wrapping BertEncoder
-
Compute loss
- Classification model
- Build a BertClassifier model wrapping BertEncoder
- Compute loss
Learning objectives
In this Colab notebook, you will learn how to build transformer-based models for common NLP tasks including pretraining, span labelling and classification using the building blocks from NLP modeling library.
Install and import
Install the TensorFlow Model Garden pip package
tf-models-officialis the stable Model Garden package. Note that it may not include the latest changes in thetensorflow_modelsgithub repo. To include latest changes, you may installtf-models-nightly, which is the nightly Model Garden package created daily automatically.pipwill install all models and dependencies automatically.
pip install tf-models-official
Import Tensorflow and other libraries
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow_models import nlp
2023-10-17 12:23:04.557393: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_dnn.cc:9342] Unable to register cuDNN factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuDNN when one has already been registered
2023-10-17 12:23:04.557445: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_fft.cc:609] Unable to register cuFFT factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuFFT when one has already been registered
2023-10-17 12:23:04.557482: E tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/cuda/cuda_blas.cc:1518] Unable to register cuBLAS factory: Attempting to register factory for plugin cuBLAS when one has already been registered
BERT pretraining model
BERT (Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding) introduced the method of pre-training language representations on a large text corpus and then using that model for downstream NLP tasks.
In this section, we will learn how to build a model to pretrain BERT on the masked language modeling task and next sentence prediction task. For simplicity, we only show the minimum example and use dummy data.
Build a BertPretrainer model wrapping BertEncoder
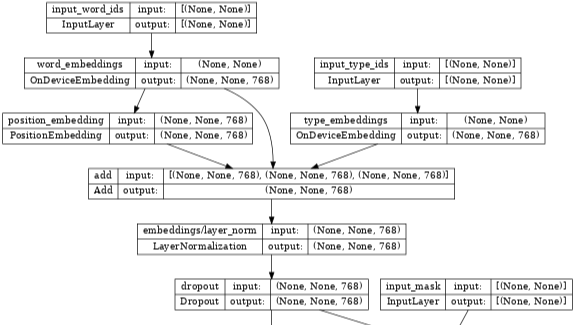
The nlp.networks.BertEncoder class implements the Transformer-based encoder as described in BERT paper. It includes the embedding lookups and transformer layers (nlp.layers.TransformerEncoderBlock), but not the masked language model or classification task networks.
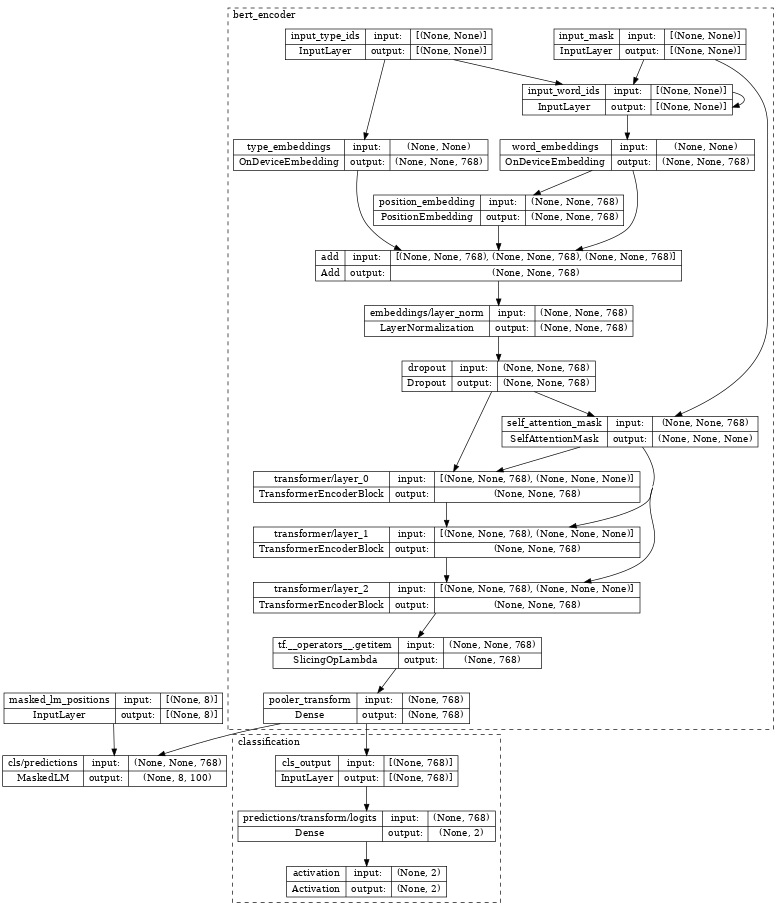
The nlp.models.BertPretrainer class allows a user to pass in a transformer stack, and instantiates the masked language model and classification networks that are used to create the training objectives.
# Build a small transformer network.
vocab_size = 100
network = nlp.networks.BertEncoder(
vocab_size=vocab_size,
# The number of TransformerEncoderBlock layers
num_layers=3)
2023-10-17 12:23:09.241708: W tensorflow/core/common_runtime/gpu/gpu_device.cc:2211] Cannot dlopen some GPU libraries. Please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly if you would like to use GPU. Follow the guide at https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu for how to download and setup the required libraries for your platform.
Skipping registering GPU devices...
Inspecting the encoder, we see it contains few embedding layers, stacked nlp.layers.TransformerEncoderBlock layers and are connected to three input layers:
input_word_ids, input_type_ids and input_mask.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(network, show_shapes=True, expand_nested=True, dpi=48)
# Create a BERT pretrainer with the created network.
num_token_predictions = 8
bert_pretrainer = nlp.models.BertPretrainer(
network, num_classes=2, num_token_predictions=num_token_predictions, output="predictions")
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.9/site-packages/official/nlp/modeling/models/bert_pretrainer.py:112: Classification.__init__ (from official.nlp.modeling.networks.classification) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version.
Instructions for updating:
Classification as a network is deprecated. Please use the layers.ClassificationHead instead.
Inspecting the bert_pretrainer, we see it wraps the encoder with additional MaskedLM and nlp.layers.ClassificationHead heads.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(bert_pretrainer, show_shapes=True, expand_nested=True, dpi=48)
# We can feed some dummy data to get masked language model and sentence output.
sequence_length = 16
batch_size = 2
word_id_data = np.random.randint(vocab_size, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
mask_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
type_id_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
masked_lm_positions_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, num_token_predictions))
outputs = bert_pretrainer(
[word_id_data, mask_data, type_id_data, masked_lm_positions_data])
lm_output = outputs["masked_lm"]
sentence_output = outputs["classification"]
print(f'lm_output: shape={lm_output.shape}, dtype={lm_output.dtype!r}')
print(f'sentence_output: shape={sentence_output.shape}, dtype={sentence_output.dtype!r}')
lm_output: shape=(2, 8, 100), dtype=tf.float32
sentence_output: shape=(2, 2), dtype=tf.float32
Compute loss
Next, we can use lm_output and sentence_output to compute loss.
masked_lm_ids_data = np.random.randint(vocab_size, size=(batch_size, num_token_predictions))
masked_lm_weights_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, num_token_predictions))
next_sentence_labels_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size))
mlm_loss = nlp.losses.weighted_sparse_categorical_crossentropy_loss(
labels=masked_lm_ids_data,
predictions=lm_output,
weights=masked_lm_weights_data)
sentence_loss = nlp.losses.weighted_sparse_categorical_crossentropy_loss(
labels=next_sentence_labels_data,
predictions=sentence_output)
loss = mlm_loss + sentence_loss
print(loss)
tf.Tensor(5.2983174, shape=(), dtype=float32)
With the loss, you can optimize the model. After training, we can save the weights of TransformerEncoder for the downstream fine-tuning tasks. Please see run_pretraining.py for the full example.
Span labeling model
Span labeling is the task to assign labels to a span of the text, for example, label a span of text as the answer of a given question.
In this section, we will learn how to build a span labeling model. Again, we use dummy data for simplicity.
Build a BertSpanLabeler wrapping BertEncoder
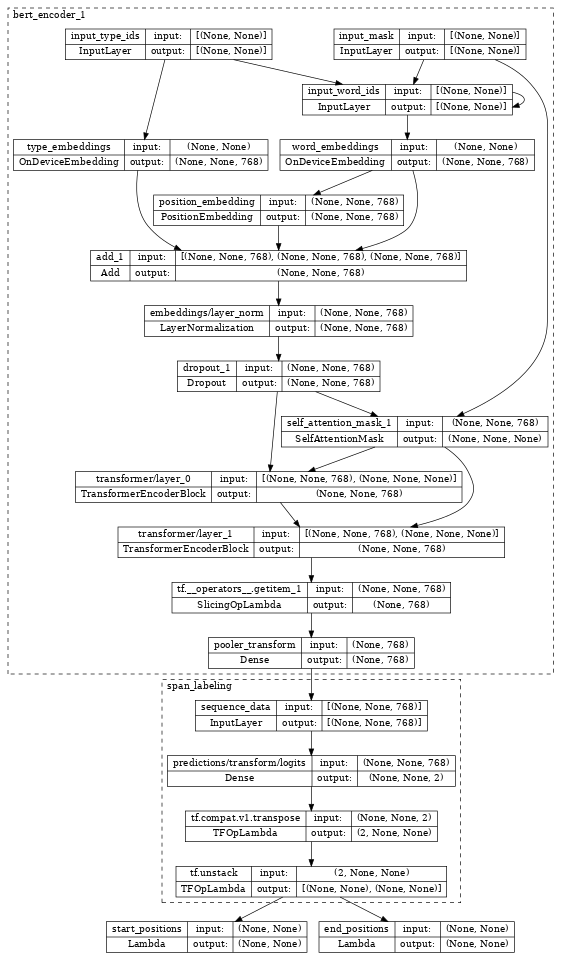
The nlp.models.BertSpanLabeler class implements a simple single-span start-end predictor (that is, a model that predicts two values: a start token index and an end token index), suitable for SQuAD-style tasks.
Note that nlp.models.BertSpanLabeler wraps a nlp.networks.BertEncoder, the weights of which can be restored from the above pretraining model.
network = nlp.networks.BertEncoder(
vocab_size=vocab_size, num_layers=2)
# Create a BERT trainer with the created network.
bert_span_labeler = nlp.models.BertSpanLabeler(network)
Inspecting the bert_span_labeler, we see it wraps the encoder with additional SpanLabeling that outputs start_position and end_position.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(bert_span_labeler, show_shapes=True, expand_nested=True, dpi=48)
# Create a set of 2-dimensional data tensors to feed into the model.
word_id_data = np.random.randint(vocab_size, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
mask_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
type_id_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
# Feed the data to the model.
start_logits, end_logits = bert_span_labeler([word_id_data, mask_data, type_id_data])
print(f'start_logits: shape={start_logits.shape}, dtype={start_logits.dtype!r}')
print(f'end_logits: shape={end_logits.shape}, dtype={end_logits.dtype!r}')
start_logits: shape=(2, 16), dtype=tf.float32
end_logits: shape=(2, 16), dtype=tf.float32
Compute loss
With start_logits and end_logits, we can compute loss:
start_positions = np.random.randint(sequence_length, size=(batch_size))
end_positions = np.random.randint(sequence_length, size=(batch_size))
start_loss = tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(
start_positions, start_logits, from_logits=True)
end_loss = tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(
end_positions, end_logits, from_logits=True)
total_loss = (tf.reduce_mean(start_loss) + tf.reduce_mean(end_loss)) / 2
print(total_loss)
tf.Tensor(5.3621416, shape=(), dtype=float32)
With the loss, you can optimize the model. Please see run_squad.py for the full example.
Classification model
In the last section, we show how to build a text classification model.
Build a BertClassifier model wrapping BertEncoder
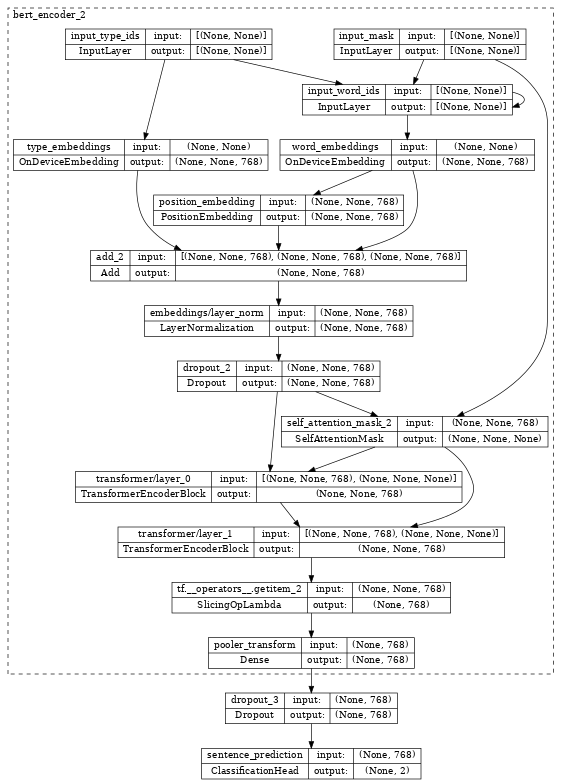
nlp.models.BertClassifier implements a [CLS] token classification model containing a single classification head.
network = nlp.networks.BertEncoder(
vocab_size=vocab_size, num_layers=2)
# Create a BERT trainer with the created network.
num_classes = 2
bert_classifier = nlp.models.BertClassifier(
network, num_classes=num_classes)
Inspecting the bert_classifier, we see it wraps the encoder with additional Classification head.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(bert_classifier, show_shapes=True, expand_nested=True, dpi=48)
# Create a set of 2-dimensional data tensors to feed into the model.
word_id_data = np.random.randint(vocab_size, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
mask_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
type_id_data = np.random.randint(2, size=(batch_size, sequence_length))
# Feed the data to the model.
logits = bert_classifier([word_id_data, mask_data, type_id_data])
print(f'logits: shape={logits.shape}, dtype={logits.dtype!r}')
logits: shape=(2, 2), dtype=tf.float32
Compute loss
With logits, we can compute loss:
labels = np.random.randint(num_classes, size=(batch_size))
loss = tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy(
labels, logits, from_logits=True)
print(loss)
tf.Tensor([0.7332015 1.3447659], shape=(2,), dtype=float32)
With the loss, you can optimize the model. Please see the Fine tune_bert notebook or the model training documentation for the full example.
:::info
Originally published on the TensorFlow website, this article appears here under a new headline and is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Code samples shared under the Apache 2.0 License.
:::