The USB, or Universal Serial Bus, is a common type of connector or port that has been an integral part of our lives for many years. Most computing devices or peripherals we use, like our keyboards and mice, rely on USB for their data or power needs. While the newer USB Type-C port is increasingly becoming more common, the legacy USB ports, such as USB Type-A and USB Type-B, remain prevalent and are unlikely to disappear anytime soon.
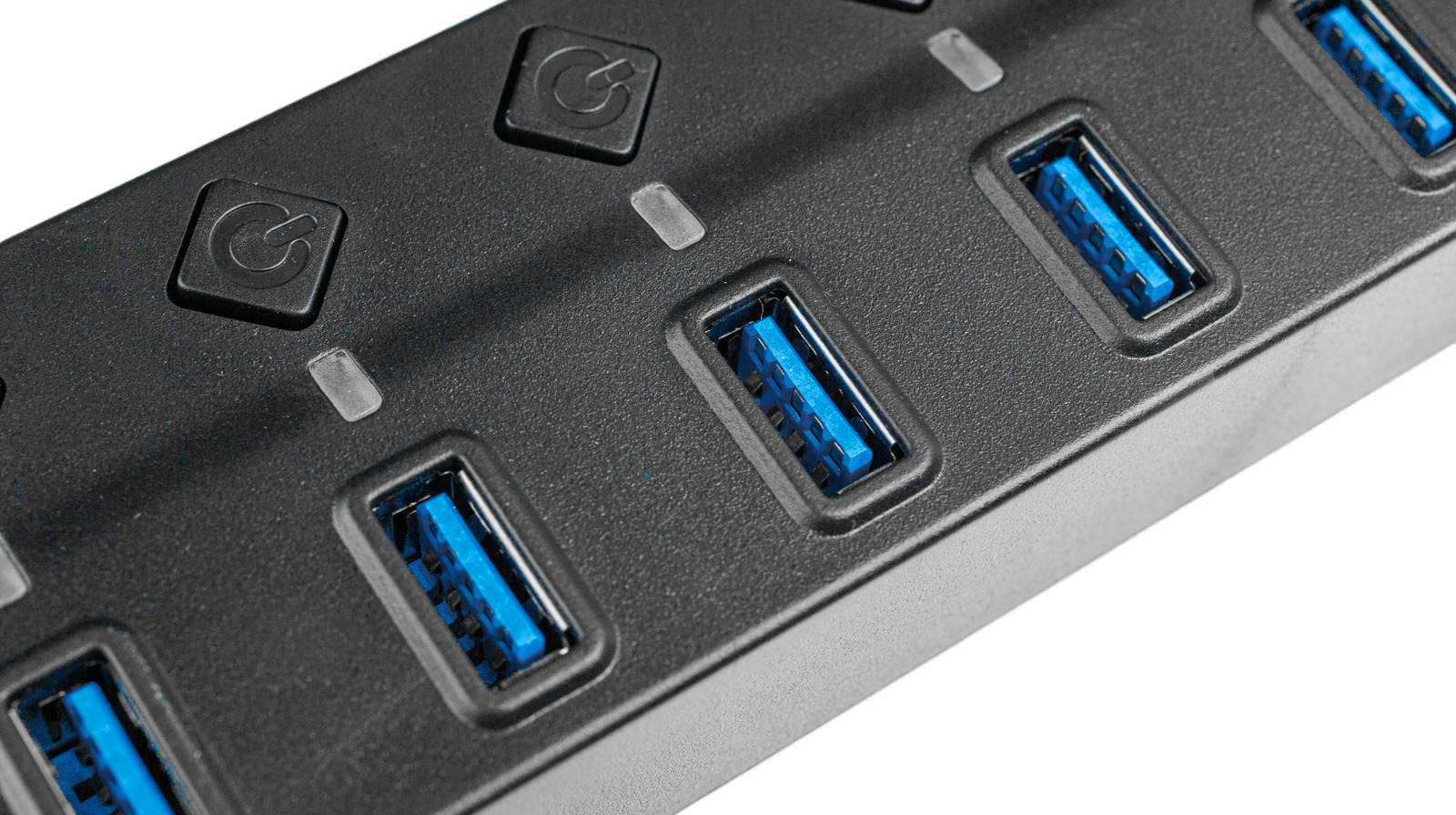
One of the unique features of the original USB-A ports that you won’t find in the modern USB-C port is the colored plastic insert. It’s main purpose is to provide support to the metal contacts and enforce correct orientation. However, it also serves another important role, particularly in USB Type-A and Type-B ports; its color helps determine the speed class, power capabilities, or other special functions of the USB port. The most common colors found on a USB port’s plastic insert are black and blue, but some USB ports also use teal, white, purple, red, and yellow to denote their capabilities.
Why are some USB ports blue?
The presence of a blue plastic insert in a USB connector or port indicates that it supports USB 3.0, also known as SuperSpeed USB, USB 5Gbps, or USB 3.2 Gen 1. USB 3.0 was released in November 2008 and supports data transfer speeds of up to 5 Gbps and power delivery of 900 mA. USB 3.0 connectors and ports, like other USB versions, are also backward compatible.
Although the blue color is commonly used on USB 3.0–compatible ports, it, like other USB colors, is only a recommendation — it’s not mandatory as per the USB specification. As a result, it’s quite possible for you to encounter USB ports with version 3.0 but featuring a black insert, simply bearing the SuperSpeed USB logo (“SS” with a trident symbol) for identification. A good example of this is the HP Omen 25L gaming desktop, which houses two SuperSpeed USB ports on top with black plastic inserts instead of blue.
So, while USB port color is a good indicator of its capabilities, you can’t blindly rely on it. It’s best to consult the manufacturer’s documentation or any accompanying logos.