When someone asks, “Who created AI?”, they usually look for a single name, such as Thomas Edison, who invented the light bulb, or Graham Bell, the inventor of the telephone. But unlike them, AI is a concept that was not created by one man or woman. Instead, it was built over decades, thanks to advances in computing and the efforts of a long list of people. So here’s the real story of who created AI.
Key players who created AI
To provide the correct answer to the question ‘Who created AI?’ we need to trace the roots of artificial intelligence, which go back to the early 20th century. Over the century, there have been major milestones in this field that have helped us reach the current era of generative AI and large language models (LLMs). But if you need a short answer, here are the key players who helped create AI.
- Alan Turing: The British mathematician who shaped the idea of AI and laid the theoretical foundation for AI. Alan Turing wondered whether machines could think and proposed the famous Turing Test to measure machine intelligence.
- John McCarthy: The computer scientist who coined the term “artificial intelligence” and created the field at the historic 1956 Dartmouth conference. He also developed the LISP programming language that was fundamental to early AI research.
- Claude Shannon: The mathematician who co-organized the 1956 Dartmouth conference and created one of the first learning machines. He developed a mechanical mouse that could learn to navigate mazes through trial and error.
- Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon: The duo were the first to build the AI program such as Logic Theorist and General Problem Solver. These programs showed that machines could reason logically and solve complex problems.
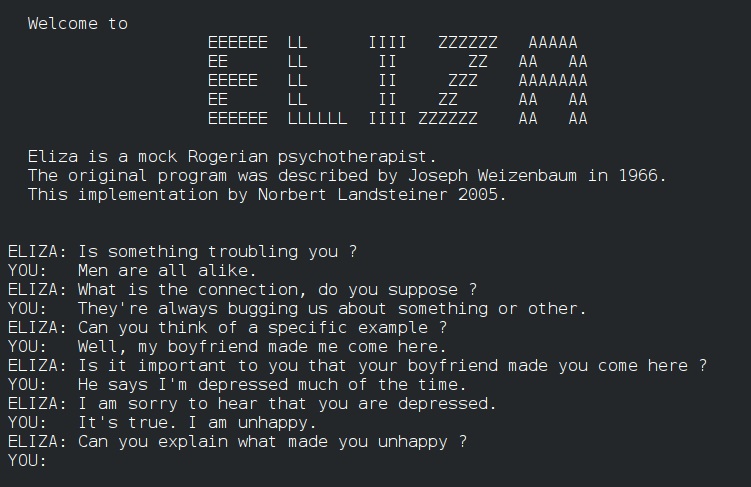
- Jozef Weizenbaum: Developed the first AI chatbot called ELIZA, which simulates human-like conversations.
- Hinton, LeCun and Bengio: The pioneers of deep learning who developed backpropagation techniques, allowing neural networks to learn from data. This is the basis of current AI systems. Geoffrey Hinton received the Nobel Prize in 2024 for the “fundamental discoveries and inventions that enable machine learning with artificial neural networks.”
- Richard Sutton and Andrew Barto: They are the pioneers of Reinforcement Learning (RL), which is used in AI reasoning models for game-playing AI systems such as AlphaGo.
- Google researchers: The team that introduced the Transformer architecture in 2017 (“Attention Is All You Need”) and it powers almost all AI chatbots including ChatGPT, Gemini and more.
The first person who started it all: Alan Turing
British cryptanalyst Alan Turing is the first person to pave the way for modern AI. He published a seminal article in 1950 entitled Computing Machinery and Intelligence, which asked the most important question in the field of AI: “Can a machine think?He also introduced his famous Turning Test, which was featured in science fiction films.
It is checked whether a machine can have a conversation (via a teleprinter) that is just as convincing as talking to another human. If it passes the test, it would not be wrong to say that the machine exhibits intelligent behavior. Suffice it to say, modern chatbots can easily pass the Turing Test to some extent. While Alan Turning may not have built modern AI, he certainly laid the foundation for it.
The Birth of AI: The Dartmouth Conference
Later, American computer scientist John McCarthy, together with Claude Shannon, Marvin Minsky and Nathaniel Rochester, would organize the Dartmouth conference in 1956 and coin the term Artificial Intelligence. Decades later, we still use it to this day. This conference featured several key players who have played a major role in shaping AI as we know it today. It not only laid the foundation for AI, but also set out the goals and how to achieve them.

McCarthy also created LISP, one of the earliest known programming languages used for AI research. It is for these reasons that John McCarthy is known as the father of AI. So if you just want to know who created AI as a field, he is the one to consider.
The first AI programs: logic theorist and general problem solver
Two of the attendees at the Dartmouth conference were Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon, who “debuted” their Logic Theorist at the same event. This was one of the first AI systems built in 1955 that could solve mathematical problems.
This was the first time a machine demonstrated human reasoning. However, it could only perform one task. So later, Newell and Simon would create the General Problem Solver, which could perform different types of problems and show the world that AI was not just a theory. Their work has helped shape the practical part of AI research.
The first AI chatbot and how AI Winter came into being
After the Dartmouth conference, AI development and research reached new heights at the time. Government agencies saw the prospect and began to invest in such projects. Such as ELIZA by Joseph Weizenbaum, developed in 1964. It was the first example of a chatbot that could respond to people like a real human. But it had limited response, often just repeating what users told it.
During the same period, Frank Rosenblatt introduced the Perceptron, the first neural network. However, it was limited by the technology of its time. Funding for the project also stopped after Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert published the book “Perceptrons.” It amplified the negativity surrounding neural networks to the point where there was no funding available for AI research, resulting in an AI winter.
The generation: backpropagation and neural networks
In the 1980s, researchers such as Geoffrey Hinton and Yann LeCun again helped make major progress in this field. They developed backpropagation algorithms to train the network using the available data instead of relying on excessive programming, allowing the computer to learn patterns and data structures just like our brains do.

It has also revived interest in neural networks and laid the foundation for deep learning, which is a huge factor in creating modern AI models.
The people who created modern AI
In the 2000s, improvements in algorithms and GPU power enabled the development of large trainable models. It also made image recognition possible. A pivotal moment came in 2012 when Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever and Geoffrey Hinton created AlexNet, a deep neural network that far outperformed other AI systems used for image recognition.
It proved that deep learning could outperform traditional AI methods and sparked interest in neural networks. Now, in 2017, a team of Google researchers introduced the transformer architecture in their article called ‘Attention Is All You Need’. This is what created AI as we know it today.
Every popular AI model such as Gemini, ChatGPT, Copilot, Grok, Perplexity or Claude is built on this Transformer model and deep learning. So if you want to know who created the AI we use today, the credit goes to the team at Google.








