Artificial intelligence seems simple when you look at clean datasets, benchmark scores, and well-structured Jupyter notebooks. The real complexity begins when an AI system steps outside the lab and starts serving billions of people across the world in different cultures, languages, devices, and network conditions. I have spent my career building these large scale systems at Meta, JPMorgan Chase, and Microsoft. At Meta, I work as a Staff Machine Learning Engineer in the Trust and Safety organization. My models influence the experience of billions of people every day across Facebook and Instagram. At JPMorgan, I led machine learning efforts for cybersecurity at America’s largest bank. Before that, I helped build widely deployed platforms at Microsoft used across Windows and Azure. Across all these places, I learned one important truth. Designing a model is not the hard part. Deploying it at planetary scale is the real challenge. This article explains why.
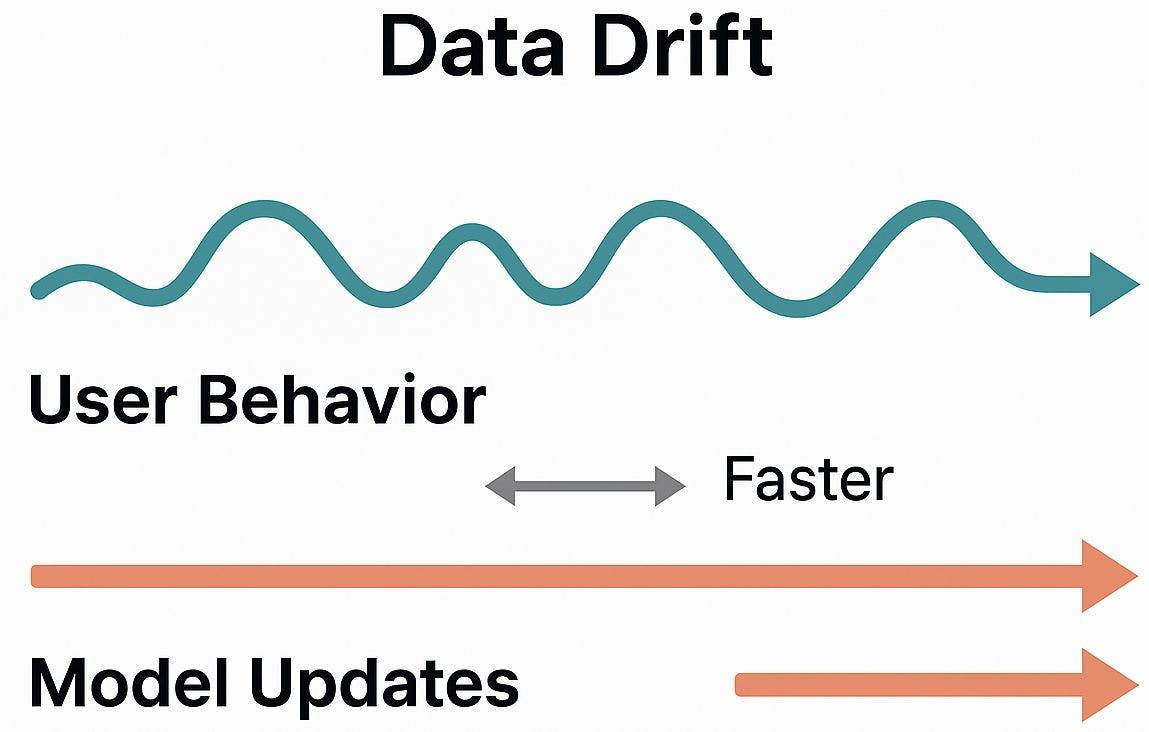
Data Changes Faster Than Models
User behavior is constantly changing. What people post, watch, search, or care about today may be very different next week. Global events, trending topics, seasonal shifts, and cultural differences all move faster than most machine learning pipelines.
This gap creates one of the biggest problems in production AI: data drift. Even a high quality model will degrade if its training data becomes stale.
Example: During major global events, conversations explode with new vocabulary and new patterns. A model trained on last month’s data may not understand any of it.
Analogy: It feels like trying to play cricket on a pitch that changes it’s nature every over.
Latency Is a Hard Wall
In research environments, accuracy is the hero metric. In production, the hero is latency. Billions of predictions per second mean that even 10 extra milliseconds can degrade user experience or increase compute cost dramatically.

A model cannot be slow, even if it is accurate. Production AI forces tough tradeoffs between quality and speed.
Example: A ranking model may be highly accurate offline but too slow to run for every user request. The result would be feed delays for millions of people.
Analogy: It does not matter how good the food is. If the wait time is too long, customers will leave.
Real Users Do Not Behave Like Your Test Data
Offline datasets are clean and organized. Real user behavior is chaotic.
People:
-
Use slang, emojis, mixed languages
-
Start new trends without warning
-
Post new types of content
-
Try to exploit algorithms
-
Behave differently across regions
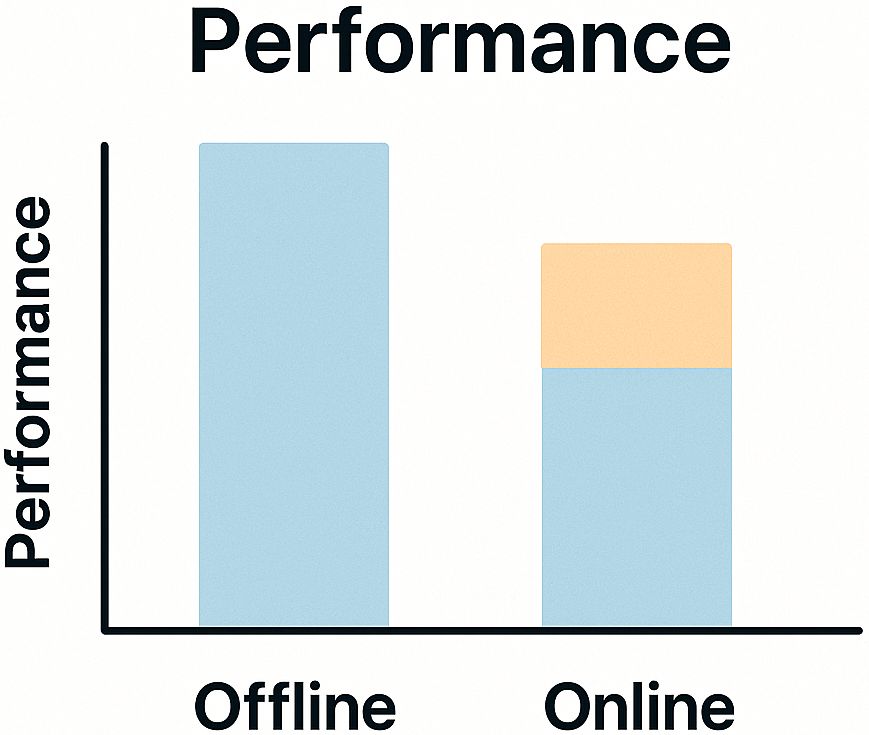
This means offline performance does not guarantee real-world performance.
Example: A classifier trained on last year’s meme formats may completely fail on new ones.
Analogy: Practicing cricket in the nets is not the same as playing in a noisy stadium.
Safety and Fairness Become Global Concerns
At planet scale, even small errors impact millions of people. If a model has a 1 percent false positive rate, that could affect tens of millions of users.

Fairness becomes extremely challenging because the world is diverse. Cultural norms, languages, and communication styles vary widely.
Example: A content classifier trained primarily on Western dialects may misinterpret content from South Asia or Africa.
Analogy: It is like designing a shoe size based on one country’s population. It will not fit the world.
Infrastructure Becomes a Bottleneck
Planet scale AI is as much a systems engineering challenge as it is a modeling challenge.
You need:
-
Feature logging systems
-
Real-time data processing
-
Distributed storage
-
Embedding retrieval layers
-
Low latency inference services
-
Monitoring and alerting systems
-
Human review pipelines
Example: If one feature pipeline becomes slow, the entire recommendation system can lag.
Analogy: It is similar to running an airport. If one subsystem breaks, flights across the world are delayed.
You Are Always Fighting Adversaries
When a platform becomes large, it becomes a target. Bad actors evolve just as quickly as models do.
You face:
-
Spammers
-
Bots
-
Coordinated manipulation
-
Attempts to bypass safety systems
-
Attempts to misuse ranking algorithms
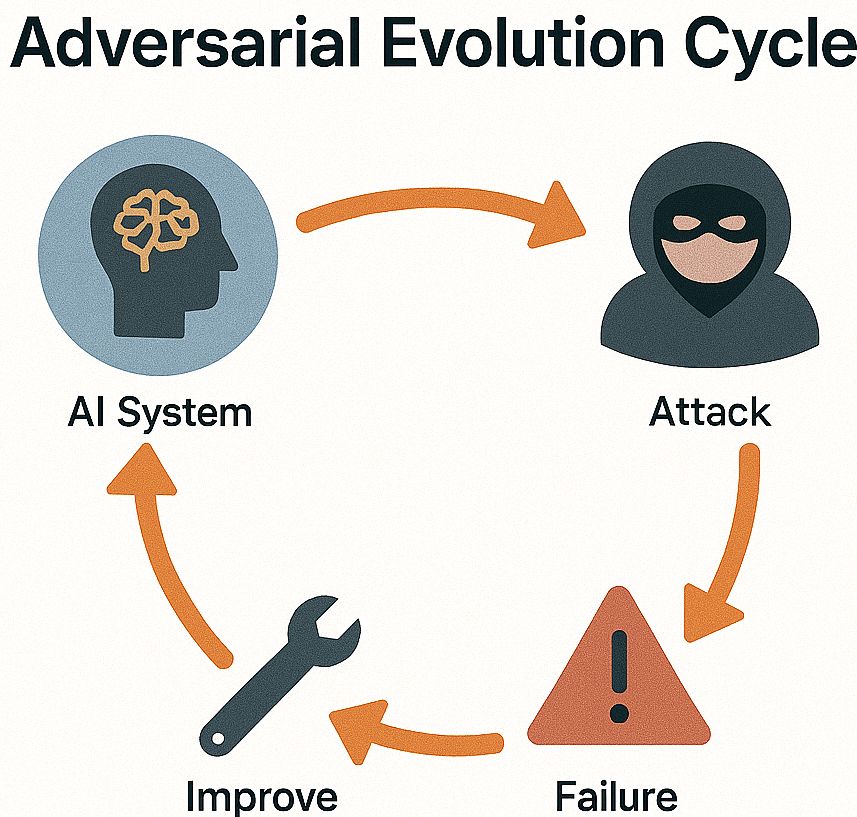
Example: Once spammers learn the patterns your model blocks, they start generating random variations.
Analogy: Just like antivirus software, you fight a new version of the threat every day.
Humans Are Still Part of the Loop
Even the best models cannot understand every cultural nuance or edge case. Humans are essential, especially in Trust and Safety systems.
Human reviewers help models learn and correct mistakes that automation cannot catch.
Example: Content moderation involving sensitive topics needs human judgment before model training.
Analogy: Even an autopilot needs pilots to monitor and intervene when needed.
Conclusion
Deploying AI at planet scale is one of the most complex engineering challenges of our time. It forces you to think beyond model architecture and consider real people, real behavior, infrastructure limits, safety risks, global fairness, and adversarial threats. I have seen these challenges firsthand across Meta, JPMorgan Chase, and Microsoft. They require thoughtful engineering, strong teams, and a deep understanding of how technology interacts with human behavior. Planet scale AI is not only about code and models. It is about creating systems that serve billions of people in a safe, fair, and meaningful way. When done well, the impact is enormous and positive. That is what makes this work worth doing.