Table of Links
Abstract, Acknowledgements, and Statements and Declarations
-
Introduction
-
Background and Related Work
2.1 Agent-based Financial Market simulation
2.2 Flash Crash Episodes
-
Model Structure and 3.1 Model Set-up
3.2 Common Trader Behaviours
3.3 Fundamental Trader (FT)
3.4 Momentum Trader (MT)
3.5 Noise Trader (NT)
3.6 Market Maker (MM)
3.7 Simulation Dynamics
-
Model Calibration and Validation and 4.1 Calibration Target: Data and Stylised Facts for Realistic Simulation
4.2 Calibration Workflow and Results
4.3 Model Validation
-
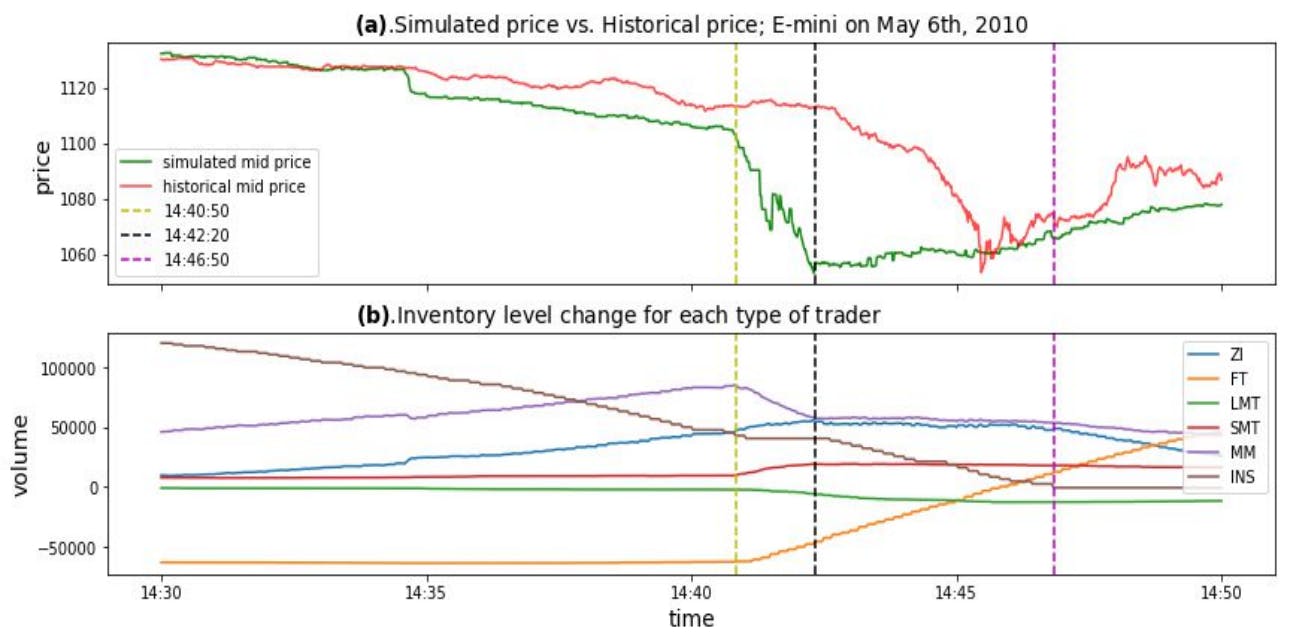
2010 Flash Crash Scenarios and 5.1 Simulating Historical Flash Crash
5.2 Flash Crash Under Different Conditions
-
Mini Flash Crash Scenarios and 6.1 Introduction of Spiking Trader (ST)
6.2 Mini Flash Crash Analysis
6.3 Conditions for Mini Flash Crash Scenarios
-
Conclusion and Future Work
7.1 Summary of Achievements
7.2 Future Works
References and Appendices
3.5 Noise Trader (NT)
3.6 Market Maker (MM)
The market makers are another group of traders in the model. The introduction of market makers in the proposed model is aimed at creating realistic limit order book dynamics. Market makers in the proposed model are more complex than previous traders. During normal trading time, market makers only submit quotes to the market. A quote includes one buy limit order and one sell limit order. The simplification that market makers only submit limit orders is motivated by Menkveld (2013), which finds that around 80% of market makers’ orders are passive. The price of the sell (buy) order is calculated by adding (subtracting) a distance from the mid-price at the corresponding timestamp, where the distance is sampled from a uniform distribution. (The price is rounded to the closest multiple of tick size before being submitted to the exchange.) In alignment with the market making behaviours during the 2010 Flash Crash event (SEC and CFTC 2010), market makers in the proposed model are associated with a position limit. Specifically, once the inventory of a market maker reaches the position limit, the market maker will stop all active quoting and actively submit market orders to reduce the inventory level. This will continue until the inventory reduces to a certain safe level, which is also a parameter of the model. At this stage, the market maker suspends trading for a certain time period. This resembles the real-world scenarios that market makers tend to suspend trading to check their own trading systems and observe market conditions after some unusual scenarios happen. After this time period, the market maker will restart the normal trading heuristics. Table 1 presents the corresponding order types that market makers will submit in different trading conditions.
3.7 Simulation Dynamics
The whole simulation runs as follows. For each step, each trader collects and processes market information. Internal variables associated with each trader are calculated. According to agent type and values of internal variables, actions are taken by the traders. These actions include limit order submission, market order submission, and order cancellation. The programmed matching engine matches these orders and updates the state of the limit order book. Finally, transactions and limit order book status are published to all traders. The whole simulation procedure is shown in Algorithm 6.
We suggest that the proposed five types of traders reflect a sufficiently realistic and diverse market environment. According to O’Hara (1995), there are three major market-microstructure trader types: uninformed traders, informed traders and market makers. The noise traders in our model correspond to uninformed traders, while market makers in the proposed model obviously correspond to the market makers in literature. The remaining three types of traders represent informed traders in our model. Specifically, fundamental traders utilise exogenous information implied by the fundamental value, while the two types of momentum traders exploit the endogenous technical indicator information. In addition, among the informed traders some perceived trading opportunities are based only on an analysis of short-horizon returns, while others focus on market information revealed by long-term return horizons. This is reflected by the division of momentum traders into long-term and short-term momentum traders. Overall, a sea of different informed and uninformed traders in the proposed model compete with each other, with market makers providing liquidity and ensuring realistic limit order book behaviours. In conclusion, the proposed model with five types of traders represents a complete range of micro-behaviours of real financial markets.
3.7.1 Fundamental Value from Kalman Smoother
The only remaining unknown variable is the fundamental value of the stock. The simulation can proceed only if the fundamental value is known and is exogenously input to the model. One difficulty is the non-observability of the fundamental value. According to the economic literature, the fundamental value of a stock equals the expected value of discounted dividends that the company will pay to the shareholders in the future. However, this methodology requires extremely strong assumptions about the future dynamics of the stock dividends. Furthermore, this approach can never reflect the intra-day change of fundamental value, while the consensus fundamental value can indeed vary during the trading day due to the continuous feed of events and news.
Authors:
(1) Kang Gao, Department of Computing, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK and Simudyne Limited, London EC3V 9DS, UK ([email protected]);
(2) Perukrishnen Vytelingum, Simudyne Limited, London EC3V 9DS, UK;
(3) Stephen Weston, Department of Computing, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK;
(4) Wayne Luk, Department of Computing, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK;
(5) Ce Guo, Department of Computing, Imperial College London, London SW7 2AZ, UK.