The team behind Amazon Key modernized its event platform to address scalability and reliability limitations arising from a tightly coupled, monolithic architecture. As service interactions grew into a complex web of dependencies, system stability and integration velocity were increasingly constrained. The redesign introduced a centralized, event-driven architecture built on Amazon EventBridge to support millions of daily events with millisecond latency, improve schema governance, and provide a sustainable path for onboarding additional service consumers.
The Amazon Key suite powers secure in-garage deliveries and property access management. Its earlier architecture relied on tightly integrated services, where changes or failures in one component could directly affect others. Event routing logic was manually implemented and lacked advanced filtering or parallel publishing capabilities. Event schemas were loosely defined and supported only basic validation of required fields. Extending validation rules or evolving contracts required additional coordination and custom development. The platform also supported a limited number of subscribers, with no standardized mechanism to scale consumer onboarding as new use cases emerged.
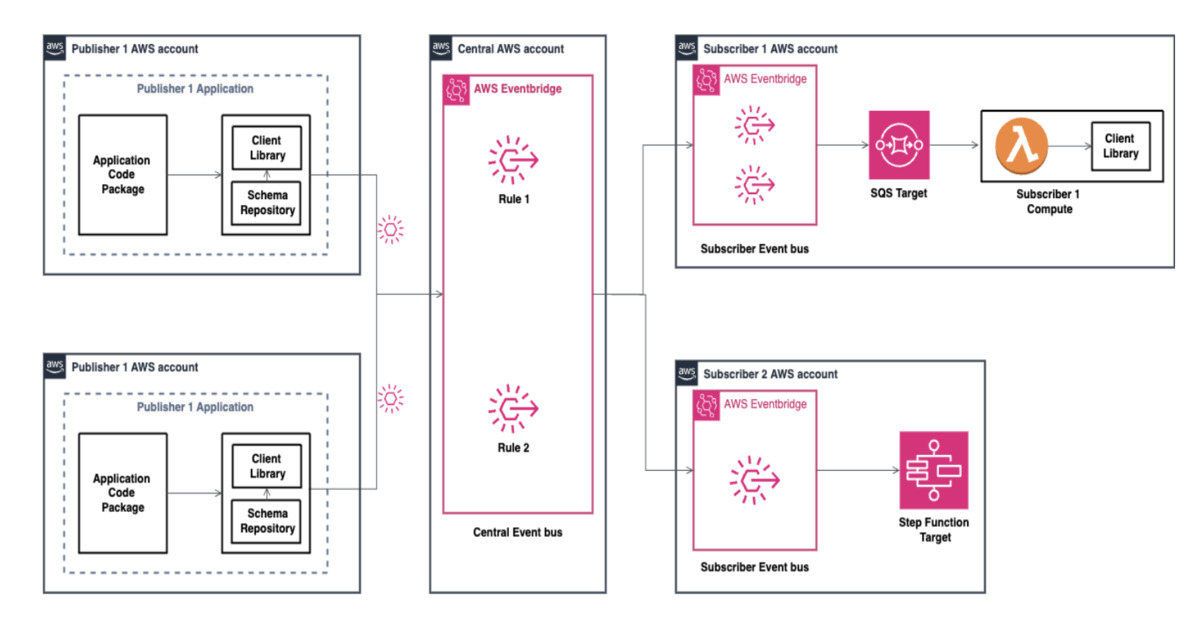
To address these constraints, the engineering team adopted a single bus, multi-account pattern. A centralized EventBridge bus in a core account receives domain events from producers. Routing rules evaluate event patterns and forward matching events to subscriber accounts, where each account maintains its own targets and processing logic. This structure provides service isolation while preserving centralized governance over routing policies, permissions, and compliance controls. Teams can deploy independently while sharing a common event backbone.
Architecture overview (Source: AWS Blog Post)
A centralized schema repository was introduced to standardize event definitions and enforce version control. Schemas serve as the authoritative source for event contracts and enable structured validation. A custom client library validates and serializes events against approved schemas before publication to EventBridge. On the subscriber side, the same library validates and deserializes events before invoking downstream services. This approach enforces consistent data contracts across producers and consumers and reduces integration errors caused by incompatible payloads.
Infrastructure provisioning for subscriber accounts is automated using reusable constructs built with the AWS Cloud Development Kit. These constructs configure event buses, define routing rules, establish IAM permissions for cross-account access, and enable monitoring and alerting. Standardization reduces repetitive infrastructure configuration and ensures consistent observability and security practices across services.

Schema validation and publication flow (Source: AWS Blog Post)
The architectural redesign has produced measurable results. The platform processes approximately 2,000 events per second with a reported 99.99 percent success rate. The team measures p90 latency of roughly 80 milliseconds from ingestion to target invocation. Operational efficiency improved as well. Event onboarding time decreased from 48 hours to four, and service integrations that previously required about 40 hours can now be completed in approximately eight. The system now supports millions of daily events while maintaining low latency and consistent reliability.