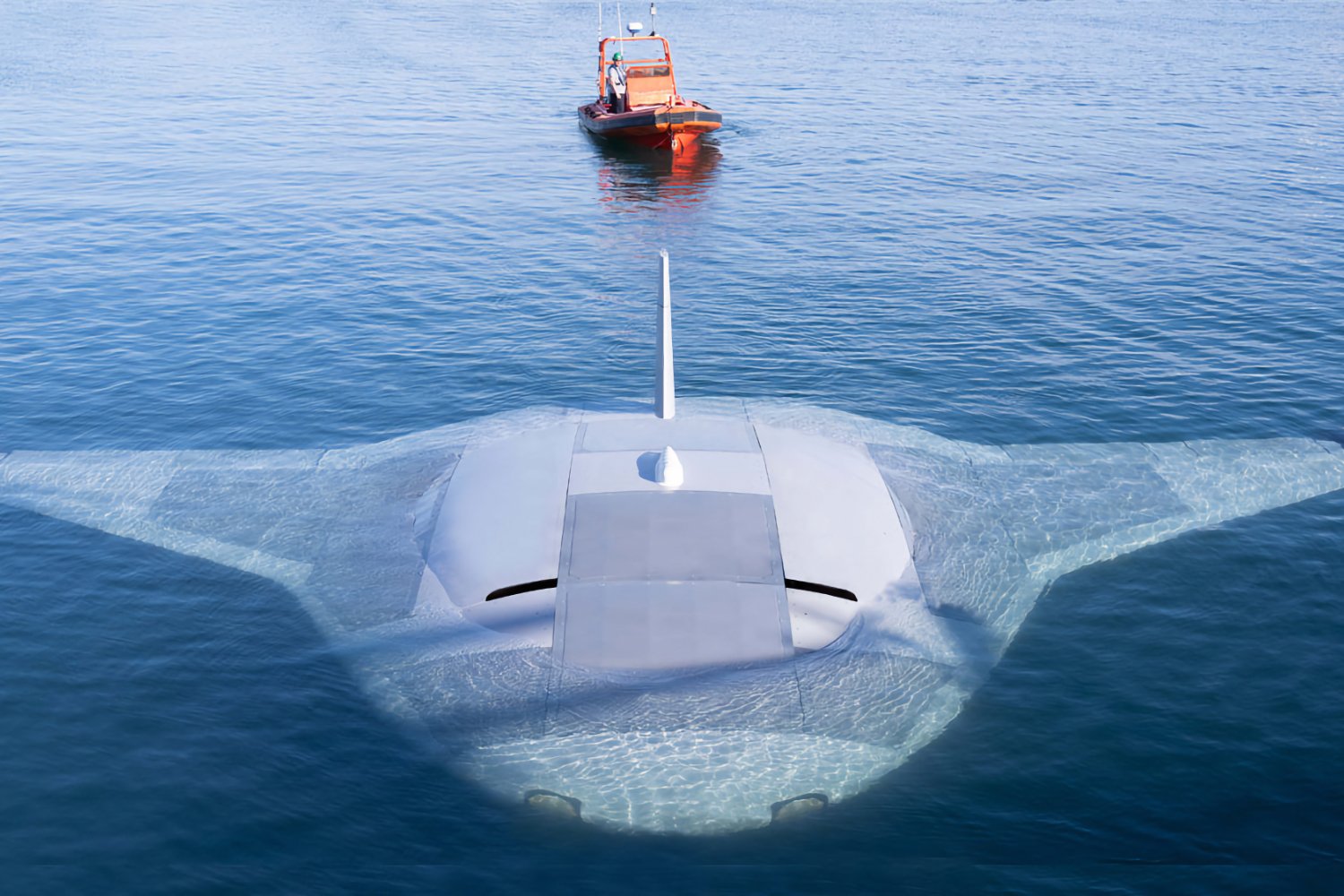
The Manta Ray program, launched in 2020 by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), aims to create autonomous underwater vehicles (UUV) capable of carrying out long-duration, long-distance missions without human intervention. The project is led by two main players, Northrop Grumman and PacMar Technologies. The last series of tests, carried out by Northrop Grumman, made it possible to validate the hydrodynamic performance of the prototype in real conditions.
An impressive drone that scares sharks
Between February and March of this year, Northrop Grumman’s underwater vehicle, described as “extra-large,” conducted comprehensive sea trials off the coast of Southern California. These tests demonstrated the ability of the Manta Ray to operate underwater using different propulsion and steering methods (buoyancy, propellers, control surfaces, etc.).
According to Kyle Woerner, Manta Ray program manager at DARPA, “ These full-scale tests validate the vehicle’s readiness to advance toward real-world operations after being rapidly assembled in the field from modular subsections. » The Manta Ray is designed to move efficiently through water using buoyant propulsion, and is equipped with multiple payload compartments of varying sizes and types, making it suitable for many types of naval missions.
Subscribe to WorldOfSoftware
Among the project’s objectives are the demonstration of new energy management techniques for UUV operations, low-power, high-efficiency underwater propulsion systems, and low-power detection and classification methods for underwater threats.
Maritime drones like the Manta Ray represent a cost-effective solution to increase the capabilities of the U.S. Navy while reducing risks to sailors. At a time when China is seen as the main rival, these technologies are a way to strengthen the U.S. presence in the Pacific region without endangering military personnel.
Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Lisa Franchetti sees robotic systems and other emerging technologies as a way to “ add more players on the field. » Last December, the Navy received the first Orca XLUUV from Boeing for additional testing. This diesel-electric submarine, weighing 85 tonnes and measuring 26 meters long, underwent sea tests to assess its capabilities above and below the surface.
The Manta Ray program is part of this vision of a hybrid fleet made up of manned and unmanned ships. DARPA, in collaboration with the Navy, is exploring new technologies like artificial intelligence and autonomy to achieve this goal. The agency recently announced contracts with several specialty contractors to build prototypes of large underwater drones.
🟣 To not miss any news on the WorldOfSoftware, subscribe on Google News and on our WhatsApp. And if you love us, .