Telecom networks have always fascinated me during global online usage peaks because they perform under heavy traffic conditions. The unpredictable nature of traffic surges in major worldwide events and sudden work-related changes demands fast solutions because they occur without warning.
Recent
What occurs when these surge episodes occur? A traditional network operation will fail to handle pressure unless it includes adaptive response mechanisms. Network self-learning algorithms enabled by AI and machine learning technologies maintain smooth operation during increased usage.
Image:
Why Self-Learning Matters in Telecom?
AI-powered self-learning
Deep Learning (CNNs)
The scanning capability of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) verifies large amounts of real-time data while optimizing network routing through anomaly detection. The combination of RNNs and CNNs according to an
Reinforcement Learning (RL)
RL controls the network traffic routes by analyzing past performance and network status. RL technology has demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing congestion while minimizing waiting periods for traffic signals in
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
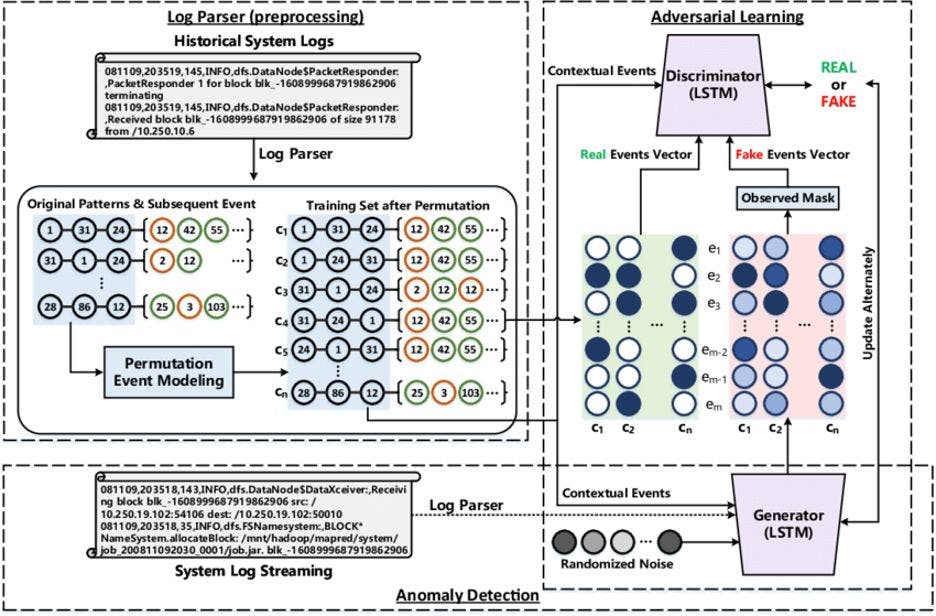
GANs produce artificial traffic patterns through which suspicious network behaviors become evident to enhance overall network protection. GANs achieved 95.8% precision along with 2.4% incorrect detection rates according to an
How does this system translate into actual practice? These algorithms use seconds to route your network through alternative pathways, preventing Zoom calls from disconnecting at critical moments.
This diagram visually explains how GANs generate synthetic traffic patterns to detect network anomalies, ensuring security during traffic surges.
Real-Time Inference
Compound ML systems retrieve data lake telemetry information from base stations combined with backhaul links and core routers. Algorithms that run on streaming data including throughput and packet loss adjust control-plane decisions in real-time periods of seconds which serve crucially during live sports broadcasts when there are unexpected video streaming surges.
Key Components for Handling Traffic Surges
1. Predictive Analytics
I have seen that Long Short-Term Memory
2. Network Slicing and Segmentation
Network infrastructure under
3. Adaptive QoS and Traffic Shaping
The natural algorithms operating within Traffic shaping systems maintain the distribution of data streams throughout different Quality of Service levels. All video conferencing users maintain the highest system ranking in priority assessments yet they receive service below social media users. Real-time traffic monitoring enables automatic adjustment of system speed controls and throttling according to policies and subscription types which have been learned for various traffic groups
Overcoming Implementation Challenges
The main challenge stems from more than just creating these AI-based solutions because it also involves integrating them into extensive telecom frameworks which contain numerous radio sites and edge routers. Implementing black-box artificial intelligence solutions in massive networks requires operators to make difficult choices between clear system decisions and securing their networks.
The common method for managing third-party AI tools across different network sections originates from ETSI Zero-Touch Network and Service Management(ZSM). The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) together with LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) methods show how an algorithm determines particular routes for traffic.
Conclusion
I watched as telecom networks changed from fixed permanent infrastructures into new flexible systems managed by Artificial Intelligence. The ability of self-learning algorithms to manage global network connectivity becomes essential because they control online connection peaks during times when all users access the system simultaneously. Telecom infrastructure uses predictive analytics along with network slicing and adaptive QoS mechanisms to manage sudden jumps in network traffic easily.
Self-learning systems represent the foundational technology that defines the telecom industry’s future and these systems are currently being implemented.