MINUTE Function: A Brief
The MINUTE function in Excel is used to extract the minute portion from a given input time value and returns the output as the numerical value (0-59).
Note: MINUTE function will return #VALUE! error, when there is an issue with your inputs or used invalid starting or ending dates. You can fix this by providing a proper time values without any hidden characters.
MINUTE Function: A Syntax
=MINUTE(time_value)
- time_value: A valid Excel time or a cell containing a time value.
- The result will always be an integer between 0 and 59.
Basic Examples of using MINUTE Function:
The example below shows how to use the MINUTE function in Excel effectively for different situations.
|
S.no |
Input Time |
Result |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
08:15:00 |
15 |
Extracted 15 minutes from the time |
|
2 |
12:45:30 |
45 |
Extracted 45 minutes from a full time value |
|
3 |
00:00:59 |
0 |
Only seconds present, so minute is zero |
|
4 |
23:00:00 |
0 |
Exact hour without any minutes |
|
5 |
14:29 |
29 |
Recognized 29 minutes from a short time format |
|
6 |
09:00:00 |
0 |
0 minutes since it’s an exact hour |
Example Explanation:
The 1st one, This time has 15 minutes, so the MINUTE function returns 15. It completely ignores the hour and second values.
The 2nd one, The time includes 45 minutes and 30 seconds, but the function only extracts 45 minutes. It doesn’t round off based on seconds.
The 3rd one, Even though the time includes 59 seconds, there are 0 minutes, so MINUTE returns 0. It only looks at the MM part of the HH:MM:SS format.
The 4th one, This is an exact hour value with 00 minutes and 00 seconds, so the function returns 0.
The 5th one, The time is written in a short format (HH:MM), but Excel still detects and returns 29 minutes correctly. The function works with both short and full time formats.
The 6th one, This is a full hour without any minute or second part. As there are no minutes, MINUTE returns 0.
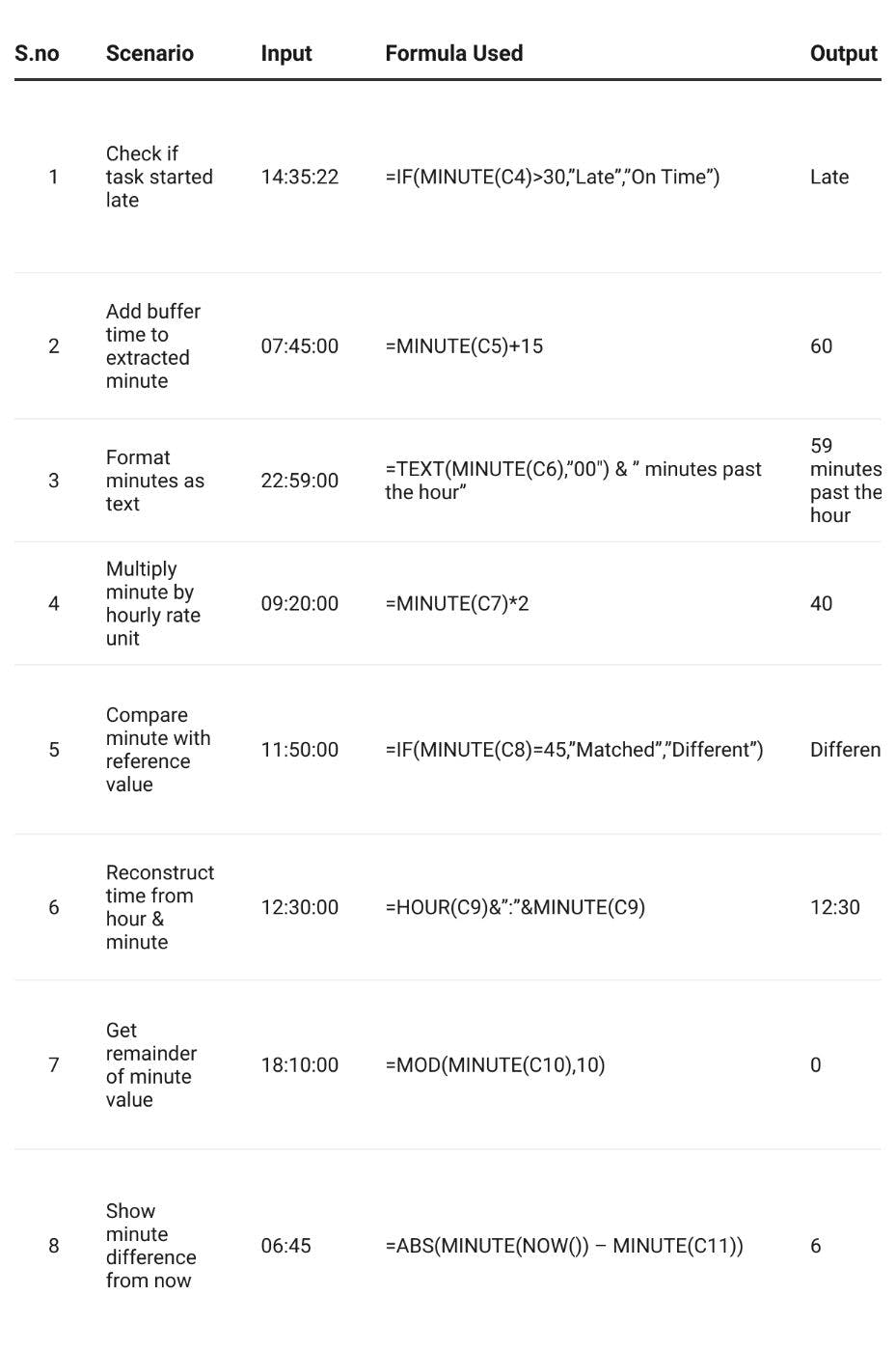
Using MINUTE Function with other Nested Functions:
Example Explanations:
First one: This formula checks if the minute value is greater than 30. If true, it returns “Late”. Otherwise, it shows “On Time”.
Second one: It takes the minute from a time and adds 15 minutes as a buffer. Useful for adding a grace period or delay in schedules.
Third one: Converts the minute into a two-digit text using the TEXT function and adds a label like “minutes past the hour”.
Fourth one: Multiplies the minute value by a fixed rate. This is helpful for calculating costs or units based on time.
Fifth one: Compares the extracted minute value to a set target (like 45). Returns “Matched” if they are equal, otherwise “Different”.
Sixth one: Combines the hour and minute from a time value using & to create a string such as “12:30”.
Seventh one: Uses the MOD function to find the remainder when minutes are divided by 10. Good for grouping into 10-minute blocks.
Eighth one: Subtracts the minute from a given time from the current time’s minute. Can return positive or negative values. Set the cell format to General to see the numeric result.
That’s it. This tutorial is first published on How to Use Excel MINUTE Function?