Table of Links
Abstract and 1. Introduction
-
Background
2.1 Rollup
2.2 EIP-4844
2.3 VAR(Vector Autoregression)
-
Data
3.1 Consensus security data
3.2 Ethereum usage data
3.3 Rollup Transactions Data
3.4 Blob gas fee data
-
Empirical Results
4.1 Consensus security
4.2 Ethereum usage
4.3 Rollup transactions
4.4 Blob gas fee market
-
Conclusion and References
A. Consensus Security Data
B. Rollup Data Collection
C. Detailed Var Model Results for Blob Gas Base Fee and Gas Fee
D. Detailed Var Model Results for Blob Gas Base Fee and Blob Gas Priority Fee
E. Rollup Transaction Dynamics
D DETAILED VAR MODEL RESULTS FOR BLOB GAS BASE FEE AND BLOB GAS PRIORITY FEE
In this subsection, we present the results of the Vector Autoregression (VAR) model analysis that examines the interactions between the blob gas base fee and the blob gas priority fee. Table 14 provides a summary of the regression results, offering an overview of the model’s fit and diagnostic statistics. Following this, Table 17 details the estimated coefficients and statistics, allowing us to understand the influence of past values on current values for each variable.
D.1 VAR model estimation output
Table 14 displays the VAR model’s key statistics. The log likelihood value is notably large at -2,335,520, suggesting the model’s fit to the data under analysis. The model’s complexity and goodness-of-fit are further quantified by AIC, BIC, and HQIC, all closely valued around 84.5. These criteria help in model selection, with lower values generally indicating a better model relative to the number of parameters used.
Table 17 outlines the VAR model results for datagas_base_fee and datagas_priority_fee_per_datagas. The model shows strong persistence in datagas_base_fee, as indicated by the significant coefficient of 0.9588 for its first lag, and an effect of prior priority fees on current base fees, though the impact diminishes over time, as seen in the insignificant coefficient for the sixth lag. In contrast, the datagas_priority_fee_per_datagas equation indicates a slight decrease in priority fees with an increase in base fees at the previous lag. This suggests an autocorrelation that indicates the complex, dynamic interplay between these fees within the network’s pricing mechanism.
D.2 Correlation matrix of residuals
Table 15 presents the correlation matrix of residuals for the VAR model involving datagas base fee and datagas priority fee per datagas. This matrix is critical for checking the assumption of no serial correlation among residuals, which is a fundamental requirement for the validity of model inferences in VAR analysis.
The values in the matrix show the correlation coefficients between the residuals of the two equations modeled. A coefficient close to zero between different variables’ residuals, such as seen here between datagas base fee and datagas priority fee per datagas, suggests that there is no significant linear relationship between the residuals. This indicates that the model does not suffer from multicollinearity issues and that the residuals are behaving as expected—randomly and independently from each other, which supports the reliability of the model’s forecasts and conclusions.
E ROLLUP TRANSACTION DYNAMICS
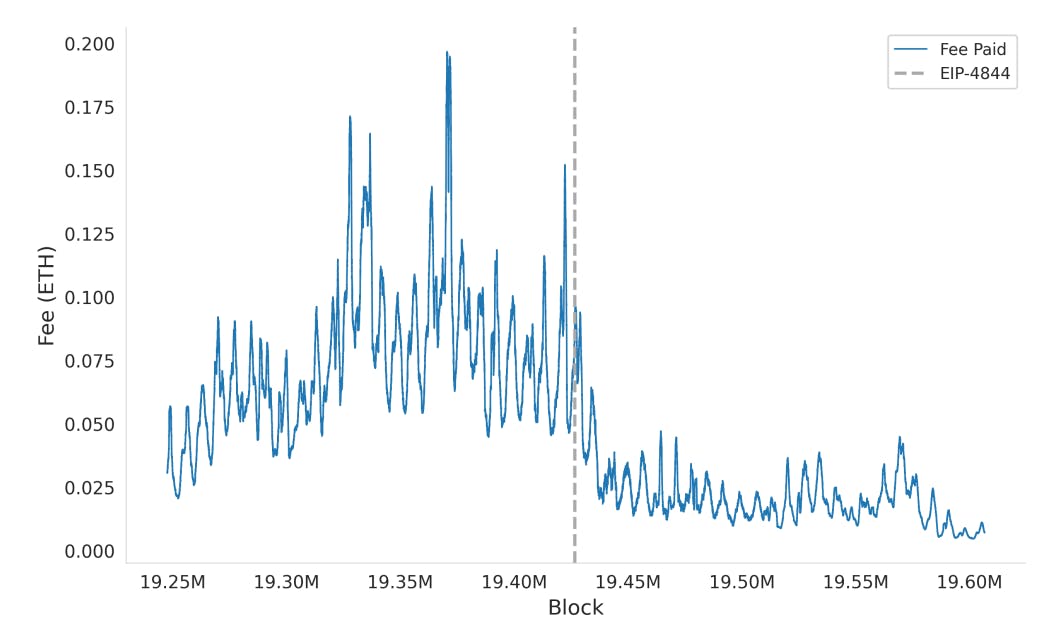
E.1 Total fee paid by rollups
Figure 19 illustrates the total fee paid by the top 10 rollups on Ethereum to use Ethereum as a Data Availability (DA) layer. The vertical dashed line indicates the implementation of EIP-4844. The figure shows a noticeable decrease in fees after EIP-4844, reflecting the impact of protocol changes aimed at reducing transaction costs for rollup operations.
E.2 Gas used by rollups
Figure ?? shows the total gas usage by rollups in all rollups, optimistic rollups, and ZK rollups. The figure shows a noticeable decrease in fees after EIP-4844, especially for optimistic rollups.
Authors:
(1) Seongwan Park, this author contributed equally to the paper from Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea ([email protected]);
(2) Bosul Mun, this author contributed equally to the paper from Seoul National University, Seoul, Republic of Korea ([email protected]);
(3) Seungyun Lee, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(4) Woojin Jeong, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(5) Jaewook Lee, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(6) Hyeonsang Eom, Seoul National University, Seoul, Repulic of Korea;
(7) Huisu Jang (Corresponding author), Soongsil University, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
This paper is